Updated April 5, 2023

Introduction to C++ any() Function
Bitset is one of the important class in the C++ library that helps to emulate strings or numbers in the form of a sequence of bits stored like an array where each of the bits is stored at consecutive positions in the array. Since the storage dataset used is an array, each bit can be referenced by a particular index that helps in fast access of elements. Any() method is one of the methods provided in Bitset Class to find if any of the bit present in the array is set that is its value is ‘1’. If none of the bit is set false is returned.
Syntax:
- Before C++11:
bool any() const;
- Since C++11:
bool any() const noexcept;
This method requires no parameters to be passed while calling. Only the reference to one of the objects of Bitset class calls this method for the bitset representation object is holding.
- Bool: Determines that the return type for this method is a Boolean, that is either true in case any one of the bit is set otherwise false.
- Const: restricts any changes to this method by any of its child classes.
After C++11 this method does not throw any exception, can be inferred using noexcept keyword mentioned in its declaration.
How any() Function Works in C++?
A bitset helps to emulate an array of bool where each bit is stored in such a way to use memory efficiently as memory consumed to store a bitset is far less than the storage of Boolean array or vector. Thus it can be inferred the information stored using bitset is stored in a compressed manner, thus helps in enhancing the performance of the array and vector operations on it. The only limitation of using bitset is the size of the array needs to be declared at compile time.
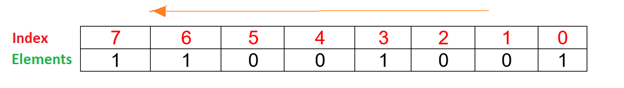
1. Each bit in bitset array can easily be accessed using indexes for eg, obj[3] points to the element stored at index 3 in the bitset from right side.
2. Bitset also gives constructor to get the bitset representation of given string and numbers. Thus one can easily use this class to store the information. It provides various methods to perform operations on the bits such as :-
- Count
- All
- Any
- Test
- Set
3. When Any() method is triggered for a bitset object, the compiler traverse the whole array of bitset from 0 to N index, where N is declared at compile-time, and checks if the bit is set i.e the value of the bit at that index is 1. If yes it breaks the loop and returns true Boolean otherwise False Boolean. Any() method working is same as loop given below:-
for(int i=0;i<bitsObj.size();i++){
if(bitsObj.test(i)){
return true;
break;
}
else{
return false;
}
}Advantage of any() Function in C++
- All the bitwise operations on bitset can be performed without any type of conversion or casting, which helps enhance the performance and efficiency.
- Main overloaded methods are &,!,==,!= also <> shifting operators. And Any() method can be used to detect if the given number contains any set bit to perform these operations otherwise ignore the bitset directly.
Examples to Implement of C++ any() Function
Below are the examples of C++ any():
Example #1
Let us consider one simple example to understand how any function in bitset works.
Code :
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
bitset<4> obj1(string("10010"));
bitset<6> obj2(string("000000"));
bool result1 = obj1.any();
if (result1)
cout << obj1 << " has one of its bits set"
<< endl;
else
cout << " None of the bits is set in "<< obj1
<< endl;
bool result2 = obj2.any();
if (result2)
cout << obj2 << " has one of its bits set"
<< endl;
else
cout << "None of the bits is set in " << obj2
<< endl;
return 0;
}Output :
![]()
Explanation: Here since obj1 10010 has a bit set at 1 and 4th index thus any method returns true for it. But in case of obj2 000000 has none of its bits as set returns false.
Example #2
In the second example, we will see the working of any function for 4 different bitset objects.
Code :
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define M 32
int main()
{
bitset<M> obj1;
bitset<M> obj3(string("00010"));
bitset<M> obj2(16);
bitset<M> bitarr;
cout << "Bitset representation of uninitialised obj1 is " <<obj1 << endl;
cout << "Bitset representation of 16 is " <<obj2 << endl;
cout << "Bitset representation of \"00010\" is " <<obj3 << endl;
cout << endl;
bitarr[3] = 1;
bitarr[2] = bitarr[3];
cout << "Bitset representation of array with 2nd 3rd bbits set is "<< bitarr << endl;
cout << "Lets check if any of the bit is set in above 4 bitset representations: ";
if( obj1.any()) cout<< "obj1: " <<"TRUE"<<endl ;else cout << "FALSE" <<endl;
if( obj2.any()) cout<< "obj2: " <<"TRUE"<<endl ;else cout <<"FALSE" <<endl;
if( obj3.any()) cout<< "obj3: " <<"TRUE" <<endl;else cout<< "FALSE" <<endl;
if( bitarr.any()) cout<< "bitarr: " <<"TRUE"<<endl; else cout<< "FALSE" <<endl;
cout << endl;
return 0;
}Output:
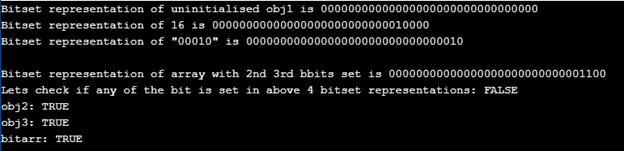
Explanation: In the above-given example, M defines the length of the bitset array for all the given bitset objects. Since obj1 is uninitialized thus its value is by default initialized to 0. Second object obj2 is a number -16 that is converted using bitset constructor to its bitset representation. The third object is in the form of bits 00010 and has bit set at index 1. And the fourth index is a bitset array uninitialized, thus stores 0 value in the start but its 2nd and 3rd bit is set at runtime. Any() method is used to find if any of the bit in the given objects is set or not.
Conclusion
Bitset representation plays an important role as it helps to work with bits representation of string or numbers. And Since the machine understands the language of “0” and “1”, working with this representation improves the performance. Any() is one of the methods provided in this class to find if any of the bit is set in the given bitset object.
Recommended Article
This is a guide to C++ any(). Here we discuss the Introduction to C++ any() Function and its Examples along with Code Implementation and Output. you can also go through our suggested articles to learn more –


