Updated April 5, 2023

Introduction to Ansible Synchronize
Ansible Synchronize is the module that can be used to do some of the common tasks which we do by using rsync on Linux machines. Though it does not have the full power of Linux rsync, but we know that those special features of rsync are needed only sometimes. We can still use command and shell module to call rsync, but that needs some other host facts and parameters to make it work successfully. Also, it needs to be done carefully. From Linux documentation, we can say that Ansible synchronize is a wrapper around rsync to perform the common task easily and smoothly via playbook.
Explaining the Ansible Synchronize
Ansible synchronizes work like rsync in many ways. But we must remember the below points while using it in our environments. These will explain this module and show its limitations:
- To work with this module, rsync must be installed on both source and target systems.
- By default, the source of files is localhost i.e. the controller machine and destination of files is the machine where the connection is made to transfer files. This default feature can be changed by using parameter delegate_to, which allows you to change your source from localhost to some other host. Thus you can copy files from a remote machine to another remote machine.
- On synchronize source machine, file’s permissions are of the user who is running the tasks on localhost or remote_user in the case when delegate_to is used.
- On synchronize destination machine, the file’s permission will be of remote_user on destination host or of become_user if become=yes is given in parameters, but to elevate the permission, password less sudo should be set up, as rsync itself does not give a way to pass sudo credentials.
- Currently, we have only below few connection types to work with Ansible synchronize viz are ssh, paramiko, local, and docker.
- Always give the full path of the destination host location, as there may be cases where you used sudo, but files will be copied to remote_user home directory.
- Linux rsync limitations related to hard links are also applied here.
- Ansible synchronizes module forces -delay-updates to avoid the broken state in case of connection failure.
How does Ansible Synchronize Works?
Ansible synchronize user below parameters and their acceptable values are listed as below. Using the combination of these parameters, we can decide the behavior and output of Ansible synchronize.
- archive: The acceptable values are yes and no. The default value is set to yes. This mirrors the rsync flag, enable recursive, links, perm, group, owner, time flag.
- hecksum: The acceptable values are yes and no. The default value is set to no. This is used to skip based on checksum.
- compress: The acceptable values are yes and no. The default value is set to yes. This is used to compress files during transfer to speed up the transfer.
- copy_links: The acceptable values are yes and no. The default value is set to no. This is used to copy the referenced items rather than links.
- delete: The acceptable values are yes and no. The default value is set to no. This is used to delete files in dest location, which does not exist on the source somehow when the transfer is completed. This works when recursive=yes is set.
- dest: The absolute or relative path on the destination machine. Which will be synced from the source.
- src: The absolute or relative path on the source machine. Which will be synced from the destination.
- dirs: The acceptable values are yes and no. The default value is set to no. This is used to transfer directories without recursive.
- dest_port: Port number of ssh on destination.
- link_dest: Default value is null. This is used to add a destination to hard links against during the rsync.
- links: This is used to copy syslinks as syslinks, not referenced items.
- mode: Acceptable values are push and pull. The default value is push.
- owner: The acceptable values are yes and no. This is used to preserve owner.
- rsync_path: This is used to specify the rsync command path on remote hosts.
- times: To preserve the modification times. The acceptable values are yes and no.
Examples of Ansible Synchronize
Now by using examples, we will try to learn about Ansible synchronize, which you might have to use in day to day operations. We will take some examples, but before going there, we first understand our lab, we used for testing purpose. Here we have an Ansible control server named ansible-controller and few remote hosts named host- remote, host-one, and host-two. We will create playbooks and run Ansible commands on the ansible- controller node and see the results on the remote hosts.
In this example, we will do the synchronization of files from source machine viz. Ansible controller node to the remote host. We have a set of files under /var/tmp/sync_folder on the Ansible controller node which will be transferred to remote host via Ansible synchronize module. For this we have a playbook like below:
---
- hosts: host-remote tasks:
- name: here we sync /var/tmp/sync_folder directory to remote host synchronize:
src: /var/tmp/sync_folder dest: /var/tmp/
ansible-playbook ansible_synchronize.yaml
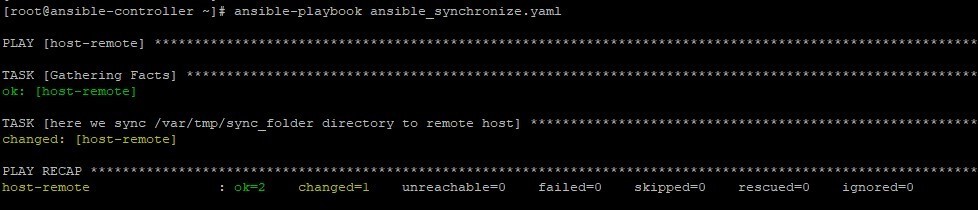
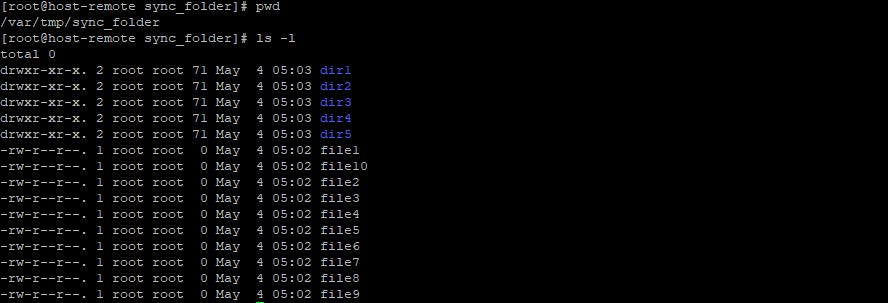
On the remote machine, we can cross-check to confirm the files have been transferred.
pwd
ls -l
In this example, we will do the synchronization of files from one remote host to another remote host. For this we have a playbook like below:
---
- hosts: host-one tasks:
- name: here we sync items from one remote host to another remote host synchronize:
src: /var/tmp/sync_folder dest: /var/tmp/ delegate_to: host-two
ansible-playbook ansible_synchronize_remote_src.yaml -v
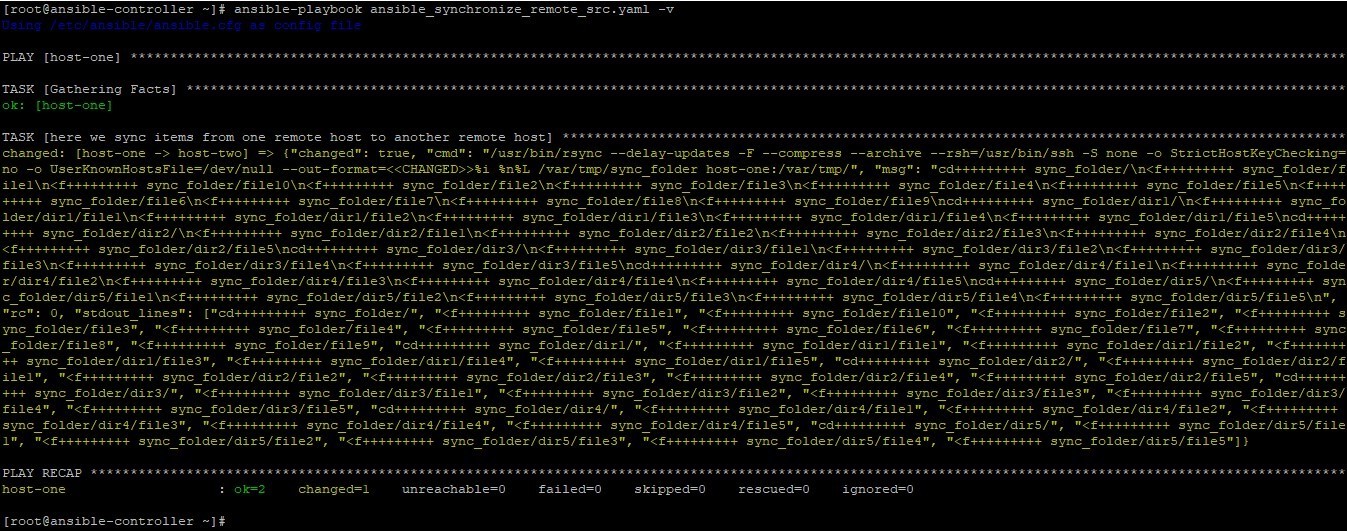
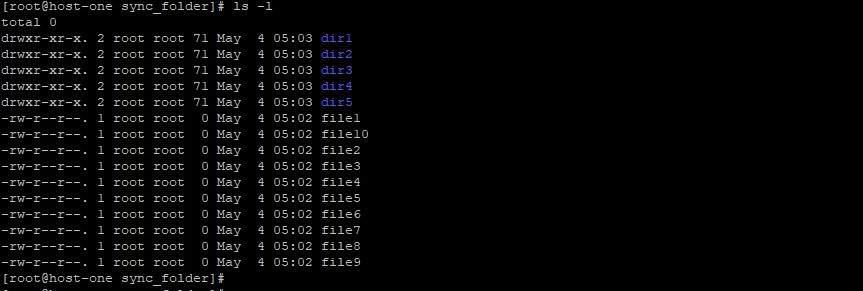
On the remote machine, we can cross-check to confirm the files have been transferred.
ls -l
Conclusion
As we saw, Ansible synchronize is powerful but easy to use the module, but we must also acknowledge that this is not the replacement of rsync in Linux systems. So keeping in mind, you must also remember all the limitations mentioned above in this article to avoid unexpected outcomes. So learn it first and then use it carefully.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Ansible Synchronize. Here we also discuss the Introduction and how does ansible synchronize works along with examples and its code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


