Updated September 12, 2023
What are Operators in C?
The C programming language utilizes operators as symbols representing precise operations to be executed on one or more operands. C provides a wide range of operators that can perform arithmetic, logical, and bitwise operations and operations on pointers and arrays. Operators are symbols that help in performing functions of mathematical and logical nature. The classification of C operators is as follows:
- Arithmetic
- Relational
- Logical
- Bitwise
- Assignment
- Conditional
- Special
Even though there are many operators, the execution of these operations happens based on the precedence given to them. Precedence is the order in which the compiler executes the code comprising numerous operators.

Table of Contents
- What are Operators in C
- Explanation of Operators in C
- C Operators Precedence
- Time and Space Complexity
Explanation of Operators in C
Below is a detailed explanation of operators in C:
#1 Arithmetic Operators
These operators are responsible for performing arithmetic or mathematical operations like addition (+), subtraction (-), multiplication (*), division (/), the remainder of the division (%), increment (++), and decrement (–).
There are two types of arithmetic operators:
-
-
-
- Unary Operators: This type of operator works with a single value (operand) like ++ and –.
- Binary Operators: This type of operator works with two operands like +,-,*,/
-
-
Here is a tabular form of the number of arithmetic operators in C with the functions they perform.
| Operator | Function |
| + | Adds two values |
| – | Subtract a second value from the first. |
| * | Multiply two values |
| / | Divide numerator by the denominator |
| % | Remainder of division |
| ++ | Increment operator – increases integer value by one. |
| — | Decrement operator – decreases integer value by one |
Example: C Program using arithmetic operators
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 12, b = 6, c;
c = a + b;
printf("a+b = %d \n", c);
c = a - b;
printf("a-b = %d \n", c);
c = a *b;
printf("a*b = %d \n", c);
c = a / b;
printf("a/b = %d \n", c);
c = a % b;
printf("Remainder when a divided by b = %d \n", c);
return 0;
}Output:

#2 Relational Operators
When we want to compare the values of two operands, we use relational operators. If we want to check that one operand is equal to or greater than other operands, we use the >= operator.
The below table lists the relational operators in C with their functions.
| Operator | Function | Example |
| == | It will check if the two operands are equal | 6 == 2 returns 0 |
| != | It will check if the two operands are not equal. | 6 != 2 returns 1 |
| > | It will check if the operand on the left is greater than the operand on the right | 6 > 2 returns 1 |
| < | It will check if the operand on the left is smaller than the right operand | 6 < 2 returns 0 |
| >= | It will check if the left operand is greater than or equal to the right operand | 6 >= 2 returns 1 |
| <= | It will check if the operand on the left is smaller than or equal to the right operand | 6 <= 2 return 0 |
Example: C Program using relational operators
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 7, b = 7, c = 10;
printf("%d == %d = %d \n", a, b, a == b); // true
printf("%d == %d = %d \n", a, c, a == c); // false
printf("%d > %d = %d \n", a, b, a > b); //false
printf("%d > %d = %d \n", a, c, a > c); //false
printf("%d < %d = %d \n", a, b, a < b); //false
printf("%d < %d = %d \n", a, c, a < c); //true
printf("%d != %d = %d \n", a, b, a != b); //false
printf("%d != %d = %d \n", a, c, a != c); //true
printf("%d >= %d = %d \n", a, b, a >= b); //true
printf("%d >= %d = %d \n", a, c, a >= c); //false
printf("%d <= %d = %d \n", a, b, a <= b); //true
printf("%d <= %d = %d \n", a, c, a <= c); //true
return 0;
}Output:
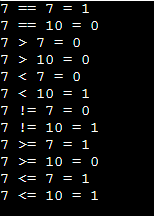
#3 Logical Operators
Logical Operators are to get True or False results.
The table below lists the logical operators used in C
| Operator | Function | Example (if a=1 and b=0) |
| && | Logical AND | (a && b) is false |
| || | Logical OR | (a || b) is true |
| ! | Logical NOT | (!a) is false |
Example: C Program using logical operators.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 8, b = 8, c = 12, result;
result = (a == b) && (c > b);
printf("(a == b) && (c > b) equals to %d \n", result);
result = (a == b) && (c < b);
printf("(a == b) && (c < b) equals to %d \n", result);
result = (a == b) || (c < b);
printf("(a == b) || (c < b) equals to %d \n", result);
result = (a != b) || (c < b);
printf("(a != b) || (c < b) equals to %d \n", result);
result = !(a != b);
printf("!(a == b) equals to %d \n", result);
result = !(a == b);
printf("!(a == b) equals to %d \n", result);
return 0;
}Output:
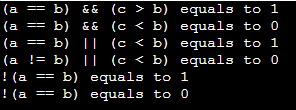
#4 Bitwise Operators
These operators are for bit-level operations on the operands. The operators first convert into bit-level and then perform the calculations.
| Operator | Function |
| & | Bitwise AND |
| | | Bitwise OR |
| ^ | Bitwise exclusive OR |
| ~ | Bitwise complement |
| << | Shift left |
| >> | Shift right |
Example: C program for Bitwise AND
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 10, b = 8;
printf("Output = %d", a&b);
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
Explanation:
10 = 00001010 (In Binary)
8 = 00001000 (In Binary)
Bit Operation of 10 and 8
00001010 & 00001000 = 00001000 = 8 (In decimal)
#5 Assignment Operators
These types of operators help us assign a value to a variable.
| Operator | Function | Example |
| = | It will assign values from right-side operands to left-side operands | a=b |
| += | It will add the right operand to the left operand and assign the result to left | a+=b is the same as a=a+b |
| -= | It will subtract the right operand from the left operand and assign the result to the left operand | a-=b is the same as a=a-b |
| *= | It will multiply the left operand with the right operand and assign the result to the left operand | a*=b is the same as a=a*b |
| /= | It will divide the left operand with the right operand and assign the result to the left operand | a/=b is the same as a=a/b |
| %= | It will calculate the modulus using two operands and assign the result to the left operand | a%=b is the same as a=a%b |
#6 Conditional Operators
Also, known as Ternary Operator or? : Operator, these operators are useful for decision-making.
Syntax:
Expression 1? Expression 2: Expression 3Here,? Represents the IF condition.
#7 Special Operators
Here are some special operators used in C
| Operator | Function |
| & | This operator is used to get the address of the variable.
Example: &a will give an address of a. |
| * | This operator works as a pointer to a variable.
Example: * a where * is a pointer to the variable a. |
| size of () | This operator gives the size of the variable.
Example: The size of (char) will give us 1. |
Example: C program using a special operator
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int *ptr, q;
q = 40;
/* It assigns the address of q to ptr */
ptr = &q;
/* display q's value using ptr variable */
printf("%d", *ptr);
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
C Operators Precedence
Generally, arithmetic, logical, and relational operators are used while coding in C. The precedence for these operators in arithmetic is greater than logical and relational. Note that all the operators in arithmetic also follow a different order of precedence. Let’s check which operators hold the highest precedence.
Order of Precedence in Arithmetic Operators
The increment and decrement (+ + and – -) operators hold the highest precedence in arithmetic operators. After that next precedence is for the unary minus ( – ) operator; next, three operators, /, *, and %, have equal precedence. The lowest precedence is for the operators like addition ( + ) and subtraction ( – ). In case of equal priority, the compiler takes charge while evaluating them. Remember the C operator associativity rule for all operators with the same precedence. Then the execution happens from left to right.
For example,
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int a = 15, b = 20, c = 32, result;
result = a * b - ++c;
printf("The result is: %d", result);
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
Explanation: Here, in the given equation, first, “++” executes; hence the value of c will be 33. Next, “* “holds the highest precedence after “++.” Hence after the execution of “a * b,” the result will be 300. Then the execution of “-” happens and results in 267.
Order of Precedence in Relational/Logical Operators
The highest precedence in relational/logical operators is logical, not (!). After that, greater than (>), greater than equal to (>=), less than (<), and less than equal to (<=) operators hold equal precedence. Then “= =” and “ != ” operators hold the equal precedence. Next comes the logical And (&&) operator. In the end, logical OR (||) holds precedence. Even for relational and logical operators, the execution of those operators who hold the same precedence happens by the compiler.
For example,
10 > 1 + 8
Output: False
Explanation: Here, we know the arithmetic operator holds the highest precedence. Hence the execution of “1 + 8” happens first. It results in 9. Next, comparing the numbers happens: “10 > 9”. So the final result will be False as 10 is not greater than 9.
Misc Operators in C
The Misc operators or miscellaneous operators are conditional operators that include three operands. In these 3, the execution of the first operand happens first. Then the execution of the second operand, if it is non-zero, or a third operand executes to provide the necessary Output. Besides the operators discussed above, C programming language supports a few other special operators like sizeof and “?:”.
| Operator | Description | Example |
| sizeof() | Finds the size of a variable | sizeof(b), if b is an integer, then the Output will be 4. |
| ?: | Conditional operator | Condition? X: Y; here, if the condition is true, the result will be X, else Y. |
| & | Address of a variable | &a returns the actual address |
| * | Pointer | *a |
Time and Space Complexity
Time and space complexity are the terms concerning the execution of an algorithm. The Time complexity is the time taken to run the algorithm as a function of the input. Space complexity is the space or memory the algorithm takes as an input function. These two terms depend on many terms like processor, operating system, etc.
Final Thoughts
C operators are the symbols used to perform relational, mathematical, bitwise, or logical operations. C language includes a lot of operators to perform various tasks as necessary in the program. Different kinds of operators are arithmetic, logical, and relational.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQS)
Q1. What are the boolean operators in C?
Answer: Boolean operators validate the relationship between the operands by returning 0 (false) or 1 (true) as Output. There are three kinds of boolean operators AND (&&), OR (||), and NOT (!). When both the inputs are true, then the AND will be true. If one of the inputs is true, then OR will be true. NOT operator provides the opposite value of the input.
Q2. What does ** mean in C?
Answer: The “**” in C is a double-pointer or pointer-to-pointer. Where * is a pointer that holds the address of the variable. ** mean the address of a variable already holding an address of a different variable.
Q3. What is the difference between prefix and postfix operators in C?
Answer: Prefix and postfix are the operators written before and after the operands. These operators are the increment (+ +) and decrement (- -) operators. For example, “++c” is the prefix operator, and “c++” is the postfix operator.
Q4. What is the Modulus operator?
Answer: The modulus operator is the arithmetic operator of C, and it works between two operands. The division of the numerator value by the denominator results in the remainder. In simpler words, the produced rest for the integer division is the modulus operator.
Q5. Does C language support operator overloading?
Answer: Operator overloading is a method of polymorphism where the programmer makes specific changes in the existing code without changing its meaning. Operator overloading is possible only in C++. Since polymorphism is possible only in an object-oriented language, C doesn’t support operator overloading.
Recommended Articles
This EDUCBA guide to C Operators discusses the operators used in C language with their syntax and examples. EDUCBA also suggests the following articles to learn more.


