Introduction to Azure Email
Third-party solutions, such as SendGrid, provide email services on Azure that may be integrated into solutions to meet a variety of use cases. For example, we can use the SendGrid Email Delivery Service on Microsoft Azure if we need a low-cost, low-maintenance solution and also have an Azure subscription.
What is an Azure Email?
From an email standpoint, Microsoft blacklists all Azure IPs; therefore, sending emails from Azure via SMTP without a relay does not guarantee that they’d be received at the other end. As a result, we could see that none of our email traffic, both inbound and outbound, was getting anywhere. Azure’s email sending generally relies on a third-party SMTP relay service. The most popular and recommended option for this is SendGrid. Numerous examples and documentation are available on combining Azure and SendGrid to post emails. At the same time, we can use another SMTP relay-compatible solution: Elastic Email, Mailjet, and SocketLabs.
How to Send an Azure Email?
SendGrid is arguably the most used email service for sending emails from Azure. The popularity of SendGrid and Azure has soared due to the availability of a free plan for Azure subscribers, which includes a monthly limit of 25,000 emails. Although the free plan is no longer available in the Azure interface, Microsoft verified that a free membership with a daily limit of 100 emails is still available.
The following are some of SendGrid’s most prevalent features and functions:
- Sending receipts automatically
- Managing distribution lists for e-mail distribution
- Obtaining real-time data
- Customer inquiries are forwarded.
- Taking care of incoming e-mails
Two Azure services provide similar functionality:
- Queue storage is a cloud messaging service that allows Azure application components to communicate with one another.
- Service Bus is a powerful messaging system for integrating applications, services, and devices. Service Bus can also connect to remotely hosted applications and services using the related Service Bus relay.
From architecture to ISP outreach and surveillance to filtering services and real-time analytics, SendGrid handles all technical specifications. As a result, it’s the greatest cloud-based email delivery provider in the world.
SendGrid’s email services can be used in a variety of ways. However, it is entirely dependent on your requirements and goals. In Azure, here’s how to set up and use SendGrid:
Please ensure you have an active SendGrid account in your Azure subscription before you begin.
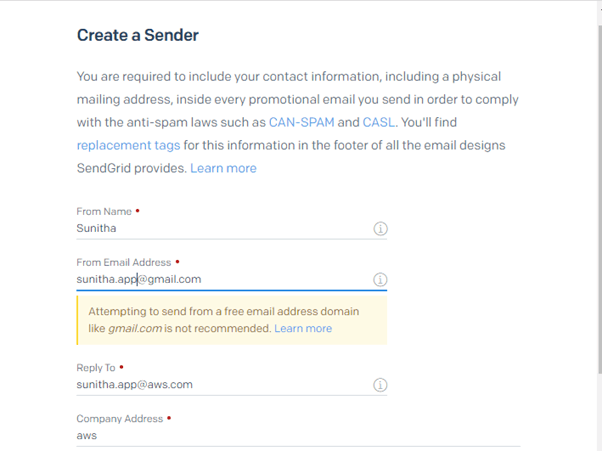
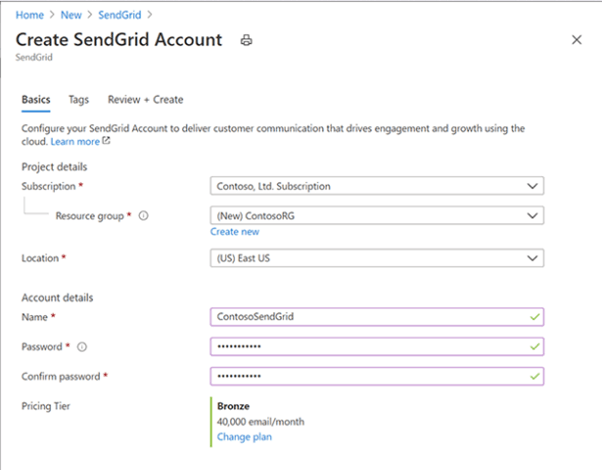
Create a SendGrid account and acquire the details you need to send an email using SendGrid by following the instructions below.
1.Log into your Azure account.
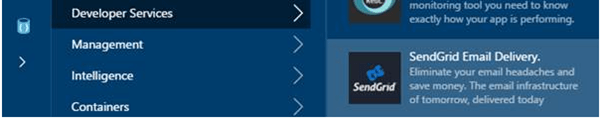
2. Look for the service ‘SendGrid Email Delivery.’
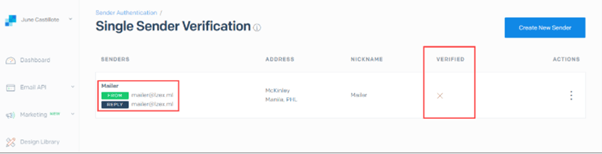
The next step is to go to the Single Sender Verification page and look for the updated sender address.
To verify the sender, locate the email sent to the sender’s address, as seen in the screenshot below. Then, confirm the sender’s identity on the Verify Single Sender button.
To send emails through SendGrid, the following requirements are typically needed:
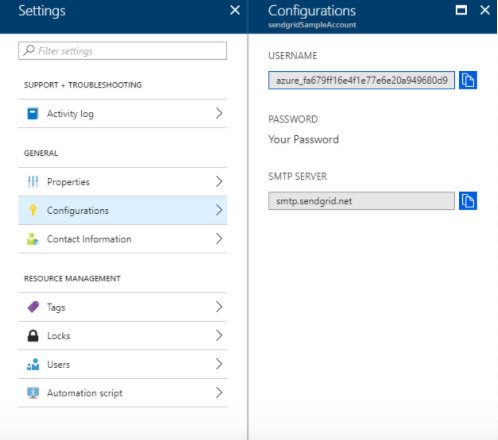
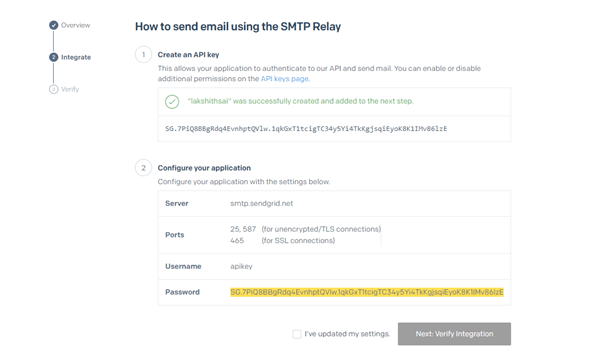
- The SMTP server ip for SendGrid is smtp.sendgrid.net.
- The SMTP security username will always be apikey.
- Use the value of the API key we created in SendGrid as your password.
- Avoid using port 25. Alternatively, use port 587.
- Only the sender address authorized by SendGrid can be used as the recipient of the emails.
$sendGridApiKey = 'SG...........P258'
$SendGridEmail = @{
From = '[email protected]'
To = '[email protected]'
Subject = 'Hello message from Azure'
Body = 'A formal mail from the account'
SmtpServer = 'smtp.sendgrid.net'
Port = 587
UseSSL = $true
Credential = New-Object PSCredential 'apikey', (ConvertTo-SecureString $sendGridApiKey -AsPlainText -Force)
}
Send-MailMessage @SendGridEmail
Check the recipient’s mailbox for the text message we sent to confirm email deliverability. The end effect would look something like this. The sender’s address indicates that the message was sent using SendGrid.net as the email service provider.
Create an Azure Subscription
We can utilize free and commercial Azure services to build the next-generation architecture for any product and user with an Azure account. A logical unit of Azure services tied to an Azure Account is called an Azure Subscription. On a subscription-by-subscription basis, we do the billing. An Azure account determines the method of recording Azure usage and the designated account administrator. In Azure Account Center, users may create accounts and subscriptions.
Here is how we segregate things for organizational and technical purposes from each other within Azure. (also a single billing subscription). And also a lot of functions could be focussed.
Azure Email Developer Services Menu (Screenshot)
SendGrid is a cloud-based emailing service that offers dependable business email delivery, scalability, real-time statistics, and easy integration through customizable APIs.
Sign up form
When generating SendGrid email calls in the code, we submit an API key to a service instead of an email address and password.
From the Developer Services option on the new Azure interface, select SendGrid Email Delivery.
Cloud Email Services
CloudMail is a sophisticated Windows mail collaboration server that enables organizations to connect with customers, workers, and partners using the company’s most important email clients, including Microsoft Outlook for Windows and Mac, as well as a wide range of mobile devices. Cloud-based email technology is a cloud platform that includes all-in-one email security, archiving, and availability solutions. Any commercial hosting solution that uses the same domain comes with CloudMail email services. It’s also a stand-alone product for $5 / month per domain.
CloudMail comes with an unlimited number of email addresses.
10 GB of Disk Capacity (more space is available for $0.50 per GB)
POP and IMAP connectivity, as well as a web interface
When we use cloud-based email, we give up control of your data to a third party who manages it offsite. This implies the supplier handles data storage and backup, which is advantageous if the firm lacks the necessary internal skills to maintain this data. If the internal server fails, one can still email and communicate with co-workers online. Internal email servers provide less reliability and availability compared to sending and receiving emails through the cloud.
Conclusion
Most Azure users will require the ability to send emails from an Azure-based application. As a result, we’ve seen a screenshot of how to use Azure and its email services.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Azure Email” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.