What is Ensemble Learning?
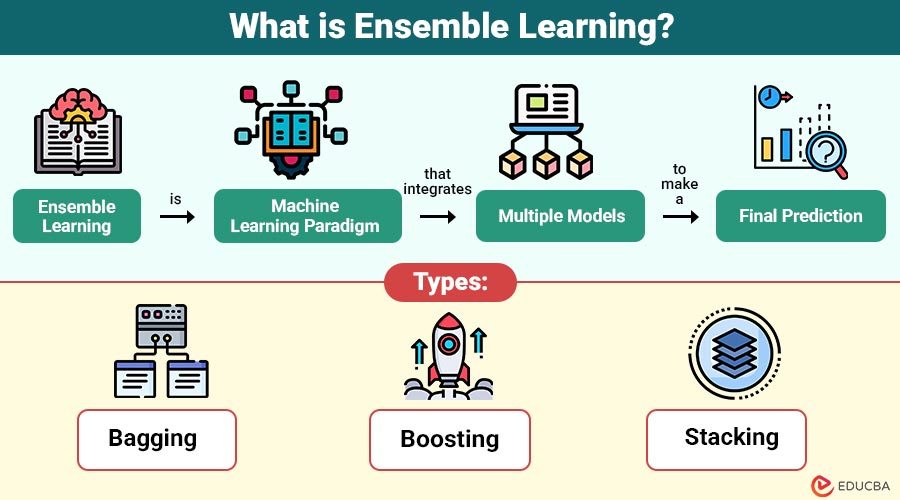
Ensemble learning is machine learning paradigm that integrates multiple models (called base learners) to make a final prediction. The idea is simple yet powerful—a group of weak learners can come together to form strong learner. Mathematically, if individual models have an accuracy slightly better than random guessing, combining them can significantly enhance overall prediction performance.
Example: Imagine a jury making a decision. Each juror (model) provides an opinion, and the collective verdict (ensemble) is typically more reliable than any single juror’s judgment.
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Why Ensemble Learning?
- Working
- Types
- Benefits
- Limitations
- Real-World Applications
- Real-World Example
Key Takeaways:
- Ensemble learning combines multiple weak models to create a stronger, more accurate predictive system.
- It enhances performance by mitigating bias, variance, and instability across various machine learning algorithms.
- Techniques like bagging, boosting, and stacking enhance model reliability through strategic model combination.
- Widely applied in finance, e-commerce, and AI, ensemble learning ensures robust real-world decision-making.
Why Ensemble Learning?
Individual machine learning algorithms often suffer from one or more of the following:
- High bias (underfitting): The model fails to accurately capture complex data patterns.
- High variance (overfitting): Although the model performs well on the training data, it does not generalize well to new data.
- Limited feature interpretation: The model struggles to interpret or utilize all input features.
Ensemble learning mitigates these issues by:
- Reducing bias: Combining diverse models captures a wider range of data patterns.
- Reducing variance: Averaging results minimizes the risk of overfitting.
- Improving stability: Small data fluctuations have less impact on ensemble predictions.
How does Ensemble Learning Work?
The ensemble learning process typically involves three stages:
1. Model Generation
Multiple base models are trained on the dataset, using different algorithms or subsets of data.
2. Combination
The predictions from all base models are aggregated using techniques like averaging, voting, or stacking.
3. Prediction
The final output is derived based on the aggregated result, which generally yields better accuracy and stability.
Types of Ensemble Learning Techniques
There are three major types of ensemble learning techniques:
1. Bagging (Bootstrap Aggregating)
Bagging reduces variance by training multiple models on different random subsets of the original dataset, created through bootstrapping (sampling with replacement). Each model is trained independently, and its predictions are averaged (for regression) or combined by voting (for classification).
Examples:
- Random Forest
- Bagged Decision Trees
2. Boosting
Examples:
- AdaBoost (Adaptive Boosting)
- Gradient Boosting
3. Stacking (Stacked Generalization)
Stacking combines predictions from multiple base models (level-0 learners) using a meta-model (level-1 learner) to make final predictions. The meta-model learns how to incorporate the outputs of the base models effectively.
Examples:
- Stacked Regression
- Blending
Benefits of Ensemble Learning
Here are the key benefits that make ensemble learning a powerful approach in improving machine learning model performance:
Limitations of Ensemble Learning
While ensemble learning enhances model performance and robustness, it also comes with several limitations:
1. High Computational Cost
2. Complexity
Ensemble models are more challenging to interpret and analyze because they combine multiple individual models, making it difficult to understand decision boundaries or assess feature importance.
3. Overfitting Risk
Ensembles may perform poorly on new data if they aren’t properly tuned, especially in boosting methods.
4. Diminishing Returns
After a certain point, adding more models to the ensemble provides minimal or no performance improvement, while still increasing computational overhead.
Real-World Applications
Ensemble learning is widely adopted across industries to boost accuracy, reliability, and decision-making in complex tasks. Here are some real-world applications:
1. Financial Forecasting
Ensemble learning enhances credit scoring, stock market prediction, and risk assessment by combining multiple models for more accurate financial insights.
2. Fraud Detection
Many models work together to spot fake or suspicious transactions, reducing mistakes and improving accuracy in finance and online security systems.
3. E-commerce
By combining models that use user behavior and product details, ensemble methods make better product suggestions and boost customer engagement on shopping sites.
4. Autonomous Vehicles
Ensemble models combine data from multiple sensors—such as cameras, lidar, and radar—to enhance object detection, navigation accuracy, and driving safety.
5. Text and Sentiment Analysis
The identification of emotions, topic classification, and opinion analysis in reviews, social media posts, and feedback are all improved when machine learning and natural language processing are combined.
Real-World Example
Here is how ensemble learning works in a practical scenario:
Random Forest in Action
Scenario:
A bank wants to predict whether a loan applicant will default.
- Step 1: Multiple decision trees are trained on bootstrapped samples.
- Step 2: Each tree votes for a class (default or not).
- Step 3: The majority vote determines the final prediction.
Result:
- Increased accuracy.
- Reduced overfitting compared to a single decision tree.
Final Thoughts
Ensemble learning is a major innovation in modern machine learning, combining multiple models to achieve higher accuracy, stability, and generalization than single models. By reducing errors through bagging, correcting mistakes through boosting, and merging models through stacking, it ensures reliable predictions. As data complexity increases, smarter and automated ensemble methods will further enhance AI performance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the main goal of ensemble learning?
Answer: The primary goal is to combine multiple models to improve prediction accuracy and robustness.
Q2. Which ensemble algorithm is best for large datasets?
Answer: XGBoost and LightGBM are highly efficient and optimized for large-scale data.
Q3. Can ensemble learning reduce overfitting?
Answer: Yes, particularly bagging helps reduce overfitting by averaging multiple independent models.
Q4. Is ensemble learning suitable for deep learning models?
Answer: Yes, ensemble methods can combine deep neural networks for improved generalization, especially in image and NLP tasks.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Ensemble Learning” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
