What is a Customer Journey Map?
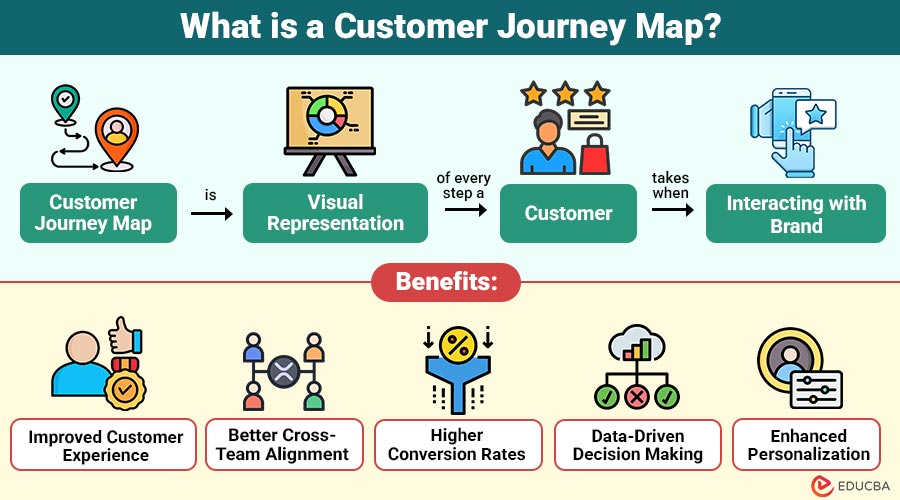
Customer journey map is visual representation of every step a customer takes when interacting with brand. It outlines user actions, thoughts, emotions, pain points, and motivations across all stages—from awareness to loyalty.
It answers critical questions:
- How do users find the brand?
- What motivates them to move to the next stage?
- Where do they face friction?
- How can the business improve its experience?
In short, a CJM transforms raw customer behavior into actionable insights for better decision-making.
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Key Components
- Stages
- Types
- How to Create a Customer Journey Map?
- Benefits
- Challenges
- Tools
- Real-World Example
Key Takeaways:
- Customer journey maps convert scattered customer interactions into structured insights that effectively guide experience-focused strategic improvements.
- Mapping emotions alongside actions reveals hidden friction points that traditional analytics often miss across multi-touch customer experiences.
- Well-maintained journey maps foster cross-functional alignment by grounding decisions in a shared, customer-centric understanding.
- Regularly updating journey maps ensures relevance as customer behaviors, expectations, and digital channels continuously evolve.
Key Components of a Customer Journey Map
A well-structured customer journey map typically includes the following components:
1. Customer Persona
Defines the ideal customer with demographics, goals, motivations, behaviors, expectations, and challenges influencing their decisions.
2. Journey Stages
Outlines the phases customers experience with a brand, from awareness through purchase to post-purchase engagement.
3. Touchpoints
Covers every interaction customers have, including ads, websites, emails, calls, chats, social media, and physical stores.
4. Customer Actions
Describes specific steps customers take during each stage, such as researching, comparing, deciding, purchasing, and reviewing.
5. Emotions & Mindset
Captures customer feelings, perceptions, motivations, uncertainties, and expectations throughout their entire interaction with the brand.
6. Pain Points
Highlights challenges, obstacles, frustrations, delays, and issues customers encounter that negatively impact their journey experience.
Stages of a Customer Journey Map
Although journey stages vary by business, the most common framework includes the following five stages:
1. Awareness Stage
Customers recognize a need and first discover the brand through exposure, messaging, and initial informational interactions online.
Common Touchpoints:
- Social media ads
- Blog posts
- Search engine results
- Influencer recommendations
Customer Mindset: Curious, exploratory
Business Goal: Build brand awareness and visibility
2. Consideration Stage
Customers actively research, compare alternatives, evaluate value propositions, and assess credibility before narrowing their preferred solution options.
Common Touchpoints:
- Product pages
- Comparison blogs
- Reviews and testimonials
- Webinars or demos
Customer Mindset: Analytical, cautious
Business Goal: Educate, differentiate, and build trust
3. Decision Stage
Customers finalize purchase decisions by assessing pricing, risk, incentives, and overall confidence in the selected solution.
Common Touchpoints:
- Pricing pages
- Free trials
- Sales calls
- Checkout experience
Customer Mindset: Confident but risk-aware
Business Goal: Reduce friction and close the sale
4. Retention Stage
Customers experience the product, judge the delivered value, receive support, and decide whether to continue long-term engagement and loyalty.
Common Touchpoints:
- Onboarding emails
- Customer support
- Product usage
- Loyalty programs
Customer Mindset: Evaluative, expectation-driven
Business Goal: Deliver value and reduce churn
5. Advocacy Stage
Customers who achieve satisfaction enthusiastically recommend the brand, influencing others through referrals, reviews, endorsements, and advocacy.
Common Touchpoints:
- Reviews
- Referrals
- Social media shares
- Case studies
Customer Mindset: Loyal, enthusiastic
Business Goal: Turn customers into brand advocates
Types of Customer Journey Maps
Different business goals require different journey mapping approaches:
1. Current-State Journey Map
Identifies gaps, problems, and areas for progress by visualizing current customer interactions, behaviors, touchpoints, and emotions.
2. Future-State Journey Map
Depicts the ideal customer experience after strategic improvements, highlighting desired interactions, emotions, and optimized touchpoints.
3. Day-in-the-Life Journey Map
Explores customers’ daily activities, motivations, and challenges beyond brand touchpoints to understand broader context and unmet needs.
4. Service Blueprint
Extends journey mapping by detailing the internal processes, systems, teams, and dependencies that support each customer-facing interaction.
How to Create a Customer Journey Map?
Below are the structured steps that guide businesses in building an effective, insight-driven customer journey map.
1. Define Objectives
Clarify goals such as conversions, onboarding, retention, or support improvements.
2. Identify Target Persona
Select a specific customer segment for accurate, focused journey mapping.
3. List Journey Stages
Define journey stages aligned with your unique business model requirements.
4. Map Touchpoints
Document every online and offline customer interaction across each stage.
5. Capture Customer Emotions
Collect emotions using surveys, interviews, reviews, and behavioral analytics data.
6. Identify Pain Points
Identify friction points causing dissatisfaction, delays, abandonment, or conversion drop-offs.
7. Identify Opportunities
Recommend improvements aligned with customer needs and measurable business objectives.
Benefits of Customer Journey Mapping
It provides value across departments and strategies.
1. Improved Customer Experience
Identifies friction points and improves touchpoints to deliver seamless, consistent, and satisfying customer experiences everywhere globally.
2. Better Cross-Team Alignment
Aligns marketing, sales, product, and support teams around shared customer insights and unified goals for organization-wide collaboration.
3. Higher Conversion Rates
Minimizes funnel drop-offs by resolving objections, improving trust, and optimizing decision-stage interactions effectively for customers consistently.
4. Data-Driven Decision Making
Integrates qualitative feedback with quantitative analytics to guide evidence-based strategies, prioritization, and business decisions across teams.
5. Enhanced Personalization
Delivers relevant content and offers by tailoring experiences to customer intent, behavior, and journey stage needs.
Challenges in Customer Journey Mapping
Below are the most common challenges organizations face when creating and maintaining effective customer journey maps.
1. Incomplete Data Across Channels
Fragmented customer data across platforms limits full visibility into interactions, behaviors, and true journey progression.
2. Overgeneralization of Personas
Broad personas oversimplify customer needs, ignoring segment-specific motivations, pain points, and behavioral differences.
3. Lack of Stakeholder Alignment
Misaligned teams interpret journey insights differently, reducing collaboration, ownership, and effective execution of improvements.
4. Static Maps that are Never Updated
Outdated journey maps fail to reflect evolving customer behavior, channels, expectations, and changing business strategies.
Tools for Customer Journey Mapping
Popular tools include:
1. Miro
Collaborative whiteboard platform enabling teams to visually map customer journeys, brainstorm touchpoints, and align stakeholders efficiently.
2. Lucidchart
Diagramming tool used to create structured customer journey maps, flowcharts, and process visuals collaboratively online.
3. Figma
Design-centric collaboration tool supporting interactive journey mapping, prototyping, and real-time feedback across cross-functional teams.
4. Smaply
Dedicated journey mapping software that documents personas, touchpoints, emotions, and experience insights systematically.
5. UXPressia
Experience management platform for mapping journeys, personas, and impact metrics with analytics-driven visual storytelling.
6. HubSpot Journey Builder
CRM-integrated tool that tracks customer touchpoints and visualizes lifecycle journeys for marketing and sales alignment.
Real-World Example
Below is a practical illustration of how a customer journey map applies to a SaaS business scenario.
SaaS Product:
- Awareness: User finds a blog via Google search
- Consideration: Reads case studies and compares competitors
- Decision: Signs up for a free trial
- Retention: Receives onboarding emails and in-app guidance
- Advocacy: Leaves a positive review on G2 and refers peers
Mapping this journey helps optimize trial onboarding, pricing clarity, and post-signup engagement.
Final Thoughts
Customer journey map is a powerful strategic asset that goes beyond traditional funnels and metrics. By visualizing customer interactions, emotions, and pain points, businesses can design experiences that truly resonate with their audience. When used correctly, it leads to improved customer satisfaction, stronger brand loyalty, and sustainable growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the main purpose of a customer journey map?
Answer: To understand and optimize the complete customer experience across all touchpoints.
Q2. Is customer journey mapping only for marketing?
Answer: No, it benefits sales, product development, customer support, and UX teams.
Q3. How often should a journey map be updated?
Answer: Ideally, every 6–12 months or when customer behavior changes significantly.
Q4. Can small businesses use customer journey maps?
Answer: Yes, even simple maps provide valuable insights and improve customer engagement.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Customer Journey Map” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.