What is AI Governance?
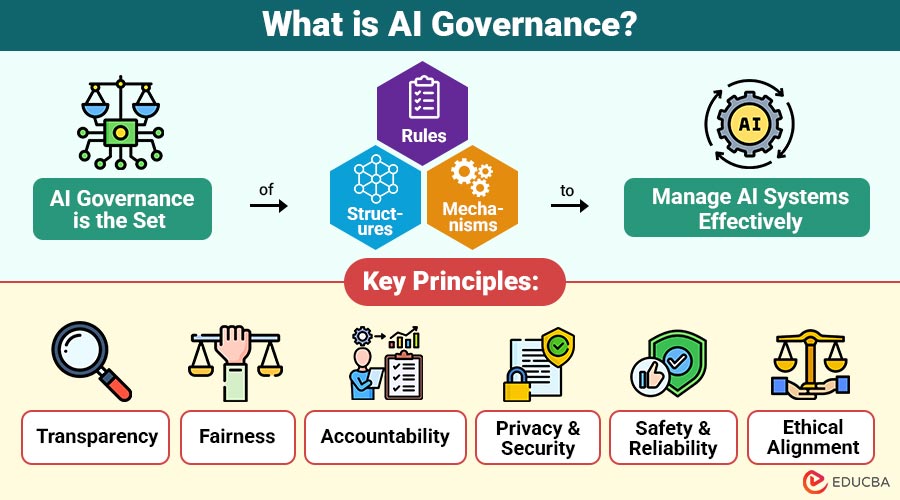
AI governance is the set of rules, structures, and mechanisms designed to manage AI systems effectively.
From voice assistants to predictive analytics and autonomous vehicles, AI is shaping the way we live and work. However, with its growing influence comes the need for clear rules, regulations, and ethical standards. This is where AI governance plays a crucial role. It involves:
- Creating standards and policies for AI design and usage.
- Defining accountability for organizations and developers.
- Ensuring compliance with legal, ethical, and social norms.
- Monitoring risks and impacts of AI on society, economy, and individuals.
In simple terms, AI governance ensures that AI works for the benefit of people while minimizing risks such as bias, misuse, or harm.
Table of Contents
- What is AI Governance?
- Why is AI Governance Important?
- Key Principles of AI Governance
- Challenges in AI Governance
- Real-World Examples
- How Businesses Can Implement AI Governance?
- The Future
Why is AI Governance Important?
The rapid growth of AI brings enormous opportunities, but also significant risks if left unchecked. Here are a few reasons why AI governance is essential:
- Amazon’s Biased Hiring Tool: In 2018, Amazon scrapped its AI hiring system after discovering it favored male candidates over female ones. The AI had learned from past hiring data, which reflected gender bias in tech. Without governance, such bias could harm equal job opportunities.
- COMPAS Recidivism Algorithm (US Courts): The COMPAS tool, designed to predict the risk of criminals reoffending, was found to show bias against African American defendants. This sparked huge debates about AI in criminal justice and the need for fairness in decision-making systems.
- Tesla Autopilot Accidents: Several self-driving accidents involving Tesla’s Autopilot raised questions about safety and accountability. Was it driver error, company responsibility, or AI malfunction? Governance frameworks help clarify liability in such cases.
- Apple Card Credit Limit Scandal: In 2019, Apple’s AI-based credit card system gave women lower credit limits than men, even when they shared finances. This led to investigations and highlighted the dangers of unchecked AI bias in finance.
- UK A-Level Exam Algorithm (2020): When COVID-19 canceled exams, the UK used an AI system to assign grades. The algorithm downgraded thousands of students, especially those from disadvantaged backgrounds, sparking public outrage. Authorities eventually scrapped it.
Key Principles of AI Governance
Effective AI governance is built on key principles that promote fairness, transparency, and safety:
- Transparency: AI systems should be explainable and understandable. Organizations must demonstrate to users how they make decisions and what data informs their decisions.
- Fairness: AI must avoid bias and treat all individuals equally, regardless of race, gender, or background.
- Accountability: Organizations and developers should be held responsible for the design, training, and outcomes of their AI systems.
- Privacy and Security: AI governance must prioritize protecting sensitive user data and safeguarding systems against cyber threats.
- Safety and Reliability: Organizations must thoroughly test and closely monitor AI to ensure it performs accurately and avoids causing harm in critical applications like healthcare or transportation.
- Ethical Alignment: AI should operate in alignment with human values, respecting human rights, dignity, and social norms.
Challenges in AI Governance
While the principles are clear, implementing AI governance is not simple. Some major challenges include:
- Rapid Technological Growth: AI evolves faster than laws and regulations can keep up.
- Global Differences: Different countries have varying regulations, making it challenging to establish a universal governance model.
- Complexity of AI Systems: Many AI systems, especially deep learning models, are “black boxes” that are hard to interpret.
- Balancing Innovation and Regulation: Excessive regulation may hinder innovation, while insufficient regulation may increase risks.
- Ethical Dilemmas: Questions like “Should AI replace human jobs?” or “How much decision-making power should AI have?” are complex to resolve.
Real-World Examples
Several countries, organizations, and companies are already implementing AI governance practices:
- European Union (EU): The EU has proposed the AI Act, which categorizes AI systems by risk (low, medium, high, and unacceptable) and regulates them accordingly. For example, AI for facial recognition in public spaces faces stricter rules than AI used for entertainment.
- United States: The U.S. has introduced the Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights, focusing on data privacy, fairness, and transparency in AI systems.
- Companies like Google and Microsoft: Tech giants, have set up internal AI ethics boards and policies to ensure responsible AI development.
- Healthcare AI Governance: Hospitals using AI-based diagnostic tools establish protocols to ensure accuracy, patient safety, and compliance with medical regulations.
How Businesses Can Implement AI Governance?
For organizations adopting AI, setting up governance is not optional—it is a necessity. Here is how businesses can do it:
- Create AI Policies: Establish internal guidelines for data use, model development, and decision-making processes to ensure consistency and transparency in these areas.
- Build Cross-Functional Teams: Involve experts from IT, legal, ethics, HR, and operations to ensure well-rounded governance.
- Conduct Regular Audits: Test AI models for fairness, accuracy, and reliability. Independent audits can strengthen accountability.
- Ensure Transparency: Provide explanations of AI decisions to customers, regulators, and employees.
- Invest in Training: Educate staff on responsible AI practices and encourage a culture of ethical innovation.
- Stay Compliant: Monitor evolving regulations worldwide and update AI systems to ensure ongoing compliance.
The Future
As AI becomes more advanced, governance will evolve too. In the future, we may see:
- Global Standards: Unified international guidelines for AI ethics and safety.
- More Explainable AI: Advances in research will make AI decisions easier to interpret.
- AI in Governance: Ironically, organizations may use AI to monitor and enforce governance rules themselves.
- Public Participation: Citizens may gain more influence in shaping policies on how society should use AI.
AI governance will not just be about control but about creating a system where innovation thrives alongside ethical responsibility.
Final Thoughts
Artificial Intelligence is a transformative technology, but its advantages also bring challenges and risks. AI governance provides the necessary frameworks to ensure AI is developed and used responsibly. By focusing on transparency, fairness, accountability, and safety, societies can harness the power of AI while protecting human rights and values. As businesses, governments, and individuals, embracing AI governance is not just an option—it is a responsibility. Done right, it will foster trust, encourage innovation, and create a future where AI positively serves humanity.
Recommended Articles
We hope this comprehensive guide to AI governance helps you understand responsible AI practices. Explore these recommended articles for additional insights and strategies to effectively manage AI.

