Updated April 4, 2023

Introduction to Anonymous Inner Class in Java
Anonymous Inner Class in Java is an inner class or nested class. An inner class is a class that is present inside an outer class. So an anonymous inner class is an inner class that has no name. It is either a subclass of a class or an implementation of an interface. So if we have to override a class or interface method, we can use an anonymous inner class. In the case of the anonymous inner class, a curly brace is followed by the semicolon.
There are two ways to create an anonymous inner class.
- Class
- Interface
Syntax:
Below is the syntax, where the class can be an abstract class or a concrete class or interface.
class t = new class()
{
// class variables and methods members
public void class_method()
{
/* some code of the class_method */
}
};Examples of Anonymous Inner Class in Java
Given below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
An example where we create an interface and a simple class that implements that interface.
Code:
package p1;
interface Emp
{
int eid = 2101;
void geteid();
}
// Implclass implement an Emp Interface and provide the defination for geteid() method
class ImplClass implements Emp
{
@Override
public void geteid()
{
// display the eid
System.out.print("Employee id is "+eid);
}
}
class Demo
{
public static void main( String[] arg )
{
// create object of Implclass which implements Emp interface
ImplClass ob=new ImplClass();
// call geteid() method which implemented by Implclass
ob.geteid();
}
} Output:

As in the above code, an interface Emp is created with the geteid() method and eid=2101. ImplClass implements an Emp Interface and provides the definition for the geteid() method. There is no need to write a separate class ImplClass; instead, it can be use as an anonymous inner class.
Example #2
Here we rewrite the above java code to see an inner class working. The ImplClass class is accessible to other classes in the application. However, the ImplClass class’s functionality is not required by the other class in the application. Therefore we need not define an outer class. In addition, an instance of this class is used only once. Therefore, with the help of an anonymous inner class, the ImplClass class’s functionality can be implemented. In the below example, we created the object of the class directly by implementing the Empinterfece.
Code:
package p1;
interface Emp
{
int eid = 2101;
void geteid();
}
class Demo
{
public static void main( String[] arg )
{
// Implclass is hidden inner class implement an Emp Interface
// Implclass class name is not created but an object is creating below
Emp ob = new Emp() {
@Override
public void geteid() {
// display the eid
System.out.print("Employee id is "+eid);
}
};
// call geteid() method which implemented by Implclass
ob.geteid();
}
}Output:

As in the above code, an object of Emp is not created; implicitly, an object of ImplClass(may not be the same name) class is created. Note that the inner class has no name, so the compiler decides a name and creates it, implementing the Emp interface.
Example #3
Java code to create an anonymous Inner class that extends a class.
Code:
package p1;
class Emp
{
void dispMesg()
{
System.out.println("This message is from main class");
}
}
class Demo
{
public static void main( String[] arg )
{
// Anonymous hidden inner class extends an Emp class
// Anonymous class name is not created but an object is creating below
Emp ob = new Emp() {
@Override
// override dispMesg() method in child Anonymous inner class
public void dispMesg() {
System.out.print("This message is from child class");
}
};
// call geteid() method which implemented by Implclass
ob.dispMesg();
}
} Output:
![]()
Example #4
Java code to create an anonymous Inner class that extends an abstract class.
Code:
package p1;
abstract class Emp
{
void dispMesg()
{
System.out.println("This message is from main class");
}
abstract void abstrct_method();
}
class Demo
{
public static void main( String[] arg )
{
// Anonymous hidden inner class extends an Emp abstract class
// Anonymous class name is not created but an object is creating below
Emp ob = new Emp() {
@Override
public void dispMesg() {
System.out.println("This message is from child class");
}
@Override
void abstrct_method()
{
System.out.println("Abstract Method");
}
};
ob.dispMesg();
ob.abstrct_method();
}
}Output:
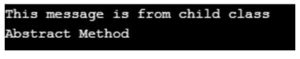
Example #5
Java code to create an anonymous Inner class that defines inside constructor or method argument where we will use the predefined Thread class and runnable interface to create and run thread.
Code:
package p1;
class Demo
{
public static void main( String[] arg )
{
// Anonymous hidden inner class extends an Emp class
// Anonymous class define constructor argument
Thread obt = new Thread(new Runnable()
{
@Override
public void run()
{
System.out.println("Runing child Thread.");
}
});
System.out.println("Runing main Thread.");
obt.start();
System.out.println("Runing main Thread.");
}
}Output:

Conclusion
An anonymous inner class is an inner class that has no class name. There are different ways to create an anonymous inner class, like extending the concrete class, extending the abstract class, and implementing an interface.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Anonymous Inner Class in Java. Here we discuss the introduction to anonymous inner class with respective examples for better understanding. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


