What is Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)?
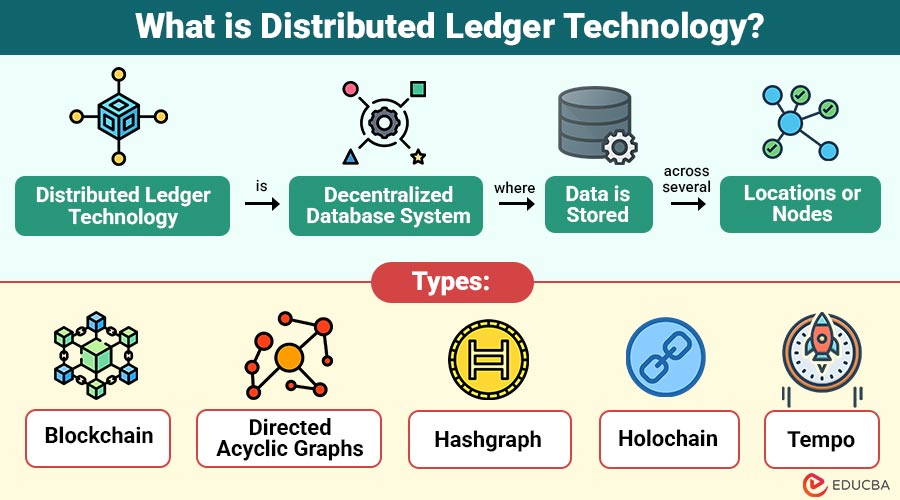
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is decentralized database system where data is stored across several locations or nodes. Unlike traditional ledgers managed by a single central authority, DLT distributes the responsibility of record-keeping across all participants in the network.
Key characteristics of DLT include:
- Decentralization: No single entity controls the ledger.
- Transparency: All participants can access and verify records.
- Immutability: Once the system records data, it cannot easily alter it.
- Security: Cryptographic methods ensure safe storage and transfer of information.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Distributed Ledger Technology decentralizes data storage, enhancing transparency, trust, and collaboration across multiple industries.
- DLT’s consensus mechanisms ensure secure, tamper-resistant records, reducing fraud and increasing accountability in digital ecosystems.
- Businesses adopt DLT for efficiency, faster settlements, reduced costs, and enhanced traceability in complex transactions.
- Despite scalability and regulatory concerns, ongoing innovation positions DLT as foundational to future digital transformation.
How Does Distributed Ledger Technology Work?
The working of DLT can be summarized in four simple steps:
1. Transaction Creation
A participant starts a transaction, such as sending funds, signing agreements, or updating records, which enters the distributed ledger.
2. Transaction Validation
The validity of transactions is confirmed by network nodes using consensus methods like Proof of Work, Proof of Stake, or Byzantine Fault Tolerance.
3. Record Updating
Once verified, the transaction is safely added to the ledger, ensuring accurate, permanent, and tamper-proof records.
4. Replication Across Nodes
The updated ledger automatically syncs across all network nodes, keeping data consistent, transparent, and equally accessible to everyone.
Types of Distributed Ledger Technology
Distributed Ledger Technology is available in several formats based on who can participate and how the network is run.
1. Blockchain
The most common DLT records transactions in linked blocks, keeps them permanent, and supports cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
2. Directed Acyclic Graphs
A graph-based ledger links transactions in a web instead of blocks, allowing fast, scalable microtransactions like IOTA.
3. Hashgraph
Employs a gossip protocol for transaction sharing, offering faster consensus, enhanced efficiency, and greater scalability compared to traditional blockchain systems.
4. Holochain
An agent-centric DLT where each user maintains their own ledger chain, validated through shared rules, ensuring energy efficiency and scalability.
5. Tempo
Uses logical clocks to order events, avoiding heavy consensus protocols, and is designed for efficient scalability in large-scale, enterprise-grade applications.
Features of Distributed Ledger Technology
Here are the key features that make Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) a powerful, reliable, and widely adopted solution across various industries.
1. Decentralization
Distributed ledger technology removes centralized intermediaries, giving all participants equal control, ensuring fairness, transparency, and preventing dominance by a single authority.
2. Transparency
Every participant can access the same updated ledger version, fostering trust, accountability, and eliminating information asymmetry across the entire network.
3. Immutability
Once the ledger records data, the system does not alter or delete it, ensuring permanence and reducing fraud.
4. Consensus Mechanisms
Consensus techniques, such as Proof of Work or Proof of Stake, guarantee correctness and guard against manipulation by ensuring nodes agree on the legitimacy of transactions.
5. Security
Strong cryptography protects transactions, keeps data safe, and prevents hacks or tampering on the network.
6. Efficiency
By eliminating intermediaries, reducing processing delays, and lowering costs, distributed ledger technology streamlines operations and ensures faster, more reliable transaction settlements.
Advantages of Distributed Ledger Technology
Here are the key advantages that make Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) a transformative force for businesses and individuals worldwide.
1. Improved Security
Cryptographic methods secure data across the network, preventing tampering, fraud, and unauthorized access, ensuring strong protection against potential cyberattacks.
2. Transparency and Trust
Open, shared records allow every participant to verify transactions, promoting accountability, reducing disputes, and fostering greater trust among network users.
3. Cost Reduction
By removing intermediaries and automating verification, distributed ledger technology significantly lowers fees, transaction costs, and administrative overhead for businesses worldwide.
4. Faster Transactions
Unlike traditional banking systems with delays, DLT enables near-instant settlements, improving efficiency and customer experience across global financial or non-financial transactions.
5. Auditability
DLT keeps a secure and unchangeable record of all transactions, making it easier to check accounts, follow rules, solve disputes, and ensure everything is accurate and trustworthy.
Disadvantages of Distributed Ledger Technology
Despite its advantages, DLT also faces certain disadvantages:
1. Energy Consumption
Consensus methods like Proof of Work demand significant computational resources, consuming excessive energy and raising environmental concerns regarding sustainability and scalability.
2. Regulatory Uncertainty
The absence of universal legal frameworks and standards creates compliance challenges, hindering adoption across industries and raising jurisdictional implementation difficulties globally.
3. Interoperability
Different DLT networks often lack seamless communication, making integration difficult and limiting collaboration between diverse platforms, industries, and global ecosystems.
4. Complexity
DLT development and deployment require advanced technical expertise, creating barriers for organizations without skilled professionals, increasing costs, and implementation difficulty.
5. Privacy Concerns
DLT’s transparency may conflict with confidentiality needs, particularly in sensitive sectors like healthcare, finance, or defense, where strict privacy is essential.
Applications of Distributed Ledger Technology
DLT is reshaping industries around the world. Some key use cases include:
1. Finance and Banking
DLT makes international payments easier, automates contracts, and prevents fraud with secure and transparent transaction records.
2. Supply Chain Management
DLT improves product tracking and authenticity, making supply chains transparent and reducing fraud in food, luxury, and medicine.
3. Healthcare
Distributed ledgers safely store patient records, improve data sharing, support interoperability, and protect privacy with cryptography and controlled access.
4. Government and Public Services
Governments use DLT for clear voting, accountable spending, and secure digital IDs, boosting efficiency, trust, and citizen engagement.
5. Real Estate
DLT makes property records secure, reduces paperwork, speeds up transactions, and removes costly middlemen.
6. Energy Sector
DLT allows direct energy trading between peers and tracks renewable energy, making markets transparent, efficient, and sustainable.
7. Entertainment and Media
DLT safeguards intellectual property rights, ensures transparent royalty payments for creators, and promotes fairer, faster revenue distribution within the media industry.
Real-World Examples
Here are some notable real-world examples of Distributed Ledger Technology that showcase its diverse applications and impact across industries.
1. Ethereum
A blockchain platform that lets developers build decentralized apps and smart contracts, creating automated and secure digital systems
2. IOTA
An IoT ledger using DAGs that enables secure, scalable, and free microtransactions everywhere.
3. Hyperledger Fabric
A business-focused blockchain system that is private, secure, and flexible, letting companies build scalable solutions for different industries
4. Ripple
A blockchain network that helps banks and financial institutions send fast, cheap, and efficient international payments.
Final Thoughts
Distributed Ledger Technology is a game-changing innovation that redefines how transactions and data are recorded, verified, and shared. By offering decentralization, transparency, and security, DLT eliminates the need for middlemen, reduces costs, and builds trust among participants. Although challenges like scalability, regulation, and compatibility exist, improvements are making DLT more efficient and accessible. DLT will play a key role in building a connected, transparent, and secure society as industries go digital.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is Distributed Ledger Technology the same as blockchain?
Answer: Not exactly. Blockchain is one type of DLT. Other types include DAGs, Hashgraph, and Holochain.
Q2. Is Distributed Ledger Technology secure?
Answer: Yes, Distributed Ledger Technology utilizes cryptography and consensus mechanisms to provide high security, although vulnerabilities depend on the implementation.
Q3. Can Distributed Ledger Technology replace banks?
Answer: DLT reduces reliance on traditional intermediaries but is more likely to complement than completely replace banks.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Distributed Ledger Technology” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

