What is Content Distribution?
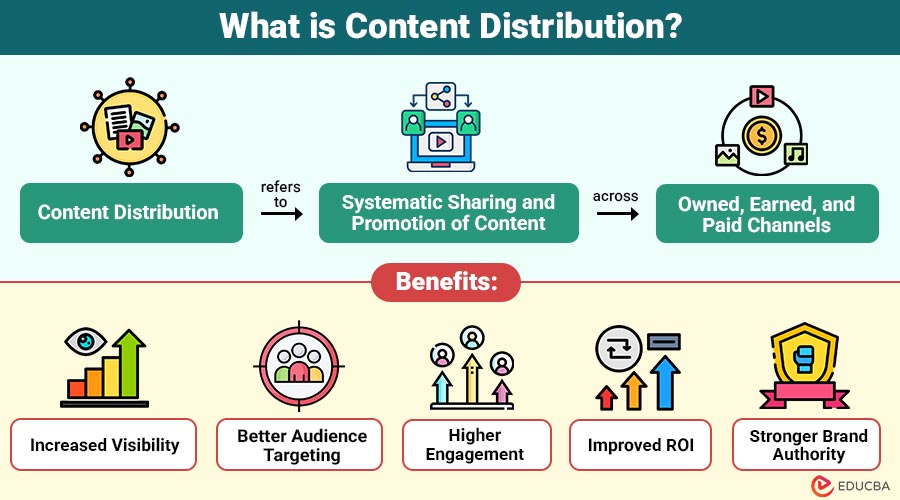
Content distribution refers to the systematic sharing and promotion of content across owned, earned, and paid channels. It aims to amplify reach, engage target audiences, and achieve specific marketing objectives. Unlike content creation, which focuses on producing blogs, videos, or social posts, distribution emphasizes how, where, and when that content is delivered.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Strategic content distribution ensures valuable content reaches the right audience at the right time.
- Combining owned, earned, and paid channels improves visibility, credibility, and overall marketing effectiveness.
- Platform-specific content formats and timing significantly influence engagement, traffic quality, and conversion outcomes.
- Continuous performance measurement and optimization are essential to maximize content impact and marketing ROI.
Importance of Content Distribution
Content distribution plays a crucial role in digital marketing success for several reasons:
1. Expanded Content Reach
Content distribution ensures your content reaches wider audiences through multiple platforms beyond search engines.
2. Brand Visibility & Authority
Consistent distribution builds brand recognition, credibility, and thought leadership across relevant digital channels.
3. Targeted Traffic & Leads
Strategic distribution attracts relevant audiences, increases high-intent visitors, and generates higher-quality leads.
4. Engagement & Conversions
Placing content on preferred platforms increases engagement, trust, and conversion likelihood.
5. Content ROI Maximization
Distribution amplifies content lifespan, performance, and returns, ensuring maximum value from creation investments.
Types of Content Distribution
It is categorized into three main types:
1. Owned Media Distribution
Owned media distribution uses brand-controlled channels to publish content, maintain messaging consistency, and directly engage audiences without intermediaries.
Examples:
- Company website or blog
- Email newsletters
- Mobile apps
- Brand-owned social media pages
Key Advantage: Full control over messaging and audience targeting.
2. Earned Media Distribution
Earned media distribution occurs when external audiences organically share, mention, or promote content, increasing credibility, trust, and reach without payment.
Examples:
- Social media shares
- Backlinks from other websites
- Media coverage
- Influencer mentions
Key Advantage: High credibility and trust, often without direct costs.
3. Paid Media Distribution
Paid media distribution leverages advertising spend to amplify content visibility, achieve immediate reach, and target specific audiences with precision.
Examples:
- Social media ads
- Native advertising
- Sponsored posts
- Display ads
Key Advantage: Immediate reach and precise audience targeting.
Content Distribution Channels
Different channels serve different goals and audiences. Selecting the right mix is essential.
| Channel Types | Examples | Best For |
| Social Media | LinkedIn, Instagram | Engagement and awareness |
| Email Marketing | Newsletters, drip campaigns | Retention and conversions |
| Search Engines | SEO, content syndication | Long-term traffic |
| Communities | Reddit, Quora, forums | Authority building |
| Influencers | Bloggers, creators | Trust and reach |
| Paid Platforms | Google Ads, Meta Ads | Scalable promotion |
Content Distribution Strategy
Here are the step-by-step actions businesses can follow to plan, execute, and optimize an effective content distribution strategy.
1. Define Distribution Goals
Start by identifying objectives such as:
- Increasing brand awareness
- Generating leads
- Driving website traffic
- Improving conversions
Clear goals guide channel selection and performance measurement.
2. Understand Your Target Audience
Analyze audience demographics, preferences, content consumption habits, and platform usage to ensure relevance and effectiveness.
3. Match Content Formats to Channels
Different platforms favor different formats:
- Blogs → SEO, LinkedIn, email
- Videos → YouTube, Instagram, TikTok
- Infographics → Pinterest, blogs
- Whitepapers → LinkedIn, email campaigns
4. Choose the Right Distribution Mix
Combine owned, earned, and paid channels to balance cost efficiency, reach, and credibility.
5. Schedule and Automate Distribution
Use content calendars and automation tools to maintain consistency and timing optimization.
6. Measure and Optimize Performance
Track metrics such as:
- Reach and impressions
- Click-through rates (CTR)
- Engagement
- Conversions
- ROI
Benefits of Content Distribution
Here are the key benefits that demonstrate how effective content distribution enhances visibility, engagement, and overall marketing performance.
1. Increased Visibility
Expands reach by exposing content to wider audiences across multiple digital platforms.
2. Better Audience Targeting
Strategic distribution enables precise audience segmentation, personalization, and the delivery of relevant content.
3. Higher Engagement
Consistent content promotion drives interactions, encourages participation, and strengthens audience connection with the brand.
4. Improved ROI
Distribution maximizes value from existing content assets by improving performance, extending their lifespan, and increasing measurable returns.
5. Stronger Brand Authority
Repeated exposure to content builds credibility, trust, and long-term industry leadership among target audiences.
Challenges in Content Distribution
Despite its benefits, content distribution presents several challenges:
1. Content Saturation
High volumes of competing content make it difficult for brands to consistently capture audience attention.
2. Platform Algorithm Changes
Frequent algorithm updates reduce organic reach, requiring constant strategy adjustments to maintain visibility.
3. Budget Constraints
Limited budgets restrict paid promotion scale, impacting reach, frequency, and overall distribution effectiveness.
4. Attribution Difficulties
Tracking content performance across multiple touchpoints makes accurate measurement of conversions and ROI challenging.
5. Maintaining Consistency Across Channels
Ensuring uniform messaging, tone, and branding across platforms requires careful coordination and resources.
Real-World Examples
Here are practical examples illustrating how businesses apply content distribution strategies across industries.
1. SaaS Company
A SaaS brand publishes a blog, shares snippets on LinkedIn, runs paid ads for webinars, and sends email newsletters—using all three media types.
2. E-commerce Brand
Product videos are distributed through Instagram Reels, influencer partnerships, and retargeting ads to boost conversions.
3. B2B Consulting Firm
Whitepapers are distributed via LinkedIn ads, email campaigns, and industry forums to generate qualified leads.
Final Thoughts
Content distribution is a critical pillar of digital marketing, determining whether content succeeds or fails. By strategically leveraging owned, earned, and paid channels, businesses can amplify their content’s impact, improve engagement, and drive measurable outcomes. A well-executed strategy transforms content from a static asset into a powerful growth engine.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is content distribution necessary for SEO?
Answer: Yes, distribution helps amplify content visibility, backlinks, and engagement, indirectly improving SEO.
Q2. Which is better: paid or organic distribution?
Answer: A balanced mix is ideal—organic builds trust, while paid delivers scalability.
Q3. How often should content be distributed?
Answer: Frequency depends on platform norms, audience behavior, and content type.
Q4. What metrics measure content distribution success?
Answer: Reach, engagement, traffic, leads, conversions, and ROI are key metrics.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Content Distribution” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
