What is Brand Positioning?
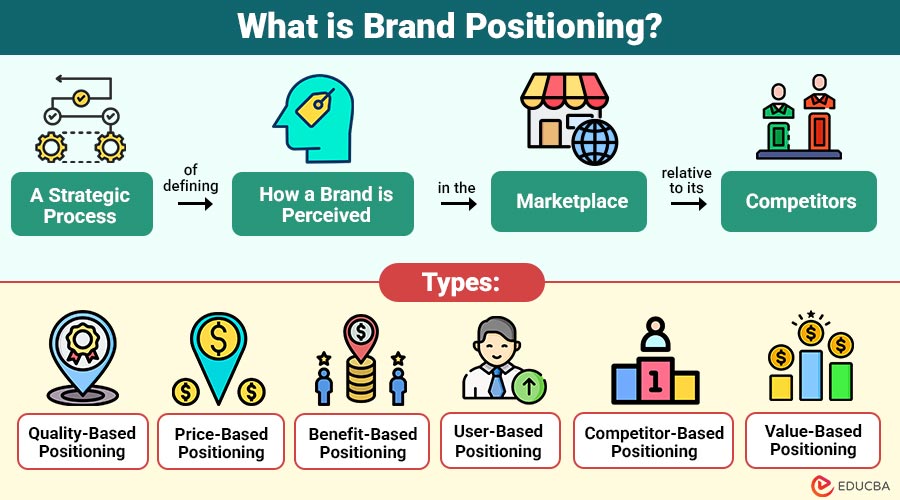
Brand Positioning refers to strategic process of defining how a brand is perceived in the marketplace relative to its competitors. It includes identifying a unique value proposition and communicating it consistently across all touchpoints so that customers associate specific benefits, emotions, or values with the brand.
For example, Tesla places itself as an innovative and sustainable luxury car brand, combining high performance with environmental consciousness.
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Importance
- Key Elements
- Steps in Developing a Brand Positioning Strategy
- Types
- Benefits
- Challenges
- Examples
Key Takeaways:
- Effective brand positioning differentiates your business, making it memorable and meaningful to target customers.
- Consistent messaging across all platforms builds trust, loyalty, and long-term emotional connections with audiences.
- Understanding competitors, audience needs, and unique value ensures strategic clarity and market relevance.
- Strong positioning enhances marketing efficiency, boosts recognition, and supports sustainable growth in competitive industries.
Importance of Brand Positioning
Brand positioning is not merely a marketing exercise—it is a strategic necessity. Here is why it matters:
1. Differentiation
It enables your brand to stand out in a saturated market by showcasing distinctive attributes, values, and advantages that competitors cannot easily replicate.
2. Customer Loyalty
Strong brand positioning fosters emotional connections with customers, leading to repeat purchases, brand advocacy, and long-term customer retention built on trust and satisfaction.
3. Value Perception
Effective positioning enhances how customers perceive your brand’s quality and credibility, allowing you to justify premium pricing and maintain strong market relevance.
4. Clarity of Message
It ensures your brand consistently communicates its core message, vision, and identity across all marketing platforms, strengthening overall audience understanding and engagement.
5. Strategic Direction
Positioning provides a clear foundation for innovation, design, and promotional strategies, aligning every organizational decision with long-term brand and business goals.
Key Elements of Brand Positioning
To successfully position a brand, marketers must focus on several core components:
1. Target Audience
Understanding who your ideal customers are—their demographics, psychographics, and behavioral traits—is the first step in positioning.
2. Market Definition
Identifying the category or industry in which your brand competes helps frame your competitive landscape.
3. Brand Promise
This is the unique benefit that differentiates your brand from others and convinces customers to choose you.
4. Brand Personality
Brands, like people, have personalities—serious, playful, luxurious, or adventurous—that influence consumer perception.
5. Brand Associations
These are the thoughts, feelings, and mental images consumers link to your brand (eg: Starbucks → premium coffee experience and community, Patagonia → environmental responsibility and adventure)
Steps in Developing a Brand Positioning Strategy
Developing a successful brand positioning plan requires a methodical approach:
Step 1: Identify Your Target Market
Study your audience’s needs, aspirations, and pain points. Tools like market segmentation and buyer personas help clarify who you are speaking to.
Step 2: Analyze Competitors
Examine your competitors’ positioning strategies to find market gaps. Identify what they do well and where they fall short.
Step 3: Define Your Unique Value Proposition
Clarify what sets your brand apart. Ask questions like:
- What makes my brand unique?
- What problem does it solve better than others?
Step 4: Craft a Positioning Statement
A positioning statement succinctly defines your brand’s target audience, category, differentiation, and benefits.
Step 5: Communicate Consistently
Integrate your positioning into all aspects of branding—advertising, packaging, customer service, and digital presence.
Step 6: Evaluate and Refine
Regularly assess consumer feedback and market trends. Positioning is not static—it evolves as markets and customer preferences change.
Types of Brand Positioning Strategies
Different businesses adopt different positioning strategies depending on their goals and audience. Here are some common types:
1. Quality-Based Positioning
This strategy highlights exceptional craftsmanship, superior materials, and reliable performance to communicate excellence and justify premium brand value.
2. Price-Based Positioning
Brands use this approach to position themselves as either the most affordable or the most premium option in the market.
3. Benefit-Based Positioning
This strategy highlights the unique benefits, features, or problem-solving capabilities that make a product or service stand out.
4. User-Based Positioning
Brands position themselves by appealing to specific user groups, lifestyles, or personalities to create emotional resonance.
5. Competitor-Based Positioning
This strategy defines the brand in contrast to a major competitor, often showcasing superiority or differentiation.
6. Value-Based Positioning
This approach emphasizes a balance between price, quality, and functionality to provide customers with the best overall value.
Benefits of Strong Brand Positioning
Here are the key benefits a brand gains through effective positioning:
1. Increased Brand Recognition
A well-defined brand positioning ensures customers easily recognize your brand’s message, personality, and values across all touchpoints.
2. Customer Trust
Consistent and authentic brand messaging builds credibility, reliability, and long-term customer loyalty through transparency and value alignment.
3. Competitive Edge
In a congested market, strong uniqueness helps your brand stand out and makes it more difficult for rivals to copy your identity.
4. Better Marketing ROI
Clear positioning allows for focused and targeted marketing campaigns, resulting in higher audience engagement, better conversions, and improved returns.
5. Emotional Connection
A distinct brand position resonates emotionally with customers, creating meaningful relationships that drive long-term loyalty and brand advocacy.
Challenges in Brand Positioning
Despite its benefits, developing a solid positioning strategy can be challenging. Some common hurdles include:
1. Market Saturation
In industries crowded with competitors, it is difficult for brands to differentiate themselves and secure a distinct, memorable position in customers’ minds.
2. Changing Consumer Preferences
Rapidly evolving trends, needs, and consumer sentiments can make existing positioning strategies outdated, requiring continuous adaptation and monitoring.
3. Inconsistent Messaging
When brand communications lack consistency across platforms, customers can become confused, reducing trust and weakening the perceived value of the brand.
4. Overextension
Expanding too quickly into multiple products or markets may dilute the core brand identity, confuse consumers, and weaken loyalty.
5. Globalization
Cultural differences, regional expectations, and varying market norms complicate international positioning, requiring brands to balance local adaptation with global consistency.
Examples of Successful Brand Positioning
Here are some notable brands and how they have effectively positioned themselves in the market:
1. Nike – “Just Do It”
Nike positions itself as a symbol of athleticism, empowerment, and perseverance. Its campaigns inspire people to push beyond limits, associating the brand with personal achievement rather than just footwear.
2. Apple – “Think Different”
Apple’s positioning focuses on innovation, creativity, and premium design. It appeals to users who value aesthetics and cutting-edge technology.
3. Dove – “Real Beauty”
Dove’s “Real Beauty” campaign reinterpreted beauty ideals and positioned the company as a supporter of confidence and authenticity.
Final Thoughts
Brand positioning is the cornerstone of long-term business success. It determines how consumers perceive, relate to, and value your brand in a crowded marketplace. A well-defined positioning strategy clarifies your purpose, strengthens customer relationships, and creates a unique market identity that withstands time and competition. Being the most relevant and memorable to your audience is more important for positioning than being the best, regardless of whether you are a startup looking to enter the market or an existing brand looking to update your image.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Can a brand reposition itself?
Answer: Yes, through rebranding, new messaging, or market shifts, companies can reposition to stay relevant (e.g., Old Spice’s transformation into a youthful brand).
Q2. What tools help in brand positioning research?
Answer: Surveys, focus groups, sentiment analysis, competitor mapping, and perceptual maps are commonly used tools.
Q3. How long does it take to establish brand positioning?
Answer: It is an ongoing process; initial recognition may take months, but strong positioning is built through consistent communication over the years.
Q4. How often should a brand revisit its positioning strategy?
Answer: Brands should review positioning every 1–2 years or when major market changes occur.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Brand Positioning” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
