What is Financial Due Diligence?
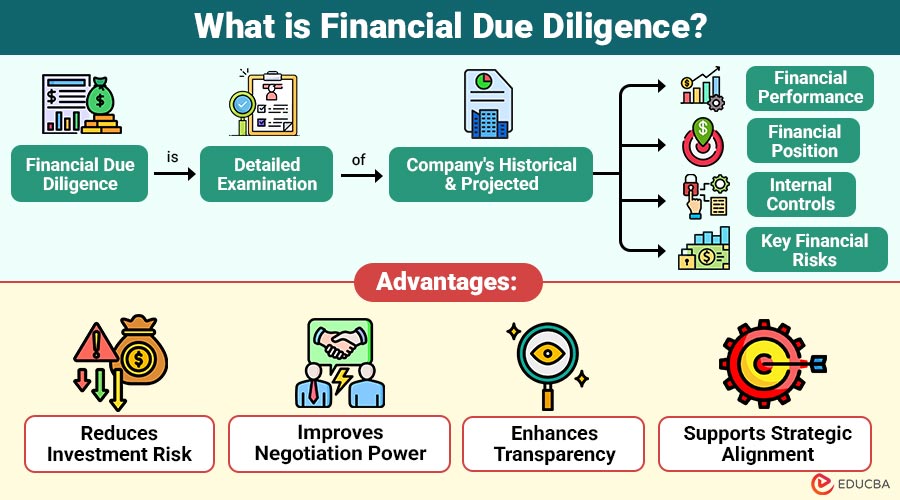
Financial Due Diligence is detailed examination of company’s historical and projected financial performance, financial position, internal controls, and key financial risks.
The objective is to confirm whether:
- Financial statements are accurate and reliable
- Earnings are sustainable
- Cash flows are predictable
- Liabilities and risks are fully disclosed
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Importance
- Scope
- Process
- Metrics
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
- Real-World Example
- When Should Financial Due Diligence be Performed?
Key Takeaways:
- Financial due diligence uncovers hidden risks, verifies statements, and ensures sustainable, predictable earnings and cash flows.
- It supports accurate valuation, guides deal structuring, and protects buyers from unexpected financial liabilities and obligations.
- It makes finances clearer, helps better decisions, and supports planning after acquisition by reviewing past and future financial results.
- While valuable, it is time-consuming, costly, data-dependent, and cannot fully eliminate all future financial uncertainties.
Importance of Financial Due Diligence
It plays an important role in safeguarding stakeholders from unexpected financial risks. Its importance includes:
1. Risk Identification
Helps uncover hidden liabilities, overstated revenues, understated expenses, and off-balance-sheet obligations.
2. Valuation Support
Ensures the purchase price reflects the company’s true financial performance and future earning potential.
3. Deal Structuring
Findings from FDDs influence deal terms, including price adjustments, earn-outs, indemnities, and warranties.
4. Decision-Making Confidence
Provides investors, lenders, and acquirers with reliable insights for strategic decision-making.
5. Post-Acquisition Planning
Highlights integration challenges, working capital needs, and post-transaction operational improvements.
Scope of Financial Due Diligence
The scope of financial due diligence may vary depending on the transaction size and complexity but typically includes the following areas:
1. Quality of Earnings
Analyzes whether reported profits are sustainable, recurring, consistent with cash flows, and free from unusual items.
2. Historical Financial Performance
Reviews income statements, balance sheets, cash flows, and key trends, including revenue growth, margins, and profitability.
3. Working Capital Analysis
4. Cash Flow and Liquidity
Examines operating cash flow, capital expenditure needs, and debt servicing to ensure sustainable business liquidity.
5. Debt and Liabilities Review
Identifies loans, lease obligations, contingent liabilities, tax exposures, and potential litigation impacting deal valuation and risk.
6. Forecasts and Projections
Evaluates management’s projections for realism, achievable growth, and alignment with historical trends and market conditions.
Financial Due Diligence Process
The process generally follows these steps:
1. Planning and Scoping
Define objectives, timelines, and key focus areas for the transaction to ensure comprehensive financial due diligence.
2. Data Collection
Gather financial statements, management reports, contracts, tax filings, and other relevant documents for detailed review.
3. Financial Analysis
Perform ratio analysis, trend evaluation, and benchmarking to assess historical performance and operational efficiency effectively.
4. Risk Assessment
Determine any operational, financial, and compliance risks that might affect future firm performance or valuation.
5. Reporting
Prepare a detailed due diligence report summarizing findings, proposed adjustments, and actionable recommendations for stakeholders.
Financial Due Diligence Metrics
Some commonly analyzed metrics include:
1. EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA
Measures a company’s profitability from operations, excluding non-recurring items, providing insight into sustainable earnings performance.
2. Gross and Operating Margins
Indicates efficiency in producing goods or services, showing the proportion of revenue retained after direct and operating costs.
3. Revenue Concentration
Assesses reliance on a few customers, highlighting potential risk if significant revenue sources are lost suddenly.
4. Customer Churn Rates
Tracks the percentage of customers lost over time, reflecting business retention, satisfaction, and recurring revenue stability.
5. Net Working Capital
Shows short-term financial health by subtracting short-term debts from short-term assets, helping ensure daily operations run smoothly.
6. Free Cash Flow
It shows money left after spending assets, used to repay debt, pay dividends, or invest in growth.
Advantages of Financial Due Diligence
Financial due diligence offers several advantages:
1. Reduces Investment Risk
Identifies potential financial weaknesses, hidden liabilities, and risks before closing, minimizing unexpected losses or deal surprises.
2. Improves Negotiation Power
Provides objective, data-driven financial insights, enabling buyers to negotiate better pricing, terms, and deal structures with confidence.
3. Enhances Transparency
Ensures the target company’s financial statements are accurate, complete, and clearly reflect true operational performance.
4. Supports Strategic Alignment
Helps buyers assess whether the target’s financial and operational profile aligns with their long-term strategic objectives.
Disadvantages of Financial Due Diligence
Despite its importance, it has certain disadvantages:
1. Time-Consuming
2. Cost Intensive
Hiring experts and doing detailed checks, especially for large or complex deals, can cost a lot and use many resources.
3. Dependence on Data Quality
The accuracy and completeness of available financial data are critical; poor data can lead to incorrect conclusions.
4. Not a Guarantee
While financial due diligence mitigates risks, it cannot eliminate all future uncertainties, unforeseen challenges, or operational surprises.
Real-World Example
Here is an example illustrating how financial due diligence impacts valuation and deal decisions:
A private equity firm plans to acquire mid-sized manufacturing company.
Findings during Financial Due Diligence:
- EBITDA included one-time government subsidies
- The inventory was overstated due to obsolete stock
- Significant customer concentration risk existed
Outcome:
When Should Financial Due Diligence be Performed?
Here are some key situations where it is typically required:
1. Business Acquisition or Sale
Performed to assess financial health, uncover risks, and ensure fair valuation before completing business acquisitions or sales.
2. Raising Equity or Venture Capital
Helps investors evaluate financial stability, growth potential, and risk before committing significant equity or venture capital.
3. Joint Ventures or Alliances
Ensures partners’ financials are transparent, aligned, and reliable, reducing risk in collaborative business arrangements.
4. Large Loans or Credit Facilities
Lenders assess borrowers’ financial strength, repayment capacity, and potential risks before approving substantial loans or credit lines.
Final Thoughts
Financial due diligence is a critical step in any significant financial transaction, offering deep insights into a company’s true financial health. It reveals hidden risks, confirms earnings, and guides valuation, deal structure, and strategy. Although time-consuming and costly, it improves transparency, reduces uncertainty, and enables confident decisions for investors, acquirers, and lenders across complex transactions globally.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is financial due diligence mandatory?
Answer: While not legally mandatory, it is highly recommended for any significant financial transaction.
Q2. Who performs financial due diligence?
Answer: Typically conducted by accounting firms, financial advisors, or transaction specialists.
Q3. How long does financial due diligence take?
Answer: It can range from a few weeks to several months, depending on deal complexity.
Q4. Can financial due diligence affect deal pricing?
Answer: Yes, findings often lead to price adjustments, earn-outs, or revised deal terms.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Financial Due Diligence” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.