What are Audit Objectives?
Audit objectives are specific, clear, and measurable goals that auditors set before conducting an audit. The main objective of the audit is that the auditor should express their accurate opinion on the financial statements, i.e., whether the statements represent the true and fair view of the financial position of the organization or not.
The auditor properly examines the company’s financial records and statements and provides reasonable assurance through their opinion that the company’s financial statements are free from misstatements and fraud.
Apart from the above, audit objectives differ for different audit types. For instance, an external audit verifies the financial statements of the company. In contrast, an internal audit checks the accuracy and functioning of the company’s internal controls relating to financial reporting, legal and policy-related compliance, etc.
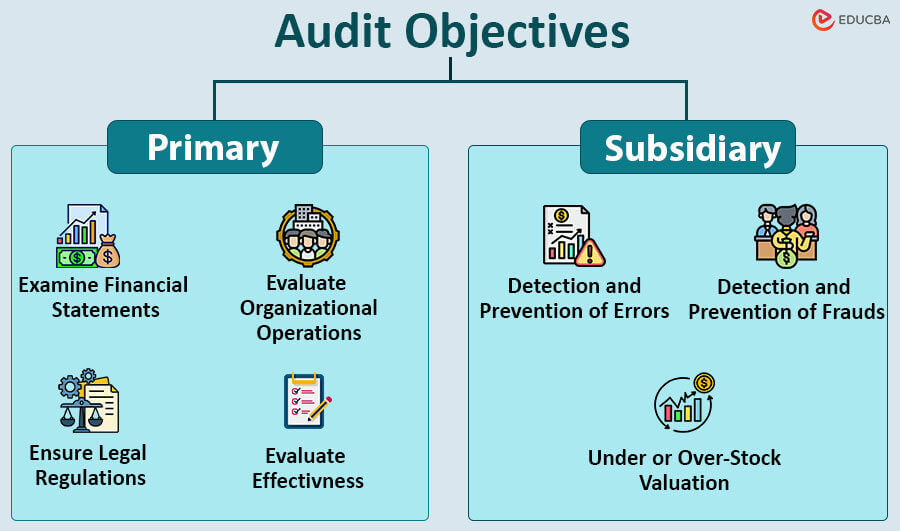
Primary & Subsidiary Audit Objectives
- Examine Financial Statements
- Evaluate Organizational Operations
- Ensure Legal Regulations
- Evaluate Effectiveness
- Detection and Prevention of Errors
- Detection and Prevention of Frauds
- Under or Over-Stock Valuation
Primary Audit Objectives
1. Examine Financial Statements
One of the first audit objectives is to examine an organization’s financial statements to ensure they are complete and accurate.
What the Auditor Does?
- Examines if the financial data is correct and all account balances are accurate.
- Uses supporting documents to verify that all reported transactions are authentic.
- Confirms if the reported assets and liabilities actually exist by cross-checking the values to supporting documents.
- Gives an expert opinion stating whether the financial statements are fair and accurate.
Example:
Company XYZ hired an auditing firm to examine its 2023 fiscal records, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. The auditors carefully confirmed a total revenue of $25 million, expenses of $19 million, net income of $7 million, assets of $55 million, and liabilities of $30 million. They verified each figure using supporting documents, transaction records, and invoices.
After a comprehensive review, the auditing firm confirmed that Company XYZ’s financial statements were accurate and as per the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
2. Evaluate Organizational Operations
The next objective is to check the organization’s operational processes and procedures. This is to identify any areas of improvement.
What the Auditor Does?
- Checks the operational process to see if the company can improve the efficiency of the operations.
- Ensures the company maintains the required product/service quality and has excellent customer satisfaction.
- Provides inputs to help the business enhance its safety measures and prevent any accidents.
- Finds cost-saving opportunities that won’t lead to any compromise in product quality.
Example:
In June 2023, ABC Manufacturing audited its production facility. The audit found that the production line was only 75% efficient, and there had been 12 workplace accidents due to safety protocol breaches. Subsequently, the company implemented process improvements and enhanced safety training for its 300 workers.
Due to these changes, efficiency jumped to 95%, resulting in a 20% increase in production output. Additionally, there were only 2 workplace accidents in the following months. Thus, ABC’s actions not only boosted productivity but also made the workplace safer and more efficient for its employees.
3. Ensure Legal Regulations
The next audit objective is to check whether an organization is following all specified laws, regulations, or internal policies.
What the Auditor Does?
- Ensures the organization complies with relevant laws and government regulations, including taxation policies.
- Assesses if the firm is also adhering to the industry-specific standards.
- Confirms that all departments are consistently following internal policies and procedures.
- Identifies areas of non-compliance that may pose legal or financial risks.
- Makes sure that the company also complies with any signed contractual obligations.
Example:
In a 2023 audit of XYZ Bank, the auditors checked if the bank adhered to anti-money laundering (AML) rules. They found issues with customer due diligence, transaction, and record-keeping, leading to non-compliance. Therefore, the regulatory authority ordered the Bank to provide employee training, report progress regularly, etc., to enhance AML adherence.
4. Evaluate Effectiveness
In this primary objective, the auditor has to evaluate the effectiveness of the organization’s programs, projects, or activities.
What the Auditor Does?
- Evaluates if the internally maintained records are effective and identify if there are any deviations in internal and reported records.
- Measures key performance indicators (KPIs) to determine the program’s performance.
- Evaluates how the firm has allocated resources to align them with their priorities and goals.
- Measures the tangible results of the program, such as improved services or stakeholder benefits.
- Examines the program’s sustainability over the long term.
Example:
After auditing a city’s public transportation system, the audit team measured bus route efficiency, on-time performance, and cost-effectiveness. As a result, they found that there were several underutilized routes and high maintenance costs. Thus, the audit’s recommendations included optimizing routes and seeking cost-saving partnerships. The changes resulted in a 15% reduction in expenses and improved on-time performance, making the city’s transportation system more efficient and cost-effective.
Subsidiary Audit Objectives
The subsidiary audit objectives help auditors easily reach their primary objectives. Subsidiary audit objectives are as follows:
5. Detection and Prevention of Errors
While pursuing subsidiary audit objectives, auditors look for errors in the financial information provided by the company.
What the Auditor Does?
- Identifies if the records include any errors (errors of omission, exclusion, standards, and compensating errors).
- Checks if the company made any errors due to carelessness or unavailable information.
- Ensures the methods the company follows to control and prevent such errors.
Example:
During a recent audit of ABC Company, auditors found a major error in the financial records. A $50,000 sales transaction was missing in the year-end financial statements. Not detecting it might have given the stakeholders misleading information about the company’s financials. Thus, to prevent such errors in the future, the auditors asked the company to implement stronger controls and cross-check mechanisms.
6. Detection and Prevention of Frauds
Another objective is to investigate financial records to uncover any financial fraud, misconduct, or irregularities.
What the Auditor Does?
- Analyzes financial transactions, contracts, invoices, and payment records to find any irregularities or fraudulent schemes.
- Traces the flow of funds involved in fraudulent activities to determine their origin, destination, and use.
- Gather and save evidence of financial misconduct, ensuring it is applicable in legal proceedings.
- Records instances of unethical behavior, conflicts of interest, or company policy violations.
Example:
In 2023, XYZ Corporation hired a forensic auditing firm because they suspected an employee embezzled their money. The auditors looked at bank records, invoices, and payroll information and found that the employee had taken $475,000 from the company over five years. This evidence led to the employee’s prosecution, and XYZ Corporation was able to recover $415,000.
7. Under or Over-Stock Valuation
As part of their subsidiary objectives, auditors also actively check whether the organization properly values stock or inventory.
What the Auditor Does?
- Confirms that all reported inventory items actually exist.
- Verifies that the firm is correctly using the mentioned inventory valuation method.
- Ensures that the company values the stocks at a lower cost or market value, as required by accounting standards (U.S. GAAP or IFRS).
- Makes sure that the firm has accurately mentioned the accounting policies they follow for inventory valuation in the financial statements.
Example:
A manufacturing company, ABC Company, reported $1.3 million for its year-end inventory. However, auditors found that their old inventory valuation method led to errors. After updating the valuation, the real inventory value was $1.62 million. This $320,000 mistake could mislead investors, affecting how they see the company’s financial health.
Advantages and Disadvantages
These are the advantages and disadvantages of following the audit objectives.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Provides clear direction for the audit process. | May limit flexibility in the audit approach. |
| Aligns the audit with stakeholder expectations and goals. | Objectives may become outdated if not regularly reviewed. |
| Helps in identifying and managing potential risks. | Overly ambitious objectives can lead to resource constraints. |
| Allows for the measurement of audit success and outcomes. | Inflexible objectives may not adapt to changing circumstances. |
| Establishes accountability for audit outcomes. | May not cover all emerging risks or issues. |
| Promotes efficient audit planning and execution. | Can be time-consuming to develop comprehensive objectives. |
| Ensures examination of compliance with relevant regulations and standards. | Objectives must be communicated and understood by all involved parties. |
| Facilitates quality control in auditing practices. | Inadequate or unclear objectives can lead to misinterpretation. |
Final Thoughts
Auditing is crucial for organizations; in some cases, it’s legally necessary. Auditors must follow all primary and secondary audit objectives to evaluate a company’s financial health accurately. Auditing helps maintain transparency, accountability, and financial integrity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the relationship between audit objectives and the audit opinion?
Answer: Audit objectives are directly related to the audit opinion. Auditors use their examination results, guided by the objectives, to form an opinion on whether the financial statements provide a true and fair view of the organization’s financial position.
Q2. Can audit objectives change during an ongoing audit?
Answer: While auditors establish audit objectives at the beginning of an audit, they can be adjusted or refined during the audit process if new information or issues arise that necessitate a change in focus.
Q3. What happens if auditors cannot achieve the audit objectives?
Answer: If auditors cannot meet audit objectives due to insufficient evidence or uncooperative management, auditors may issue a qualified or adverse opinion, indicating limitations in their examination.
Q4. Who sets the audit objectives?
Answer: Auditors establish Audit objectives in consultation with relevant stakeholders, including management and regulatory bodies. The objectives should align with the purpose and goals of the audit engagement.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Audit Objectives., where we define the 7 important primary and secondary audit objectives. Look at the following articles to learn more –


