What is Anomaly Detection?
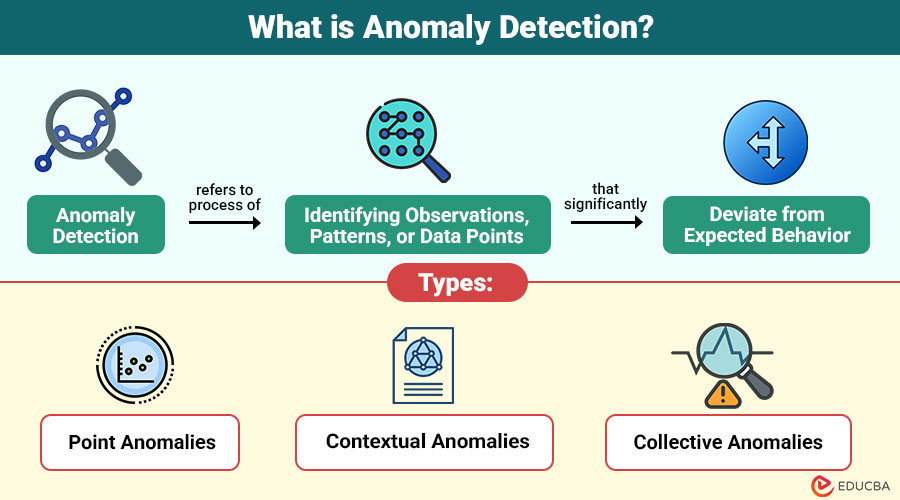
Anomaly detection refers to process of identifying observations, patterns, or data points that significantly deviate from expected behavior.
These deviations may represent:
- Fraudulent activity
- System malfunctions
- Cyber intrusions
- Unexpected user behavior
- Medical abnormalities
- Operational inefficiencies
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Anomaly detection identifies abnormal patterns early, enabling rapid issue resolution before major operational disruptions occur.
- Machine learning models enhance detection accuracy by analyzing complex data behaviors beyond traditional statistical approaches.
- Industries use anomaly detection to prevent fraud, maintain system stability, and improve the efficiency of real-time decision-making.
- Automated alerts and monitoring workflows help organizations reduce risks, increase reliability, and maintain continuous operational safety.
Why Anomaly Detection Matters?
Here are the key reasons why anomaly detection is critical for modern data-driven systems:
1. Early Warning Systems
It provides timely alerts by identifying unusual patterns before issues escalate into major operational failures.
2. Risk Mitigation
It helps organizations proactively reduce financial, security, and performance risks by detecting threats or irregular behaviors instantly.
3. Operational Stability
By continuously monitoring systems, anomaly detection ensures smooth operations and prevents unexpected disruptions impacting business performance.
4. Automated Decision-making
Machine-driven anomaly insights enable faster automated decisions, eliminating human delays and improving overall responsiveness to emerging situations.
5. Customer Protection
It safeguards customers by spotting fraudulent activities, unusual transactions, or abnormal usage patterns in real time.
How Does Anomaly Detection Work?
Anomaly detection follows a structured process:
1. Data Collection
Data is gathered from sensors, logs, transactions, networks, and user activities to enable comprehensive anomaly monitoring.
2. Data Preprocessing
Preprocessing cleans data, removes duplicates, handles missing values, normalizes formats, and efficiently converts categorical features.
3. Feature Engineering
Key attributes like transaction amount, latency, CPU usage, temperature, and login frequency are extracted thoughtfully.
4. Modeling Normal Behavior
Machine learning models analyze historical patterns to establish a reliable baseline representing normal system behavior accurately.
5. Scoring and Detection
Incoming data is scored by evaluating deviations from the established baseline and identifying statistically significant anomalies.
6. Alerts and Action
When anomaly scores exceed predefined thresholds, automated alerts trigger investigations or corrective actions immediately.
Types of Anomaly Detection
Anomalies are classified into three primary categories:
1. Point Anomalies
A point anomaly occurs when a single data value sharply deviates from expected patterns, indicating potential irregular activity.
2. Contextual Anomalies
A contextual anomaly appears when data that is normally acceptable becomes abnormal under specific conditions, contexts, or situational factors.
3. Collective Anomalies
A collective anomaly arises when multiple related data points together create unusual patterns that individually seem normal but collectively suspicious.
Approaches to Anomaly Detection
Here are the major approaches used to identify unusual patterns across different data types and environments:
1. Statistical Methods
Statistical methods learn what normal data looks like and flag anything different, but they don’t work well with complex or very large datasets.
2. Machine Learning Methods
Machine learning finds unusual patterns using different methods based on whether example labels are available or not.
3. Deep Learning Methods
Deep learning models handle complex, high-volume data using architectures such as LSTMs, VAEs, and GANs for advanced anomaly detection.
4. Time Series Anomaly Detection
Time series techniques analyze sequential patterns using forecasting models to identify unusual trends in dynamic, continuous data streams.
Applications of Anomaly Detection
Here are the applications where anomaly detection delivers significant real-world value:
1. Finance & Banking
It identifies credit card fraud, suspicious transactions, and unusual account behavior to strengthen financial security.
2. Cybersecurity
It detects intrusions, malware behaviors, and DDoS attack patterns, helping organizations safeguard systems from evolving cyber threats.
3. Healthcare
Anomaly detection flags abnormal vitals, diagnostic inconsistencies, and emerging disease trends to support timely medical intervention.
4. Manufacturing & IoT
It identifies machine failures, predicts maintenance needs, and monitors sensor irregularities to improve operational reliability and safety.
5. Retail & E-commerce
Anomaly detection uncovers unusual customer behaviors, detects fake reviews, and highlights supply chain disruptions affecting retail performance.
6. Cloud & DevOps
It monitors server issues, latency abnormalities, and network anomalies to ensure stable, efficient cloud infrastructure operations.
Real-World Examples
Here are real-world examples showing how anomaly detection is applied across industries:
1. Credit Card Fraud Detection (Banking)
2. Predictive Maintenance (Manufacturing)
Sensors on machines detect abnormal vibrations or temperatures, preventing costly breakdowns.
3. User Behavior Analysis (Tech Platforms)
Companies like Google, Amazon, and Netflix use anomaly detection to identify unusual login attempts, account breaches, or bot activity.
4. Healthcare Monitoring (IoT Devices)
Wearables detect sudden changes in heart rate, oxygen levels, or movement patterns.
Final Thoughts
Anomaly detection has become essential for modern data-driven organizations across industries like finance, cybersecurity, manufacturing, and healthcare. With easy-to-use AI tools, businesses can spot problems quickly, save money, avoid failures, and work more smoothly. For data scientists, developers, leaders, and students, learning anomaly detection is important to handle today’s fast-changing digital world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What causes anomalies in data?
Answer: Operational errors, cyberattacks, equipment failures, unusual user behavior, system overloads, or environmental changes.
Q2. Can anomaly detection work without labeled data?
Answer: Yes. Unsupervised methods like Isolation Forest or Autoencoders work well when labels are unavailable.
Q3. What are the common machine learning algorithms used for anomaly detection?
Answer: Popular algorithms include Isolation Forest, One-Class SVM, Local Outlier Factor (LOF), Autoencoders, LSTM models for time series, and clustering-based methods like K-Means.
Q4. Which industries use anomaly detection the most?
Answer: Banking, cybersecurity, manufacturing, healthcare, and cloud services.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Anomaly Detection” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
