What is Business Process Mapping?
Business Process Mapping is the practice of visually documenting how work flows within an organization. It uses symbols, shapes, and arrows to represent tasks, decision points, stakeholders, and outcomes.
A process map helps answer key questions such as:
- What activities are performed?
- Who is responsible for each task?
- How do tasks connect or depend on one another?
- What resources or tools are involved?
- What is the outcome or deliverable?
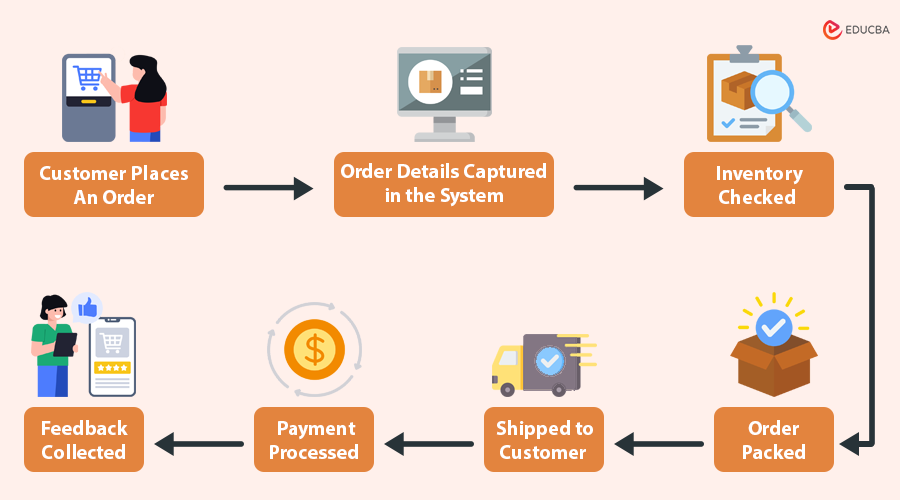
For example, in an order fulfillment process, the map may show:
This makes it easier for managers and employees to identify duplication of efforts, communication gaps, or delays in the workflow.
Table of Contents
- What is Business Process Mapping?
- Why is Business Process Mapping Important?
- Benefits of Business Process Mapping
- Types of Business Process Maps
- Steps to Create a Business Process Map
- Tools for Business Process Mapping
- Best Practices for Business Process Mapping
- Common Challenges in Business Process Mapping
- Applications of Business Process Mapping
Why is Business Process Mapping Important?
Process mapping extends beyond documentation; it plays a crucial role in helping organizations achieve success. Its importance lies in how it connects people, technology, and resources.
- Clarity and transparency: Employees across the organization can clearly see how they perform tasks and where their roles fit within the organization.
- Standardization: Establishes uniform ways of working, reducing inconsistencies and errors.
- Problem identification: Spot inefficiencies such as unnecessary approvals, repeated data entry, or redundant steps.
- Improved communication: Teams across different functions (e.g., finance, HR, operations) can collaborate effectively because they have a clear understanding of the big picture.
- Compliance and auditing: Regulatory-intensive industries, such as healthcare, finance, and manufacturing, utilize process maps to demonstrate compliance with laws and standards.
- Change management: Teams use process maps as a reference point when redesigning processes to plan and execute change effectively.
Benefits of Business Process Mapping
Organizations that adopt business process mapping often see transformational results. The benefits include:
- Enhanced efficiency: Mapping helps identify repetitive steps and bottlenecks, allowing for more efficient processes. For instance, automating manual data entry can save hours each week.
- Cost reduction: Streamlined processes reduce wastage of time, resources, and labor. Example: A logistics company mapping delivery routes can optimize fuel costs.
- Improved customer experience: Customers benefit from faster, more consistent services. Example: Banks utilize process maps to streamline loan approvals and minimize turnaround time.
- Employee empowerment: When employees clearly understand their roles, accountability increases, and performance improves.
- Risk management: Mapping reduces errors by ensuring every step has defined responsibilities and checks.
- Continuous improvement: Maps provide a baseline for measuring KPIs, making it easier to track improvements and drive innovation.
- Training & onboarding: New employees can learn processes quickly with the help of visual maps rather than lengthy documents.
Types of Business Process Maps
There are multiple ways to visualize business processes, each with unique applications:
- Flowcharts: Simple and widely used; they display sequential steps with decision points. Example: Employee leave approval process.
- Swimlane diagrams: Separate responsibilities into “lanes” for different departments or roles, showing interactions clearly. Example: Customer order process across sales, finance, and operations.
- Value stream maps: Originating from Lean methodology, these maps highlight value-adding vs. non-value-adding steps, often used in manufacturing and supply chains.
- Workflow diagrams: Focus on how tasks, documents, or information flow across systems and teams. Example: IT ticket resolution.
- SIPOC diagrams: High-level overview capturing Suppliers, Inputs, Processes, Outputs, and Customers; useful for Six Sigma projects.
- Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN): A clear and detailed method professionals use to map complex processes, making automation and compliance easier.
Steps to Create a Business Process Map
Creating a process map involves more than drawing boxes; it requires planning, collaboration, and analysis:
- Define the objective: Why are you mapping this process? (e.g., reduce costs, train employees, comply with regulations).
- Select the process: Focus on a single workflow rather than trying to map the entire organization at once.
- Gather information: Interview employees, review existing documents, and observe the process in action.
- Identify inputs and outputs: Every process has a trigger (input) and a result (output). Example: Customer inquiry → Resolved service request.
- List roles and responsibilities: Use RACI (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) to define roles.
- Draw the process map: Select the appropriate mapping tools (e.g., flowchart, swimlane, BPMN).
- Validate with stakeholders: Review the draft with employees and managers to ensure accuracy and completeness.
- Analyze and improve: Identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and opportunities for automation to enhance efficiency.
- Implement and monitor: Update workflows and track key metrics, including time saved, error reduction, and improved customer satisfaction.
Tools for Business Process Mapping
Modern tools make mapping faster, collaborative, and more effective. Popular ones include:
- Microsoft Visio: Industry standard for professional diagrams.
- Lucidchart: Cloud-based tool enabling real-time collaboration.
- Bizagi: Specialized in BPMN and automation.
- io (diagrams.net): Free, versatile tool for flowcharts and diagrams.
- ARIS: Advanced enterprise-level business process analysis platform.
- Miro: Online whiteboard suitable for brainstorming and collaborative mapping.
- Creately: Easy-to-use tool for teams with templates for multiple mapping styles.
Best Practices for Business Process Mapping
To get the most value out of process mapping, organizations should follow these proven practices:
- Involve stakeholders early: Include people who execute the tasks daily to ensure accuracy.
- Keep it simple: Avoid overloading maps with unnecessary detail. Create different layers (high-level overview + detailed breakdown).
- Use standard symbols: Stick to BPMN or flowchart symbols to avoid confusion.
- Focus on value: Highlight critical paths and value-adding activities.
- Update regularly: Update maps whenever there are organizational or system changes.
- Leverage technology: Use collaborative tools for transparency and version control.
- Link to KPIs: Connect process outcomes to measurable business goals, such as cost savings, turnaround time, or customer satisfaction.
Common Challenges in Business Process Mapping
Despite its advantages, organizations face hurdles such as:
- Employee resistance: Workers may fear increased monitoring or job cuts.
- Over-complexity: Maps that are too detailed confuse rather than clarify.
- Management apathy: Lack of leadership support can stall the initiative.
- Outdated maps: Processes change, but maps often remain static.
- Integration issues: Difficulty connecting maps with automation platforms or enterprise systems.
Applications of Business Process Mapping
Organizations apply business process mapping across industries in versatile ways:
- Human resources: Recruitment, employee onboarding, performance appraisal, and exit process.
- Finance: Invoice processing, payroll management, and expense approvals.
- Customer service: Complaint handling, ticket escalation, service delivery.
- Supply chain: Procurement, vendor management, logistics, distribution.
- Healthcare: Patient admission, treatment protocols, and discharge planning.
- Information technology: Software development lifecycle, system maintenance, cybersecurity workflows.
- Education: Enrollment, examination, course scheduling, and student feedback cycles.
Final Thoughts
Business Process Mapping is not just about creating workflow diagrams; it is a practical tool that helps organizations work more efficiently, adhere to rules, and deliver better experiences for their customers.
When done correctly, it enhances communication, fosters transparency, reduces costs, and sets the foundation for process automation and digital transformation. Process mapping enables small businesses to achieve efficiency and large enterprises to strive for operational excellence by helping them visualize, analyze, and continually improve their workflows.
By investing in process mapping today, businesses can unlock long-term benefits of agility, cost savings, and customer satisfaction.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the difference between a process map and a workflow diagram?
Answer: A process map provides a detailed and structured overview of an entire process, including its roles, decisions, and outcomes. At the same time, a workflow diagram focuses mainly on the sequence of tasks and their flow.
Q2. Should process mapping include every minor task?
Answer: No. Focus on critical steps that impact outcomes and efficiency. Overloading maps with minor details can make them confusing and less useful.
Q3. How does process mapping relate to process improvement methodologies like Lean or Six Sigma?
Answer: Process mapping is often the first step in Lean or Six Sigma projects. It helps identify waste, redundancies, and inefficiencies before implementing improvements.
Q4. How do I choose the right type of process map for my organization?
Answer: The choice depends on the process complexity, audience, and purpose. Use flowcharts for simple processes, swimlane diagrams for cross-department workflows, and BPMN for complex or regulated processes.
Q5. Are there risks to not involving employees in process mapping?
Answer: Yes. Excluding employees can result in inaccurate maps, missed inefficiencies, and lower adoption of process improvements, since those performing tasks daily offer critical insights.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide on business process mapping helped you understand how to visualize and improve workflows. Explore our related articles on process improvement strategies, workflow automation, and Lean management techniques.