What is Robotics Automation?
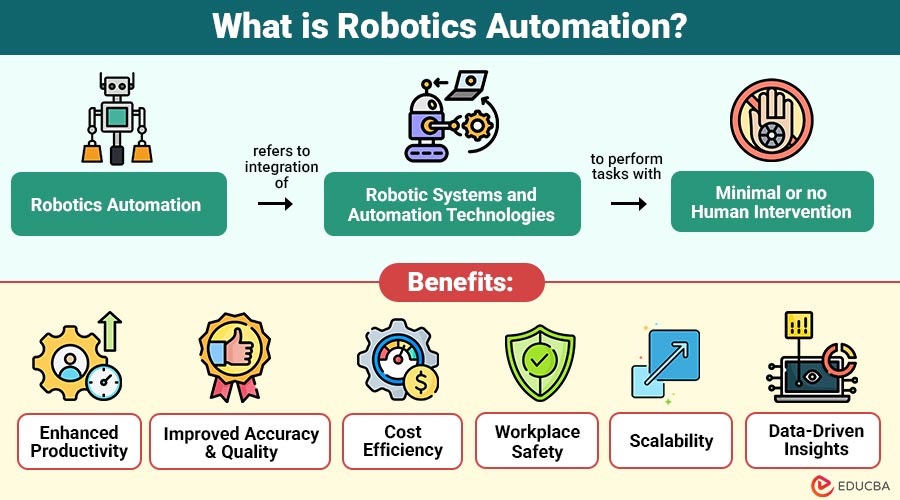
Robotics Automation refers to the integration of robotic systems and automation technologies to perform tasks with minimal or no human intervention. It involves the use of programmable machines—robots—that can carry out complex or repetitive activities autonomously or semi-autonomously.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Robotics automation enhances productivity by performing repetitive tasks efficiently while consistently minimizing human errors.
- Integration of AI and sensors enables robots to adapt, learn, and optimize complex operational processes.
- Long-term savings, improved quality, and workplace safety benefits offset high initial costs.
- Robotics reshapes industries, creating new technical roles while demanding reskilling and ethical consideration for implementation.
Key Components of Robotics Automation
Here are the essential key components that make up a robotics automation system:
1. Robots
These are the core physical machines designed to execute tasks. Robots can range from simple robotic arms used in factories to complex humanoid robots or autonomous drones.
2. Sensors
Sensors collect data from the environment (e.g., proximity, temperature, pressure, or vision) and allow the robot to make informed decisions and react in real-time.
3. Actuators
Actuators convert electrical signals into physical movement, enabling robots to perform actions such as gripping, lifting, or moving.
4. Controllers
Controllers serve as the robot’s “brains,” analyzing information, carrying out commands, and coordinating motions.
5. Software and Algorithms
Software enables the programming and automation of robotic tasks. With AI and machine learning algorithms, robots can learn, adapt, and optimize performance over time.
6. Connectivity and Integration
Integration with other systems (such as the Internet of Things, cloud computing, or enterprise software) enhances automation, data sharing, and decision-making.
Types of Robotics Automation
Robotics automation can be categorized based on application and level of autonomy:
1. Industrial Robotics
Used in manufacturing and production lines, these robots handle tasks like welding, painting, and assembly with precision and speed.
2. Service Robotics
These robots assist humans in performing services such as healthcare support, cleaning, or hospitality tasks.
3. Collaborative Robots
Cobots work alongside humans in shared workspaces, offering flexibility and safety while improving productivity.
4. Autonomous Mobile Robots
These robots navigate independently using sensors and AI, commonly found in logistics, warehousing, and delivery services.
5. Process Automation Robots
Also known as Robotic Process Automation (RPA), these software robots automate repetitive digital tasks such as data entry, billing, and reporting.
How Robotics Automation Works?
The process of robotics automation involves several stages:
1. Task Identification
Identify repetitive, hazardous, or time-consuming tasks suitable for automation to enhance productivity, safety, and operational efficiency across processes.
2. System Design
Engineers create a customized robotic system by selecting suitable hardware, sensors, actuators, and control software to perform desired operations effectively.
3. Programming
Robots are programmed using algorithms or AI-based learning models to follow predefined instructions, adapt to conditions, and optimize task performance.
4. Integration
The robotic system is connected to existing enterprise software, IoT devices, and workflows for seamless communication and coordinated operational efficiency.
5. Operation and Optimization
Deployed robots gather real-time data, analyze performance, and use machine learning to improve precision, efficiency, and adaptability in tasks continuously.
Applications of Robotics Automation Across Industries
Here are some key applications of robotics automation in various sectors:
1. Manufacturing
Robotics automation has long been the backbone of the manufacturing industry. Robots perform welding, painting, and assembly with speed and precision, ensuring consistent product quality and reducing downtime.
2. Agriculture
Robotics automation in agriculture includes automated tractors, crop monitoring drones, and harvesting robots that increase productivity and reduce labor dependency.
3. Construction
Robots are used for bricklaying, 3D printing of structures, and site inspections, improving efficiency and worker safety.
4. Retail
Automated checkout systems, inventory robots, and smart warehouses streamline retail operations and enhance customer experience.
5. Defense and Security
Robots are used for surveillance, bomb disposal, reconnaissance, and border security, reducing risk to human personnel.
Benefits of Robotics Automation
Here are the benefits that robotics automation brings to businesses and industries:
1. Enhanced Productivity
Robots can operate continuously without fatigue, working 24/7, significantly increasing overall operational efficiency and reducing production bottlenecks.
2. Improved Accuracy and Quality
Automation reduces human errors, maintaining consistent output quality, precision, and reliability, which ensures superior products and customer satisfaction.
3. Cost Efficiency
While initial setup costs are high, long-term savings come from reduced labor, minimized errors, and optimized operational efficiency.
4. Workplace Safety
Robots perform hazardous or repetitive tasks, minimizing workplace accidents, protecting employees, and creating a safer industrial environment.
5. Scalability
Robotic systems can be easily scaled or reprogrammed to accommodate increased production, product variety, or changing operational demands.
6. Data-Driven Insights
Robotics collects detailed performance and process data, enabling better decision-making, continuous optimization, and improved operational strategies.
Challenges in Robotics Automation
Here are some of the key challenges faced when implementing robotics automation:
1. High Initial Investment
The cost of robots, maintenance, and system integration can be prohibitive for small businesses.
2. Job Displacement Concerns
Automation may replace certain repetitive or manual jobs, leading to workforce displacement if reskilling initiatives are lacking.
3. Technical Complexity
Implementing and maintaining robotic systems requires specialized knowledge and ongoing technical support.
4. Cybersecurity Risks
Robots are susceptible to cyber threats that could interfere with operations as they are linked to networks.
5. Ethical and Regulatory Issues
The use of robots in sensitive areas like healthcare or defense raises ethical and legal questions.
6. Integration with Legacy Systems
Difficulty in seamlessly connecting robots with outdated machinery or software can hinder efficiency and increase implementation costs.
Final Thoughts
Robotics Automation stands as one of the most transformative forces of the 21st century. By merging mechanical precision with artificial intelligence, it is not only redefining productivity but also reshaping how humans interact with technology. While challenges like cost, ethics, and job displacement remain, the benefits—efficiency, safety, and innovation—far outweigh the drawbacks. In a rapidly changing digital landscape, embracing robotics automation is no longer an option—it is a necessity for businesses that aim to stay efficient, agile, and future-ready.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How is robotics automation different from traditional automation?
Answer: Traditional automation relies on fixed systems with limited flexibility, while robotics automation uses intelligent, programmable machines that can adapt, learn, and make decisions based on data.
Q2. What is the impact of robotics automation on employment?
Answer: While robotics automation may replace certain manual roles, it also creates new opportunities in the robot maintenance, AI development, system design, and data management. Reskilling and education are key to adapting to this shift.
Q3. How does AI enhance robotics automation?
Answer: AI allows robots to analyze data, recognize patterns, make decisions, and continuously improve performance—transforming them from simple mechanical tools into intelligent systems.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Robotics Automation” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
