What Is an Audience Targeting?
Audience targeting involves strategically identifying distinct groups of individuals who are most likely to engage with your product, service, or message, and customizing your marketing approach to connect with them effectively.
Rather than sending the same message to a broad audience, marketers apply audience targeting to divide consumers into groups based on traits such as age, geography, interests, digital behavior, and personal values. This approach results in stronger engagement, more personalized customer experiences, and a higher return on investment.
A fitness apparel brand wants to promote a new line of eco-friendly workout gear. Instead of advertising to everyone, the brand targets women aged 25–35 in urban areas who show interest in sustainability, fitness, and healthy living on social media. As a result, the campaign reaches a highly relevant audience, increasing conversions and brand loyalty.
Table of Contents
- Meaning
- Importance
- Audience Targeting vs. Mass Marketing
- Types
- How to Implement?
- Case Study
- Platforms
- Challenges
- Best Practices
Key Takeaways
- Audience targeting enables marketers to connect with specific groups using data like demographics, behavior, interests, and values.
- Personalized campaigns result in better engagement, reduced marketing waste, and higher ROI compared to mass marketing.
- Key targeting types include demographic, geographic, behavioral, psychographic, technographic, and contextual targeting.
- Implementation requires defining business goals, creating personas, segmenting audiences, and optimizing through analytics.
- Tools like Facebook Ads, Google Ads, LinkedIn, Mailchimp, and programmatic platforms streamline targeting efforts.
- Spotify’s Wrapped campaign is a standout example of behavioral and psychographic targeting done right.
- Marketers must stay vigilant against challenges like privacy issues, over-segmentation, and data inaccuracies.
- Best practices include using first-party data, running regular tests, and focusing on value-based messaging.
Why Audience Targeting Matters?
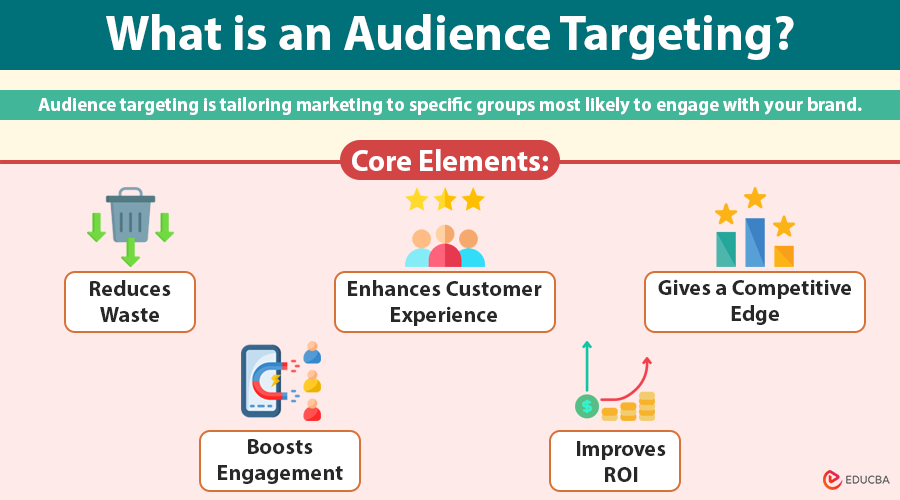
Audience targeting helps marketers move from guesswork to precision. When brands know exactly who they are speaking to, they can create more effective campaigns and build stronger relationships. Here’s why it matters:
- Reduces waste: Marketers focus their efforts on high-potential leads instead of reaching irrelevant audiences.
- Boosts engagement: Targeted content resonates more, leading to higher click-through rates, shares, and interactions.
- Enhances customer experience: Personalized messaging creates a more meaningful and relevant experience for each user.
- Improves ROI: Businesses invest their budget where it has the most impact on people who are more likely to convert.
- Gives a competitive edge: A deep understanding of the audience allows brands to anticipate needs and stand out in crowded markets.
Audience Targeting vs. Mass Marketing
| Aspect | Audience Targeting | Mass Marketing |
| Approach | Focuses on specific consumer segments using data and insights | Broadcasts a general message to a wide, undifferentiated audience |
| Message Personalization | Tailors messages based on user behavior, interests, and preferences | Uses a one-size-fits-all message for all audiences |
| Efficiency | Maximizes efficiency by targeting only high-potential leads | Often wastes resources on uninterested or irrelevant audiences |
| Return on Investment | Delivers higher ROI due to targeted and relevant communication | Generates lower ROI due to broad and imprecise reach |
| Examples | Instagram ad for fitness apparel shown to women aged 20–35 in metro cities | TV commercial for a new beverage shown nationwide to all demographics |
Key Types of Audience Targeting
To reach the right audience effectively, marketers use different targeting methods based on consumer characteristics, behavior, and context. Here are the six most common types:
1. Demographic Targeting
Marketers segment their audience based on measurable statistics such as age, gender, income, education, marital status, and occupation.
2. Geographic Targeting
This method targets users based on location, such as city, region, country, or zip code. It’s highly effective for promoting location-based offers.
3. Behavioral Targeting
Marketers analyze consumer actions like website visits, purchase history, and content engagement to serve relevant ads.
4. Psychographic Targeting
This digs into values, interests, lifestyles, and personality traits to shape marketing campaigns that resonate emotionally.
5. Technographic Targeting
This targets audiences based on their devices, browsers, operating systems, or software usage.
6. Contextual Targeting
Marketers place ads on platforms where the surrounding content aligns with the ad’s message.
How to Implement Audience Targeting?
To make audience targeting effective, marketers must follow a clear, data-driven process that aligns with business objectives and customer insights. Here’s how to implement it step by step:
1. Define Your Business Goals
Start by determining your primary marketing objective, be it increasing brand recognition, capturing leads, boosting conversions, or maintaining customer loyalty. This will inform how you define and approach your target audience.
2. Create Detailed Buyer Personas
Build fictional but data-backed profiles of your ideal customers. Include key demographic and psychographic traits such as age, job role, motivations, interests, and pain points. These personas help humanize your audience.
3. Use Data and Analytics
Rely on tools like Google Analytics, Facebook Audience Insights, and CRM platforms to identify patterns in customer behavior. Use this data to understand where your audience comes from and what they respond to.
4. Segment Your Audience
Divide your audience into clear segments based on shared behaviors, needs, or characteristics. Effective segmentation allows you to deliver tailored experiences instead of one-size-fits-all messages.
5. Craft Tailored Campaigns
Create marketing messages tailored to each audience segment by using personalized visuals, headlines, offers, and content that align with their specific interests and values.
6. Monitor and Optimize
Once you launch your campaign, monitor its effectiveness using KPIs, A/B testing, heatmaps, and conversion tracking tools. Analyze the results to fine-tune your targeting strategy and continually enhance performance.
Case Study
Spotify’s Wrapped Campaign
Brand: Spotify
Objective: Increase user engagement and brand loyalty.
Audience Targeting in Action:
Spotify uses detailed listener data—such as preferred genres, favorite artists, and listening habits—to create its year-end “Spotify Wrapped” campaign. Each user receives a personalized summary of their music trends, which they can share on social media.
Results:
- Over 60 million users engaged with Spotify Wrapped in one year.
- Massive brand visibility due to user-generated sharing.
- Deepened emotional connection between users and the platform.
Why It Worked:
Spotify effectively used behavioral and psychographic targeting to deliver hyper-personalized content that resonated with each listener. This campaign demonstrates how targeted, data-driven marketing can amplify engagement and generate organic brand promotion.
Common Platforms That Support Audience Targeting
Marketers use various digital platforms to implement precise audience targeting. These platforms provide features that enable marketers to deliver the right message to the right audience at the most effective moment.
1. Facebook & Instagram Ads
Meta’s ad platforms allow for highly detailed targeting based on user interests, behavior, demographics, device usage, and more. Marketers can also build custom and lookalike audiences for refined targeting.
2. Google Ads
Google supports search, display, video, and shopping ads with targeting options such as keywords, demographics, in-market audiences, and remarketing. It enables you to reach users based on intent and online behavior.
3. LinkedIn Ads
Ideal for B2B marketing, LinkedIn allows targeting by job title, company size, industry, seniority level, and more. It is especially effective for professional services and enterprise solutions.
4. Email Marketing Tools
Platforms like Mailchimp, ActiveCampaign, and Klaviyo enable businesses to divide their contact lists using factors like user activity, buying behavior, interaction history, and demographic details. These tools help deliver automated, highly personalized email campaigns with greater accuracy.
5. Programmatic Advertising Platforms
These platforms use AI and real-time bidding to automate ad placement across the web. They analyze audience data in real time to ensure ads appear in front of the most relevant users across various websites and apps.
Challenges in Audience Targeting
While audience targeting offers precision and personalization, it also comes with certain obstacles that marketers must manage carefully:
1. Privacy Concerns
With stricter data protection laws like GDPR and CCPA, businesses must handle user data ethically and transparently. Mishandling data can lead to legal consequences and loss of consumer trust.
2. Over-Segmentation
Creating too many small or hyper-specific segments can dilute your messaging, making campaigns harder to manage and less impactful. Simplicity and balance in segmentation are key.
3. Data Inaccuracies
Outdated or incorrect data can mislead targeting efforts, resulting in irrelevant messaging and inefficient ad spend. Clean, accurate, and updated data is essential for effective targeting.
4. Audience Fatigue
When users repeatedly see the same ads or messages, they may lose interest or even become annoyed. This overexposure leads to lower engagement and ad blindness over time.
Best Practices for Effective Audience Targeting
To get the most out of audience targeting, marketers should follow these best practices:
- Leverage first-party data for accuracy: Use data collected directly from your customers, such as website behavior, purchase history, and email interactions, to build reliable and customized segments.
- Test and iterate constantly: Regularly run A/B tests and analyze performance metrics to identify what resonates with each audience segment and continuously refine your strategies.
- Combine multiple targeting types: Blend demographic, behavioral, psychographic, and contextual data to create deeper, more holistic audience profiles for better personalization.
- Respect user privacy and ensure compliance by staying up to date with regulations like GDPR and CCPA. Make data collection transparent and prioritize ethical handling of user information.
- Deliver value-focused messaging: Instead of hard selling, craft messages that solve problems, address needs, or add value to the user’s experience to build long-term relationships.
Final Thoughts
Audience targeting is no longer a luxury; it is a necessity for modern marketing. By understanding who your ideal customers are and tailoring your messaging accordingly, you move beyond guesswork into intentional, data-driven engagement. When done well, audience targeting does not just improve campaign performance; it strengthens brand loyalty, increases ROI, and creates meaningful customer relationships. However, success depends on a balance of smart data use, thoughtful segmentation, and respect for user privacy. The brands that excel at this are the ones that truly listen to their audiences and respond with relevance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
Q1. How do I know if my audience targeting is working?
Answer: Track KPIs like click-through rates (CTR), conversion rates, bounce rates, engagement metrics, and return on ad spend (ROAS). A/B testing and audience behavior analysis also help determine targeting effectiveness.
Q2. Can small businesses use audience targeting effectively?
Answer: Yes. Tools like Facebook Ads Manager, Google Ads, and email marketing platforms offer powerful targeting features accessible to small businesses with limited budgets. Even basic segmentation can significantly improve campaign results.
Q3. What tools help in collecting first-party data for targeting?
Answer: Tools like Google Analytics, CRM systems (e.g., HubSpot, Salesforce), email platforms (e.g., Mailchimp), and e-commerce platforms (e.g., Shopify) help gather and organize first-party data efficiently.
Q4. What is the difference between audience targeting and market segmentation?
Answer: Market segmentation is a broader strategy that divides a market into groups based on shared characteristics. Audience targeting takes it further by applying those segments to create and deliver personalized marketing messages through specific channels.
Recommended Article
We hope this guide on audience targeting was insightful. To deepen your understanding, explore related articles on digital advertising strategies, customer segmentation techniques, and data-driven marketing for better ROI.

