What is Haptic Feedback?
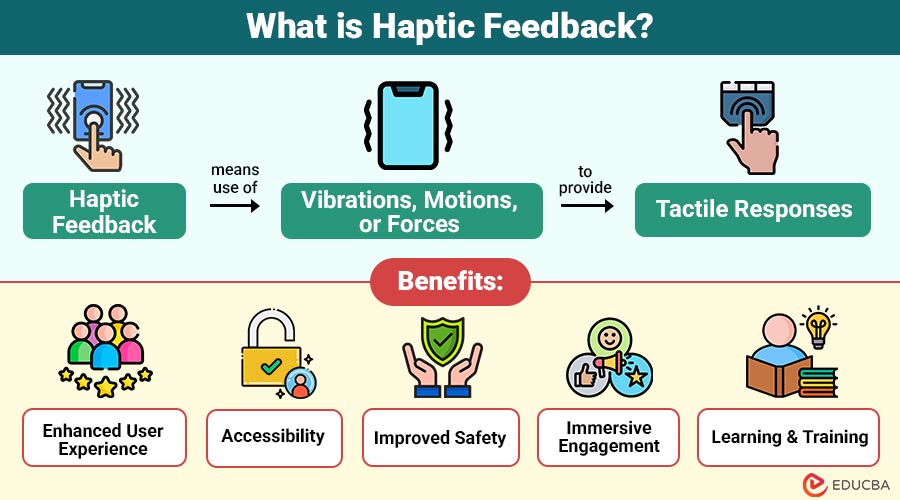
Haptic feedback means the use of vibrations, motions, or forces to provide tactile responses. The Greek word haptikos, which means “able to touch or perceive,” is where the word “haptic” originates.” Essentially, haptic feedback mimics the sense of touch in digital interfaces.
For example:
- When you tap a smartphone screen, you feel a small vibration.
- When a car’s steering wheel vibrates, it alerts the driver to a potential lane departure.
- When a gaming controller rumbles to simulate the recoil of a weapon.
Through more immersive, sensitive, and intuitive interactions, this technology helps close the gap between humans and machines.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Haptic feedback transforms digital interaction by letting users feel responses instead of only seeing.
- From smartphones to simulators, haptics boosts realism, safety, and accessibility across various industries.
- Barriers such as battery drain, high costs, and inconsistent standards hinder the widespread adoption of haptic technology.
- Future advancements promise realistic mid-air interactions, healthcare innovation, and lifelike VR/AR experiences.
How does Haptic Feedback Work?
Haptic systems rely on specialized components to generate tactile sensations. The two most common methods include:
1. Eccentric Rotating Mass Motors
2. Linear Resonant Actuators
Linear Resonant Actuators employ a magnetic mass and spring mechanism to produce precise vibrations. Compared to ERMs, they deliver faster responses, smoother feedback, and higher accuracy, enhancing tactile experiences in modern devices.
3. Advanced Haptic Systems
Advanced haptic technology uses tiny vibrations, sound waves, or electric forces to create realistic touch feelings in VR gloves, car dashboards, and medical training tools.
Types of Haptic Feedback
Haptic technology can be classified into different types based on how sensations are created.
1. Vibrotactile Feedback
Vibrotactile feedback relies on vibrations to mimic touch sensations. It is the most common form of haptics, widely integrated into smartphones, gaming controllers, and wearable devices to enhance user interaction.
2. Force Feedback
Force feedback provides physical resistance or force, simulating real-world interactions. It is commonly utilized in joysticks, racing wheels, and surgical simulators to deliver realistic tactile sensations during complex operations.
3. Surface Haptics
Surface haptics change the feel of a touchscreen to create textures or patterns that you can feel. Car makers and smartphone companies are testing this technology to make screens more interactive.
4. Ultrasonic & Mid-Air Haptics
Ultrasonic and mid-air haptics employ focused ultrasound waves to create touch sensations without physical contact. They are emerging in VR and AR systems, enabling immersive, futuristic interactions without handheld devices.
Applications of Haptic Feedback
Haptic feedback is transforming industries by enhancing applications across major areas.
1. Consumer Electronics
- Smartphones: Tactile responses when typing, unlocking, or receiving notifications.
- Wearables: Vibrations on smartwatches for health alerts or fitness reminders.
- Tablets & Laptops: Precision touchpads that simulate button clicks.
2. Gaming & Entertainment
- Game Controllers: Immersive vibrations that simulate explosions, gunfire, or driving sensations.
- VR/AR Systems: Gloves and suits that provide touch sensations for hyper-realistic experiences.
- Cinemas & Theme Parks: Motion chairs with haptic elements for 4D entertainment.
3. Automotive Industry
- Safety Systems: Steering wheel vibrations to warn of lane departure.
- Infotainment Systems: Touchscreen haptics for button feedback without visual distraction.
- Driver Assistance: Tactile alerts for parking assistance and collision warnings.
4. Healthcare & Medical Training
- Surgical Simulators: Force feedback for realistic training of medical professionals.
- Rehabilitation Devices: Haptic therapy tools for motor skill recovery.
- Patient Care: Smart prosthetics that restore a sense of touch.
5. Education & Training
- Virtual Labs: Hands-on learning in physics, biology, or engineering through touch-enabled simulations.
- Flight & Driving Simulators: Haptic controls for pilot and driver training.
- Remote Learning Tools: Remote Learning Tools: Haptics enable tactile virtual lessons, boosting STEM engagement.
Benefits of Haptic Feedback
Here are the key benefits that haptic feedback brings across industries and everyday interactions:
1. Enhanced User Experience
Haptic feedback provides users with a natural, intuitive, and engaging way to interact with devices by simulating touch sensations, making interactions smoother, more realistic, and emotionally satisfying across digital environments.
2. Accessibility
By offering tactile cues through vibrations and force responses, haptic feedback supports individuals with visual or hearing impairments, enabling them to receive critical information without relying solely on sight or sound.
3. Improved Safety
In cars and factories, haptic alerts (like vibrations) help people notice warnings without looking or listening. This reduces distractions, helps them react faster, and prevents accidents.
4. Immersive Engagement
In gaming, VR, and AR, haptic technology makes touch feel real—like textures, resistance, and impacts—making experiences more immersive and enjoyable.
5. Learning & Training
Challenges of Haptic Feedback
Despite its advantages, haptic feedback faces several challenges that affect its adoption, performance, and user experience:
1. Technical Limitations
Small and compact devices often lack sufficient space to accommodate sophisticated haptic components, limiting performance and making it challenging to deliver precise, high-quality tactile sensations effectively.
2. Power Consumption
High-performance haptic systems require significant energy, often draining battery life quickly in mobile and wearable devices, which impacts usability, efficiency, and user satisfaction in daily usage.
3. Cost of Implementation
Creating and using advanced haptic technologies, like mid-air or complex feedback, is expensive, so they are mostly found in high-end devices and not widely accessible.
4. User Perception
Too much or badly designed vibration can annoy users instead of helping, reducing their satisfaction with haptic devices.
5. Standardization
Absence of universal industry standards makes cross-platform haptic development inconsistent and complex, creating challenges in ensuring compatibility, seamless integration, and uniform tactile experiences across various devices and ecosystems.
Future of Haptic Feedback
The future of haptic technology looks highly promising, with innovations pushing the boundaries of human-computer interaction. Some emerging trends include:
1. Haptic VR/AR Integration
Advanced gloves and full-body suits let users realistically feel virtual objects, making VR/AR experiences more immersive, interactive, and lifelike.
2. Healthcare Innovation
Smart prosthetics and medical tools with touch technology can bring back or improve the sense of touch. This will help patients recover better, make surgeries more accurate, and improve overall healthcare quality.
3. Mid-Air Haptics
Touchless haptic interfaces let users feel sensations in the air without touching anything, making shared or high-contact spaces cleaner, easier to use, and more convenient.
4. Automotive UX
Touch dashboards with haptic feedback can replace regular buttons, making controls easier, safer, and less distracting for drivers.
5. Retail Revolution
Virtual shopping powered by haptics will let customers feel fabrics, surfaces, or product textures digitally, creating immersive, realistic experiences that boost online retail confidence.
Real World Examples
Here are some practical implementations that showcase how haptic feedback is transforming devices and industries worldwide:
1. Apple iPhone Taptic Engine
Delivers precise, refined vibrations for notifications, typing, and gestures, creating a smooth, responsive, and intuitive user interaction experience.
2. Sony PlayStation DualSense Controller
It provides adaptive triggers and vibration feedback that feel real, making games more immersive and enjoyable.
3. Meta Quest VR
Uses advanced haptic gloves that simulate realistic touch sensations, allowing users to feel textures and objects within virtual reality environments.
4. Smart Prosthetics
Equipped with sensory haptics to mimic real touch, restoring tactile sensations and improving usability, comfort, and quality of life for amputees.
Final Thoughts
Haptic feedback has become an essential part of modern technology, transforming interactions across smartphones, gaming, healthcare, and automotive industries. By replicating touch, it enhances engagement, accessibility, and safety. Despite challenges like cost, power usage, and lack of standardization, ongoing innovations promise more immersive, intuitive experiences—allowing people to not only see and hear but genuinely feel technology’s impact.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the main purpose of haptic feedback?
Answer: The main purpose of haptic feedback is to enhance user interaction by providing tactile sensations, making digital experiences more natural and intuitive.
Q2. Is haptic feedback the same as vibration?
Answer: Not exactly. While vibration is a basic form of haptic feedback, advanced haptics include force feedback, surface textures, and even mid-air touch sensations.
Q3. Does haptic feedback drain battery life?
Answer: Yes, continuous or intense haptic use can consume more power, especially in small devices like smartphones and wearables.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Haptic Feedback” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

