What is Brand Equity?
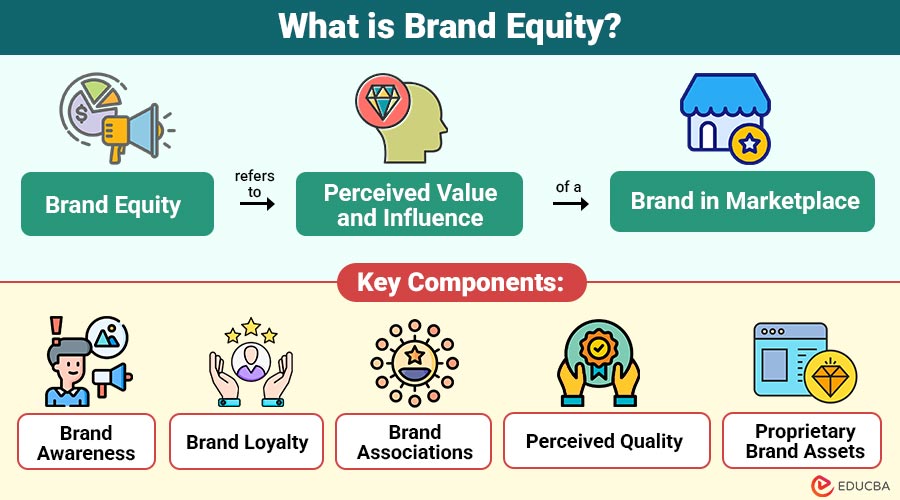
Brand equity refers to perceived value and influence of a brand in the marketplace. It represents the additional worth a product or service gains simply by being associated with a recognized brand name. Essentially, it is the premium that customers are willing to pay, the preference they show for a brand, and the emotional connection they develop with it.
For instance, a customer might choose an Apple iPhone over a generic smartphone, even if the technical specifications are similar. The reason is the perceived quality, trust, and status associated with the Apple brand, which clearly reflects strong brand equity.
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Importance
- Key Components
- Types
- Measuring Brand Equity
- Strategies
- Real-World Examples
- Challenges
Key Takeaways:
- Strong brand equity allows companies to command higher prices while maintaining customer trust and loyalty.
- Emotional connections with consumers enhance brand perception, fostering advocacy, repeat purchases, and long-term relationships.
- Assessing brand performance using consumer insights and market data helps strengthen reputation and competitive advantage.
- Consistent quality, clear identity, and innovative marketing are essential to building and sustaining brand equity.
Importance of Brand Equity
Provides multiple important factors that directly impact a company’s growth and profitability.
1. Premium Pricing
Strong brand equity enables companies to charge higher prices as customers perceive superior quality, trust, and added value in their offerings.
2. Customer Loyalty
Brands with strong equity foster lasting relationships, reducing churn while encouraging repeat purchases and positive word-of-mouth recommendations among satisfied customers.
3. Market Expansion
Established brands leverage their reputation to launch new products or expand into untapped markets more easily, gaining quicker acceptance and trust.
4. Financial Performance
Enhances profitability, boosts stock value, attracts investors, and ensures long-term sustainability and growth in competitive markets.
Key Components of Brand Equity
Here are the main key components that collectively define and strengthen a value:
1. Brand Awareness
The level to which consumers recognize and remember a brand increases purchase likelihood and shapes their preferences during buying decisions and comparisons.
2. Brand Loyalty
Reflects customers’ emotional attachment, consistent repurchase behavior, and resistance to competitors, strengthening long-term relationships and ensuring steady brand growth.
3. Brand Associations
The ideas, qualities, and emotions linked to a brand in consumers’ minds, such as trust, innovation, performance, or social responsibility.
4. Perceived Quality
Consumers’ judgment about a brand’s overall excellence and reliability represents a key factor, influencing purchase decisions, satisfaction levels, and long-term brand trust.
5. Proprietary Brand Assets
Includes trademarks, patents, logos, and other intellectual properties that legally protect the brand and strengthen its distinct market position.
Types of Brand Equity
It can be classified into two major types:
1. Customer-Based Brand Equity (CBBE)
Customer-based brand equity focuses on the perception of customers. Kevin Lane Keller, a marketing expert, suggests that customers build CBBE when they know the brand, feel positively about it, and remain loyal to it. This type of equity relies heavily on brand image, awareness, and emotional connection.
2. Financial or Market-Based Brand Equity
Financial brand equity measures the monetary value of a brand in the marketplace. A company’s market value, price premium, and revenue generated from branded products often reflect this. High financial brand equity allows a company to charge premium prices and achieve higher margins.
Measuring Brand Equity
Quantifying brand equity is essential for making strategic business decisions. Several methods are used:
1. Brand Awareness Metrics
Measure how well consumers recognize and recall a brand using surveys, online search trends, and social media engagement data.
2. Brand Loyalty Metrics
Evaluate customer commitment through repeat purchases, retention rates, and Net Promoter Score (NPS) to gauge satisfaction and advocacy.
3. Brand Perception Metrics
Assess consumer opinions using brand image studies, satisfaction surveys, and social sentiment analysis to understand brand reputation and positioning.
4. Financial Metrics
Analyze price premiums, market share, and brand valuation reports to determine the monetary value and financial strength of a brand.
Strategies to Build and Enhance Brand Equity
Building it is a long-term effort requiring consistent attention across multiple areas.
1. Deliver Quality Products and Services
Consistency in product quality is foundational. Customers associate reliability and satisfaction with strong brands.
2. Develop Strong Brand Identity
A clear brand identity—logo, colors, tagline, messaging—helps consumers easily recognize and connect with the brand.
3. Create Emotional Connections
Brands that evoke emotions like trust, joy, or nostalgia tend to have stronger equity. Storytelling, brand purpose, and CSR activities help forge these connections.
4. Invest in Marketing and Communication
Consistent advertising, social media engagement, influencer partnerships, and PR campaigns increase brand visibility and awareness.
5. Foster Customer Loyalty Programs
Rewarding repeat purchases and creating membership programs reinforce loyalty and enhance perceived value.
6. Leverage Brand Extensions
Introducing new products under an established brand can transfer existing equity to new offerings, enhancing acceptance and reducing marketing costs.
Real-World Examples
The following brands illustrate how effective strategies in building awareness, loyalty, associations, and perceived quality translate into strong brand equity:
1. LEGO
LEGO has built decades of brand equity through creativity, quality, and nostalgia. Its bricks are recognized globally, and the brand is synonymous with imaginative play.
How LEGO Builds Brand Equity:
- Focus on creativity, problem-solving, and fun.
- Strong storytelling via movies, video games, and themed sets.
- High-quality, durable products that parents trust.
Result:
LEGO commands loyalty across generations, allowing premium pricing and successful brand extensions like LEGO video games and movies.
2. Starbucks
Starbucks has created a premium coffee experience that goes beyond just beverages. Its brand represents comfort, personalization, and community.
How Starbucks Builds Brand Equity:
- We offer a consistent in-store experience and quality coffee products.
- Companies provide personalized service, loyalty programs, and mobile app convenience.
- Strong emotional branding around community, relaxation, and lifestyle.
Result:
Customers willingly pay more than for generic coffee due to the experience and emotional connection Starbucks provides.
3. Patagonia
Patagonia’s brand equity comes from its strong environmental and ethical stance. Consumers have faith in the brand because of its outdoor items’ sustainability and excellence.
How Patagonia Builds Brand Equity:
- Emphasis on eco-friendly, sustainable practices and transparency.
- These are products associated with high durability and outdoor adventure.
- Activism and social responsibility create emotional connections with conscious consumers.
Result:
Patagonia enjoys loyal customers who advocate for the brand, enabling long-term growth and premium pricing.
Challenges in Managing Brand Equity
Managing is not without hurdles. Brands face multiple challenges that can weaken their perceived value and customer loyalty:
1. Brand Dilution
Extending a brand into unrelated categories can confuse consumers, weaken its identity, and reduce overall perceived brand value and strength.
2. Negative Publicity
Social media amplifies negative reviews or controversies, damaging brand reputation, customer trust, and long-term loyalty among existing and potential consumers.
3. Changing Market Trends
Brands must constantly innovate to remain relevant, competitive, and emotionally linked in the face of swift changes in consumer behavior and tastes.
4. Competitive Pressure
New entrants and substitute products challenge established brands, forcing them to strengthen differentiation, marketing efforts, and customer engagement strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is brand equity the same as brand value?
Answer: No. Brand equity refers to customer perception and loyalty, while brand value quantifies its financial worth.
Q2. How long does it take to build brand equity?
Answer: Building strong brand equity is a long-term process that can take years, depending on market conditions and brand strategies.
Q3. Can small businesses have strong brand equity?
Answer: Yes. Even small businesses can build strong brand equity through exceptional customer experience, quality products, and authentic branding.
Q4. How does digital marketing affect brand equity?
Answer: Digital marketing boosts brand awareness, customer engagement, and emotional connection, directly enhancing brand equity.
Final Thoughts
Brand equity is more than just marketing term—it is a critical business asset. Strong brands allow for premium pricing, foster consumer loyalty, and set your company apart in a crowded market. Measuring, nurturing, and leveraging requires a combination of quality products, emotional connection, consistent marketing, and strategic growth. By investing in brand equity, companies not only strengthen their relationship with customers but also secure a sustainable competitive advantage and long-term profitability.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Brand Equity” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

