What is Revenue Forecasting?
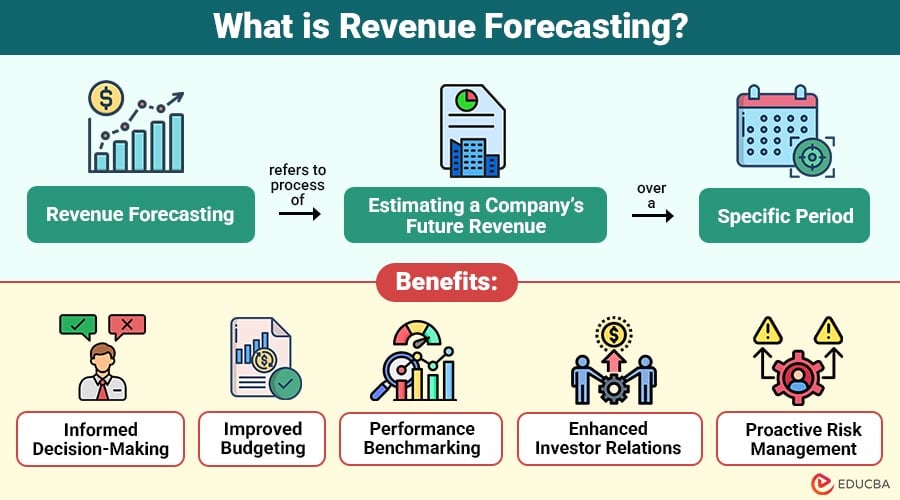
Revenue forecasting refers to process of estimating a company’s future revenue over a specific period. This estimate is based on historical data, market trends, economic indicators, and internal business metrics, including sales performance, customer behavior, and product demand.
Essentially, revenue forecasting answers the question, “How much money will the business generate in the coming months or years?” Unlike simple budgeting, which sets financial targets, revenue forecasting is predictive—it provides a realistic projection grounded in data.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Revenue forecasting enables data-driven planning by predicting future income, supporting budgeting, growth strategies, and financial stability.
- Accurate forecasts improve cash flow management, optimize resource allocation, and strengthen investor confidence across business cycles.
- Combining multiple forecasting methods and integrated data sources increases accuracy and resilience against market uncertainty and volatility.
- Regularly updating forecasts and validating assumptions helps businesses adapt quickly to change and mitigate risks effectively.
Importance of Revenue Forecasting
Revenue forecasting is important in several key ways:
1. Cash Flow Management
Helps companies maintain liquidity to fund operations, pay salaries, manage expenses, and support investments.
2. Resource Allocation
Accurate revenue forecasts enable effective allocation of workforce, marketing spend, production capacity, budgets, and operational priorities.
3. Investor Confidence
Reliable revenue forecasts build investor confidence by demonstrating growth potential, financial stability, transparency, and the soundness of management decisions.
4. Strategic Planning
Supports planning by guiding expansion, market entry, product launches, capacity planning, and long-term goals.
5. Risk Mitigation
Early revenue forecasts identify potential shortfalls, enabling proactive measures to reduce overall financial risk and uncertainty.
Key Methods of Revenue Forecasting
Below are the most commonly used methods, each suited to different business needs and data availability.
1. Historical Analysis
Historical analysis uses past revenue data to predict future trends. This method assumes that previous patterns will continue and is ideal for stable businesses with consistent sales.
Pros:
- Simple and cost-effective
- Relies on existing data
Cons:
- May not account for sudden market changes
- Less accurate for new businesses
2. Market Research
Market research forecasts revenue by analyzing industry trends, competitor performance, and consumer demand. Surveys, focus groups, and market reports help estimate potential sales.
Pros:
- Provides insights into market opportunities
- Helps identify external growth factors
Cons:
- Time-consuming and resource-intensive
- Predictions may vary based on data accuracy
3. Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics uses statistical models and AI to forecast revenue based on historical and real-time data. Machine learning algorithms identify patterns and generate highly accurate predictions.
Pros:
- Highly accurate with sufficient data
- Can adjust predictions based on changing trends
Cons:
- Requires technical expertise
- Relies heavily on data quality
4. Sales Pipeline Forecasting
Sales pipeline forecasting estimates revenue based on ongoing deals, lead conversion rates, and sales cycle duration. B2B companies commonly use this method.
Pros:
- Reflects near-term revenue potential
- Ties forecast to actionable sales data
Cons:
- Less reliable for long-term projections
- Dependent on the sales team’s accuracy
5. Bottom-Up Forecasting
Bottom-up forecasting aggregates revenue estimates from individual departments or product lines. It involves summing expected sales at a granular level to create a comprehensive company forecast.
Pros:
- Detailed and realistic
- Involves cross-functional input
Cons:
- Time-consuming
- Complex for large organizations
Revenue Forecasting Process
Implementing an effective process involves several key steps:
1. Data Collection
Collect historical sales, customer behavior, market trends, and internal performance data for accurate forecasting analysis.
2. Define Forecasting Period
Select a forecasting timeframe (monthly, quarterly, or annual) and align projections with business planning requirements.
3. Choose Forecasting Method
Select suitable forecasting techniques based on data quality, business model complexity, and market predictability.
4. Build Forecast Model
Use statistical methods, spreadsheets, or AI tools to create structured revenue projection models.
5. Validate Assumptions
Check forecast assumptions against market conditions, seasonality patterns, economic factors, and known business constraints.
6. Monitor and Update
Regularly compare forecasted revenue with actual results and continuously refine forecasting models for accuracy.
Benefits of Revenue Forecasting
It offers multiple benefits, including:
1. Informed Decision-Making
Enables managers to make strategic, operational, and financial decisions supported by reliable data insights.
2. Improved Budgeting
Accurate revenue forecasts help organizations plan expenses, control costs, and allocate investments more effectively.
3. Performance Benchmarking
Forecasting enables businesses to compare actual revenue against targets, evaluate performance gaps, and identify opportunities for improvement.
4. Enhanced Investor Relations
Reliable revenue projections build stakeholder trust by demonstrating financial stability, transparency, and future growth potential.
5. Proactive Risk Management
Identifies potential shortfalls early, enabling preventive measures to mitigate financial risks and disruptions.
Challenges in Revenue Forecasting
Despite its importance, it comes with challenges:
1. Data Limitations
Incomplete, outdated, or inaccurate data reduces the reliability of forecasts, leading to misleading revenue predictions and decisions.
2. Market Volatility
Economic fluctuations, competitors’ strategies, or regulatory changes can quickly invalidate assumptions underlying revenue forecasts.
3. Complex Business Models
Multiple product lines, subscriptions, pricing structures, or seasonality make accurate revenue forecasting more difficult.
4. Human Error
Subjective assumptions, optimism bias, or calculation errors can adversely affect forecasting accuracy and reliability.
Best Practices for Accurate Revenue Forecasting
To improve forecasting accuracy, businesses should follow these best practices:
1. Leverage Technology
Use AI-powered analytics tools to process large datasets, identify patterns, and improve forecasting accuracy significantly.
2. Integrate Data Sources
Combine sales, marketing, finance, and external market data to create comprehensive, reliable revenue forecasts.
3. Consider Seasonality
Adjust revenue forecasts to reflect predictable seasonal demand variations, trends, and cyclical business patterns.
4. Collaborate Across Teams
Engage sales, finance, and operations teams to incorporate diverse perspectives and improve forecast reliability.
5. Scenario Planning
Develop optimistic, realistic, and pessimistic revenue scenarios to account for uncertainty and inform strategic decision-making.
6. Regular Updates
Continuously review actual performance and update forecasts as new data, insights, or market changes arise.
Real-World Examples
Here are some practical examples showing how different industries apply revenue forecasting in real business scenarios.
1. SaaS Companies
Subscription-based businesses forecast revenue using churn rates, renewal rates, and new subscriptions. Accurate forecasting helps manage cash flow and plan product development.
2. Retail Chains
Retailers analyze historical sales, seasonal trends, and promotions to estimate revenue, thereby enabling better inventory management and marketing spend allocation.
3. Manufacturing Firms
Manufacturers use order pipelines, supplier lead times, and market demand to forecast revenue and support efficient production planning.
Final Thoughts
Revenue forecasting is a powerful tool that transforms uncertainty into actionable insights. By predicting future income, organizations can allocate resources wisely, manage risks, and drive sustainable growth. While challenges remain, leveraging technology, integrating data, and adhering to best practices can significantly enhance forecasting accuracy. In today’s competitive business landscape, mastering revenue forecasting is no longer just an advantage—it is a necessity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How often should revenue forecasts be updated?
Answer: Forecasts should be reviewed monthly or quarterly, with adjustments made as new data emerges or market conditions change.
Q2. Can small businesses benefit from revenue forecasting?
Answer: Absolutely. Even basic forecasts help small businesses manage cash flow, plan growth, and make informed decisions.
Q3. Which method is best for startups?
Answer: Startups often rely on bottom-up forecasting and market research since historical data may be limited.
Q4. How accurate are revenue forecasts?
Answer: Accuracy depends on data quality, forecasting method, and external market factors. Combining multiple approaches typically improves reliability.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Revenue Forecasting” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

