What is Capital Expansion?
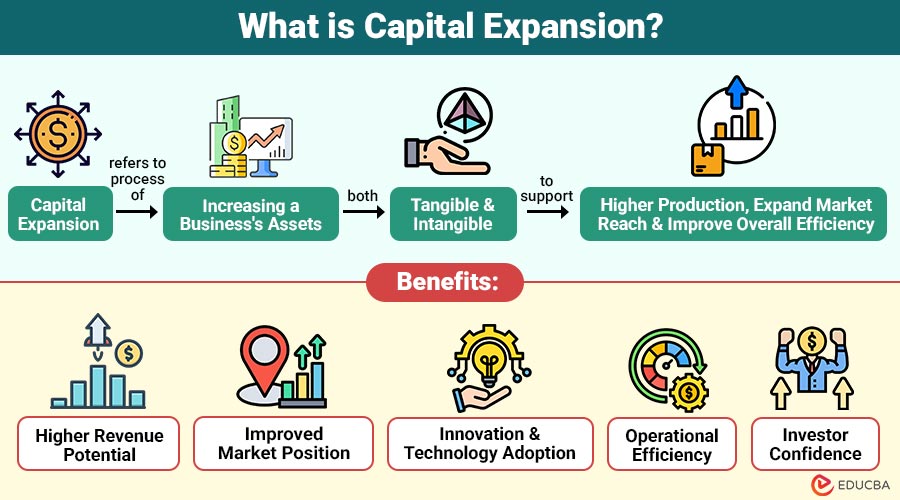
Capital expansion refers to the process of increasing a business’s assets—both tangible and intangible—to support higher production, expand market reach, and improve overall efficiency. It can involve physical investments, such as new machinery, buildings, and technology, as well as financial investments, such as equity infusions, debt financing, or reinvesting retained earnings.
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Key Components
- Importance
- Methods
- Key Considerations Before Capital Expansion
- Benefits
- Risks
- Real-World Examples
- Capital Expansion Strategies for Small Businesses
Key Takeaways:
- Capital expansion enables long-term growth by strategically investing in assets, markets, technology, and organizational capabilities.
- Successful capital expansion requires strong financial stability, market analysis, operational readiness, and disciplined risk management.
- Businesses can fund capital expansion through equity, debt, retained earnings, partnerships, or strategic mergers and acquisitions.
- Poorly planned expansion increases financial strain, operational complexity, and market exposure, significantly reducing long-term profitability.
Key Components of Capital Expansion
Here are the key components of capital expansion that organizations typically focus on to drive sustainable growth and scalability.
1. Physical Assets
Expanding physical assets involves building factories, warehouses, and retail outlets or upgrading production equipment to increase operational capacity and efficiency.
2. Human Capital
Human capital expansion focuses on hiring skilled professionals and investing in training programs to improve productivity, innovation, and performance.
3. Financial Capital
Financial capital expansion involves raising funds through equity, debt, or internal reserves to support strategic growth initiatives and scalability.
4. Intellectual Capital
Intellectual capital expansion includes investing in research, patents, data, or proprietary technologies to strengthen long-term competitive advantage and innovation.
5. Market Expansion
Market expansion focuses on entering new geographic regions or targeting new customer segments to increase revenue and brand presence.
Importance of Capital Expansion
Capital expansion is vital for businesses aiming for sustainable growth. Some key reasons include:
1. Revenue Growth
Additional capital provides resources to increase production capacity, boost sales volumes, and generate higher revenues across multiple business segments.
2. Competitive Advantage
Investing in advanced technology, skilled talent, and modern infrastructure helps businesses differentiate themselves and outperform competitors in dynamic markets.
3. Economies of Scale
Capital expansion enables higher production levels, lowering per-unit costs and improving operational efficiency, margins, and overall long-term profitability.
4. Market Diversification
Expanding into new markets reduces dependence on single revenue sources, spreads risk, and improves stability during economic or industry downturns.
5. Innovation Enablement
With more capital, companies can fund research and development initiatives, accelerating innovation in products, services, and business models.
Methods of Capital Expansion
Businesses can pursue capital expansion through various methods, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
1. Equity Financing
Equity financing raises capital by selling company shares to investors, supporting growth without debt but reducing existing ownership stakes.
Advantages:
- No repayment obligation.
- Attracts investors who may provide strategic guidance.
Disadvantages:
- Dilution of ownership.
- Pressure to deliver consistent returns to shareholders.
2. Debt Financing
Debt financing involves borrowing funds from lenders to finance expansion, requiring regular interest payments and principal repayment over time.
Advantages:
- Maintains ownership control.
- Interest payments are tax-deductible.
Disadvantages:
- Repayment obligations can strain cash flow.
- Increased financial risk during downturns.
3. Internal Financing (Retained Earnings)
Internal financing uses accumulated business profits to fund expansion, avoiding external debt or investors while relying on available cash reserves.
Advantages:
- No need for external investors or debt.
- Demonstrates financial stability to stakeholders.
Disadvantages:
- Limited by available profits.
- May slow other investment opportunities if profits are tied up.
4. Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A)
Mergers and acquisitions enable expansion by combining with or purchasing other companies to quickly gain markets, customers, and capabilities.
Advantages:
- Rapid growth compared to organic methods.
- Access to established resources and customer bases.
Disadvantages:
- Complex integration process.
- Cultural and operational challenges.
5. Joint Ventures and Strategic Partnerships
Joint ventures and partnerships involve collaborating with other firms to share resources, risks, and expertise for mutual expansion goals.
Advantages:
- Shared risk and cost.
- Access to new technologies and markets.
Disadvantages:
- Profit sharing reduces individual gains.
- Dependence on partner performance.
Key Considerations Before Capital Expansion
Capital expansion is not without risks. Companies must carefully evaluate multiple factors before initiating expansion strategies:
1. Financial Stability
Evaluate whether the company has sufficient cash flow, reserves, or financing options to sustainably support expansion without financial strain.
2. Market Analysis
Analyze customer demand, competition, pricing trends, and market size to confirm that expansion opportunities are viable and profitable in the long term.
3. Operational Capacity
Assess whether existing management, employees, systems, and infrastructure can efficiently support increased scale and operational complexity.
4. Regulatory Compliance
Review legal, regulatory, and tax requirements in target markets to avoid compliance risks, penalties, or unexpected operational restrictions.
5. Risk Management
Identify economic, financial, and operational risks associated with expansion and develop contingency plans to minimize potential negative impacts.
Benefits of Capital Expansion
When executed strategically, capital expansion can significantly enhance a company’s growth trajectory:
1. Higher Revenue Potential
Expanding capacity and market reach allows businesses to increase sales volumes, diversify income streams, and achieve stronger revenue growth.
2. Improved Market Position
Capital expansion strengthens brand presence, improves competitive standing, and increases influence within existing and newly entered markets.
3. Innovation and Technology Adoption
Additional capital supports the adoption of advanced technologies and innovation, helping companies improve their offerings and stay ahead of the competition.
4. Operational Efficiency
Investing in additional resources and streamlining procedures boosts output, lowers expenses, and improves overall operational effectiveness.
5. Investor Confidence
Successful expansion demonstrates long-term growth potential, financial strength, and strategic vision, increasing trust and interest among investors.
Risks of Capital Expansion
While capital expansion has numerous advantages, it also comes with potential risks:
1. Financial Risk
Excessive borrowing or overextension of funds may increase debt burdens, strain cash flows, and potentially lead to financial distress.
2. Operational Strain
Rapid expansion can overwhelm employees, management systems, and supply chains, reducing efficiency and negatively impacting overall service quality.
3. Market Uncertainty
Economic slowdowns, regulatory shifts, or intensified competition can disrupt expansion plans and reduce expected returns on investment.
4. Cultural Misalignment
In mergers or partnerships, differing corporate cultures may cause conflicts, lower morale, and hinder effective collaboration and integration.
5. Resource Misallocation
Poor investment decisions can divert capital to unprofitable initiatives, leading to sunk costs, inefficiencies, and long-term financial losses.
Real-World Examples
Here are a few well-known companies that demonstrate how effective capital expansion supports large-scale growth and market leadership.
1. Amazon
Amazon continuously invests in warehouses, logistics infrastructure, and technology, enabling it to expand globally and dominate e-commerce and cloud computing markets.
2. Tesla
Tesla expanded its manufacturing capacity with Gigafactories across continents, increasing production and driving growth in electric vehicle adoption.
3. Starbucks
Starbucks leveraged both organic growth and acquisitions to expand its presence worldwide, adapting to local markets while efficiently scaling operations.
Capital Expansion Strategies for Small Businesses
Even small businesses can leverage capital expansion with careful planning:
1. Start Small, Scale Gradually
Small businesses should pursue incremental expansion steps, reinvesting profits carefully to minimize risk and ensure sustainable long-term growth.
2. Seek Strategic Investors
Partnering with strategic investors provides funding, industry expertise, mentorship, and valuable market insights to support smarter expansion decisions.
3. Leverage Technology
Using automation and digital tools enhances efficiency, reduces costs, and supports growth without requiring heavy investments in physical infrastructure.
4. Focus on Niche Markets
Targeting underserved or specialized market segments helps small businesses achieve higher returns with limited capital resources.
5. Monitor Cash Flow Closely
Maintaining strong cash flow visibility ensures financial stability and prevents overextension when planning and executing expansion initiatives.
Final Thoughts
Capital expansion drives business growth by enabling higher production, market entry, technology adoption, and efficiency improvements. Although it involves risk and investment, strategic planning, sound financial management, and market analysis ensure sustainable success. By understanding expansion methods, benefits, and challenges, businesses can scale effectively, remain competitive, and create long-term value for stakeholders and employees.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the difference between capital expansion and working capital?
Answer: Capital expansion refers to investing in long-term assets for growth, while working capital is used for day-to-day operational needs.
Q2. Is capital expansion suitable for startups?
Answer: Yes, but startups must carefully balance growth with cash flow and risk management to avoid overextension.
Q3. How can companies fund capital expansion without external debt?
Answer: Companies can use retained earnings, equity financing, or strategic partnerships to fund expansion without borrowing.
Q4. What are the risks of expanding too quickly?
Answer: Rapid expansion may strain resources, increase costs, disrupt operations, and create financial instability.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Capital Expansion” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

