What does External Growth mean?
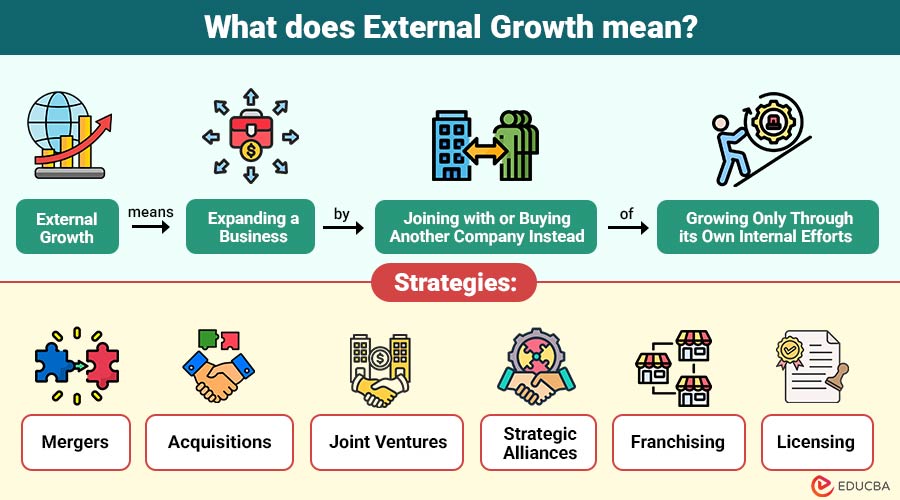
External growth means expanding a business by joining with or buying another company instead of growing only through its own internal efforts. It helps a business grow faster by gaining new customers, products, or markets.
For example, if a small tech company buys another company with advanced software, it can quickly improve its product range and reach more customers without building everything from scratch.
Table of Content:
- What does External Growth mean?
- Strategies
- Key Drivers Behind External Growth
- How to Implement External Growth Successfully
- External Growth vs. Internal Growth
- Benefits
- Challenges
Key Takeaways:
- External growth helps companies expand quickly by acquiring or partnering with other businesses.
- Strategies such as mergers, acquisitions, alliances, and franchising offer rapid access to new markets, talent, and technology.
- While growth is rapid, challenges such as high costs, cultural differences, and integration issues must be managed carefully.
- With proper planning, due diligence, and a strong integration strategy, external growth can deliver long-term success and a stronger competitive position.
External Growth Strategies
External growth strategies help a business expand by working with or buying other companies. These methods allow faster growth than relying only on internal efforts.
- Mergers: Two companies join together to form a single, stronger company. This helps them share resources, reduce costs, and compete better in the market.
- Acquisitions: One company buys another to gain new customers, products, or technology quickly. It is a fast way to grow and expand into new markets.
- Joint Ventures: Two or more companies work together on a specific project by sharing skills, money, and resources. It reduces risk and allows both sides to benefit.
- Strategic Alliances: Companies form partnerships to support each other without merging fully. For example, they may share technology, distribution networks, or marketing support.
- Franchising: A business allows others to use its brand, products, and business model. This helps the company grow quickly in many locations at less cost.
- Licensing: A company permits another company to use its technology, design, or brand in exchange for a fee, helping expand reach and income.
Key Drivers Behind External Growth
Key drivers behind external growth are the main reasons why companies expand by partnering with, merging with, or buying other businesses.
- Entering New Markets: Companies grow externally to reach new geographic areas or different customer groups faster than building from scratch.
- Access to New Technology: By merging with or buying another company, businesses can quickly gain advanced tools, software, or production methods that improve their products and efficiency.
- Skilled Talent Acquisition: External growth helps companies bring in experienced employees, specialists, and strong management teams without long hiring processes.
- Economies of Scale: When two companies join together, they can produce more at lower costs, buy materials cheaply, and operate more efficiently.
- Faster Expansion: External growth enables businesses to expand quickly by leveraging another company’s strengths and resources, accelerating market entry.
- Competitive Advantage: Companies may merge or acquire others to reduce competition, strengthen their market position, or gain unique capabilities that help them stand out.
How to Implement External Growth Successfully?
Implementing external growth effectively requires careful planning and execution. Key steps include:
- Conduct Market Research: Identify the right companies, industries, or markets that align with your growth goals. Understand trends, opportunities, and potential risks.
- Perform Financial and Operational Due Diligence: Evaluate the target company’s finances, assets, liabilities, and operational strengths to ensure a sound investment.
- Analyze Strategic Fit: Check if the target company aligns with your long-term business goals, culture, and values to avoid future conflicts.
- Plan Post-Merger Integration: Develop a clear plan for combining teams, systems, and processes. Communicate changes effectively to employees and stakeholders.
- Leverage Technology and Resources: Ensure smooth integration of technology, supply chains, and operations to maximize efficiency.
- Monitor and Evaluate Performance: Track progress after growth initiatives and make adjustments where necessary to achieve desired results.
Following these steps improves the likelihood of achieving successful and lasting external growth.
External Growth vs. Internal Growth
| Aspect | External Growth | Internal Growth |
| Definition | Expanding by merging with, acquiring, or partnering with other companies. | Expanding using the company’s own resources and capabilities. |
| Speed | Faster growth due to acquiring existing resources, markets, or customers. | Slower growth as it depends on internal development and time. |
| Investment | Often requires a higher financial investment for acquisitions or partnerships. | Usually lower cost, but requires investment in internal resources and infrastructure. |
| Risk | Higher risk because of integration issues and uncertain markets. | Lower risk, as the company has control over the growth process. |
| Market Reach | Immediate access to new markets and customers. | Gradual market expansion over time. |
| Innovation & Skills | Gains technology, talent, or expertise from other companies. | Depends on internal R&D and training programs. |
Benefits of External Growth
It offers several advantages that help a business expand faster and compete better. Key benefits include:
- Faster Expansion: Companies can grow quickly by acquiring existing markets, customers, and resources instead of building everything internally.
- Instant Access to New Markets: Mergers or acquisitions help businesses enter new regions or customer segments immediately.
- Stronger Product or Service Portfolio: By acquiring or partnering with other companies, businesses can expand their product or service offerings and enhance overall value.
- Improved Technology and Skills: External growth enables companies to acquire new technologies, expertise, and innovation without lengthy development time.
- Economies of Scale: Combining operations reduces costs, improves efficiency, and increases bargaining power with suppliers.
- Competitive Advantage: It helps businesses eliminate competition or strengthen their market position.
- Higher Revenue Potential: More customers, better resources, and improved products lead to stronger financial performance.
Challenges of External Growth
While external growth offers many benefits, it also poses several challenges that businesses must manage carefully. Key challenges include:
- Cultural Differences: When two companies merge, their work cultures may clash, causing misunderstandings and reduced employee morale.
- High Costs: Acquisitions and partnerships require large financial investments, including legal fees, due diligence, and integration expenses.
- Integration Problems: Combining systems, processes, and teams can be difficult and time-consuming, leading to operational delays.
- Regulatory Approvals: Governments may require stringent checks and approvals, which can slow or block growth plans.
- Communication Issues: Poor communication during mergers can create confusion among employees and customers.
- Risk of Overestimating Value: Companies may pay too much for an acquisition or partner with the wrong business, resulting in financial losses.
- Management Complexity: Larger combined organizations can become harder to manage and coordinate efficiently.
Final Thoughts
External growth provides businesses with powerful opportunities to expand quickly, enter new markets, and strengthen their competitive position. However, its success depends on careful planning, proper integration, and smart decision-making. When managed well, external growth can lead to long-term stability, higher profits, and a stronger market presence, helping companies achieve sustainable success in a dynamic business environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is external growth suitable for small businesses?
Answer:- Yes, small businesses can use external growth through partnerships or small acquisitions to scale faster.
2. Does external growth always require a large investment?
Answer:- No, strategies like alliances and licensing can be low-cost options.
3. Can external growth fail?
Answer:- Yes, poor planning or cultural mismatch can cause failure.
4. Is external growth faster than internal growth?
Answer:- Yes, it offers quicker access to markets, resources, and customers.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide on External Growth helped you understand business expansion strategies. For more insights, explore these related articles below: