Definition of Marketing
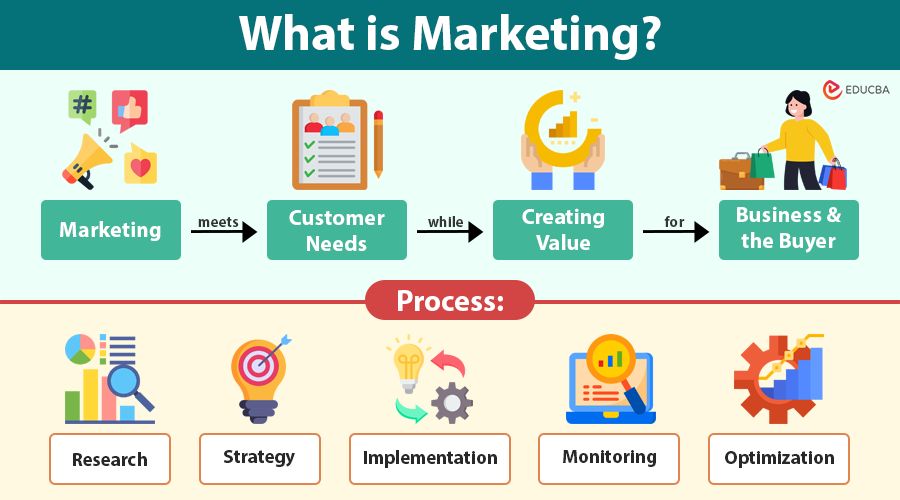
Marketing is the process of identifying customer needs and promoting, delivering, and sustaining products or services that fulfill those needs while creating value for both the business and the customer.
When a bakery discovers that customers want healthier snacks, it uses customer-focused marketing to create a range of low-sugar muffins. It promotes them through social media and local events. This approach meets customer needs while driving business growth.
Marketing principles apply across industries, including highly specialized fields where understanding the audience is critical. This is especially true for biotech marketing companies, where clear communication, compliance awareness, and value-driven messaging shape how complex products reach the right stakeholders.
Table of Contents
- Definition
- Importance
- Core Principles
- Types
- Process
- Consumer Behavior
- Branding & Storytelling
- Ethics & Responsibility
Key Takeaways
- Marketing is more than just selling; it is about understanding customer needs and creating long-term value.
- The 4 Ps—Product, Price, Place, and Promotion form the foundation of every marketing strategy.
- Market segmentation allows businesses to target the right audience with tailored messaging.
- Traditional and digital marketing together enhance reach and effectiveness.
- Ethical marketing builds trust and strengthens brand reputation.
- Marketing strategies must evolve in response to changing consumer behavior and trends.
Why Marketing Matters?
Marketing is a core driver of business growth and sustainability. Here are six essential reasons why marketing matters for any organization:
1. Attracts Potential Customers
Marketing helps businesses reach and engage people who may not yet be aware of their products or services. By utilizing channels such as social media, search engines, advertising, and content marketing, companies can generate awareness and drive interest among new audiences. Without a strategic marketing approach, even the best offerings may remain hidden from the right buyers.
2. Builds Brand Awareness
Consistent marketing efforts create visibility and recognition. Through well-crafted messaging, design, and storytelling across various platforms, businesses shape how people perceive their brand. A strong presence fosters familiarity, which in turn builds trust, laying the foundation for lasting customer relationships and long-term loyalty.
3. Communicates Product Benefits
Marketing explains how a product or service solves a problem or fulfills a need. It clarifies what makes the offering valuable, different, or superior to competitors. Whether through a website, brochure, video, or sales pitch, marketing ensures that customers understand the features, benefits, and reasons to choose a brand.
4. Creates Customer Loyalty
Marketing keeps customers engaged after the sale. By delivering personalized experiences, maintaining ongoing communication, offering loyalty programs, and providing useful content, businesses can nurture long-term relationships. Loyal customers not only return for repeat purchases but also become advocates who refer others, thereby increasing brand credibility.
5. Supports Sales Efforts
Marketing lays the groundwork for sales success. It attracts qualified leads, nurtures prospects, and educates customers before they even speak to a sales representative. Through tools like email campaigns, landing pages, product demos, and social proof, marketing helps shorten the sales cycle and increase conversion rates.
6. Adapts to Market Trends
Marketing teams monitor consumer behavior, industry shifts, and emerging technologies. They use this data to adjust strategies, refresh campaigns, and introduce new offerings. Staying responsive to change enables businesses to remain relevant, competitive, and aligned with customer expectations in a rapidly evolving market.
The Core Principles of Marketing
Understanding marketing begins with mastering its core principles. These foundational elements guide how businesses identify opportunities, engage customers, and deliver value.
1. The 4 Ps of Marketing
The marketing mix, often called the 4 Ps, represents the key components marketers must manage to bring a product to market successfully:
- Product – Define what you’re offering and ensure it solves a real customer problem. Whether it’s a physical item, service, or experience, the product must meet a need and deliver clear value.
- Price – Set a price that reflects the perceived value while staying competitive. Consider factors such as cost, customer willingness to pay, pricing models (subscription vs. one-time), and profit margins.
- Place – Decide where and how customers will access your product. Choose between online platforms, retail stores, wholesalers, or a combination of these, based on where your target audience shops.
- Promotion – Communicate the product’s value through strategic messaging and campaigns. Utilize various channels, including advertising, social media, content marketing, public relations, and influencer partnerships, to effectively reach your target audience.
2. Market Segmentation
Marketers rarely market to “everyone.” Instead, they divide the broad market into distinct segments to better understand and serve customer groups.
Common segmentation bases include:
- Demographics – Age, gender, income, education, occupation
- Psychographics – Lifestyle, values, personality, interests
- Geographic – Country, city, region, climate, urban vs. rural
- Behavioral – Buying patterns, brand loyalty, product usage, decision-making style
By identifying segments, marketers tailor products and messaging to suit the unique preferences and needs of each group.
3. Targeting and Positioning
Once a business segments the market, it chooses which segments to focus on, a process known as targeting. Not all segments offer the same value, so marketers analyze size, accessibility, and profitability before selecting a target audience.
After targeting, marketers move to positioning, which involves shaping how the target audience perceives the brand. A strong positioning strategy highlights the brand’s strengths, competitive advantages, and relevance to customer needs. This ensures the brand occupies a distinct, meaningful place in the customer’s mind.
Types of Marketing
Marketing has undergone significant evolution over the years. Today, businesses choose from a variety of types depending on their goals, budget, and target audience. The two main categories are Traditional and Digital Marketing.
1. Traditional Marketing
Traditional marketing includes offline promotional methods that have been used for decades. These tactics are often most effective for reaching local or broader audiences through physical and broadcast media.
Key traditional marketing channels include:
- TV and Radio Advertising: Brands create commercials to air during popular shows or specific time slots, reaching a mass audience.
- Billboards and Outdoor Ads: Eye-catching visuals placed in high-traffic areas help boost visibility and brand recall.
- Flyers and Brochures: Printed materials offer detailed information and are distributed at events, stores, or through direct mail.
- Newspaper and Magazine Ads: These print placements help reach niche readers or local communities through trusted publications.
Traditional marketing helps establish trust and increase brand visibility, particularly in regions with low internet penetration or among audiences who favor offline communication channels.
2. Digital Marketing
Digital marketing uses online platforms and technologies to connect with audiences in real-time. It offers powerful tools for precision targeting, automation, and performance tracking.
Common digital marketing strategies include:
- Social Media Marketing: Brands engage users on platforms like Instagram, Facebook, LinkedIn, and X (formerly Twitter) through organic content and paid ads.
- Email Campaigns: Personalized emails nurture leads, promote offers, and keep customers informed.
- Content Marketing: Marketers create valuable content (blogs, videos, infographics) to educate, inspire, and attract their target audience.
- SEO (Search Engine Optimization): Businesses optimize their website content to rank higher on search engines, driving organic traffic.
- Paid Advertising (PPC): Pay-per-click campaigns on platforms like Google Ads or Meta Ads drive immediate visibility and traffic.
- Influencer Marketing: Brands partner with online influencers who promote their products to loyal followers, often in niche communities.
Digital marketing allows businesses to track performance, adjust strategies in real-time, and target specific customer segments based on behavior, interests, and demographics.
The Marketing Process
The marketing process provides a strategic framework for attracting, engaging, and retaining customers. It ensures that every marketing activity aligns with business goals and delivers measurable results. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how the process works:
1. Research
Marketers begin by gathering data to understand the market landscape. They analyze:
- Customer behavior – What motivates customers to buy? What are their needs and pain points?
- Preferences and trends – What channels do they use? What content do they consume?
- Competitors – Who else is offering similar products or services? What are their strengths and weaknesses?
This research lays the foundation for informed decision-making and effective strategy development.
2. Strategy
After collecting insights, marketers develop a clear strategy that defines:
- Marketing goals – Increase brand awareness? Generate leads? Drive sales?
- Target audience – Who is the ideal customer?
- Key messages and value propositions – What makes the offering unique or compelling?
They also select the optimal mix of marketing channels (e.g., digital, traditional, or a combination of both) and allocate budgets accordingly.
3. Implementation
At this stage, marketers execute the strategy by launching campaigns across selected platforms. Activities may include:
- Publishing content
- Running advertisements
- Sending emails
- Hosting events
- Engaging on social media
Consistency, creativity, and timing play a major role in the success of the campaign rollout.
4. Monitoring
Marketers continuously track campaign performance using key performance indicators (KPIs), such as:
- ROI (Return on Investment)
- Conversion rates
- Click-through rates (CTR)
- Website traffic
- Customer engagement
Monitoring ensures that teams can quickly identify what is working and what is not.
5. Optimization
Based on performance data, marketers need to improve results. They may:
- Adjust targeting parameters
- Refine messaging or visuals
- Shift budgets to higher-performing channels
- Test different content formats (A/B testing)
Optimization is a continuous improvement cycle that helps maximize the impact of marketing efforts.
Consumer Behavior in Marketing
Understanding consumer behavior is essential for creating effective marketing strategies. It helps marketers uncover what drives customer decisions and how to influence them in meaningful ways.
1. Motivation Behind Buying Decisions
Marketers study what triggers a consumer to make a purchase. These motivations can be:
- Functional – Solving a specific problem or fulfilling a need
- Emotional – Seeking happiness, comfort, or status
- Social – Wanting to belong, impress others, or follow trends
By identifying these drivers, marketers can craft messages that directly appeal to the reasons why people make purchases.
2. Emotional Influences on Purchasing
Emotions play a powerful role in consumer choices. People often make decisions based on how they feel rather than on pure logic. Marketers use storytelling, design, color psychology, and branding to connect with customers on an emotional level and build trust.
3. Cultural and Social Factors
Culture, family background, social norms, and peer influence heavily shape consumer behavior. For example:
- A consumer’s cultural values may determine their spending habits
- Family roles influence buying decisions for household products
- Social media trends and influencers guide preferences among younger audiences
Marketers must adapt their strategies to reflect these social contexts and cultural sensitivities.
4. The Buying Decision Process
Consumers typically go through several stages before making a purchase:
- Problem recognition – Realizing a need
- Information search – Looking for options
- Evaluation of alternatives – Comparing choices
- Purchase decision – Making the final choice
- Post-purchase behavior – Satisfaction or regret
By mapping this process, marketers can deliver the right message at the right stage of the customer journey.
5. Benefits of Understanding Consumer Behavior
When marketers understand how and why people buy, they can:
- Create highly targeted campaigns
- Improve product positioning
- Personalize communication
- Enhance customer experiences
- Increase conversion rates and loyalty
This knowledge makes marketing efforts more relevant, persuasive, and impactful.
Branding and Storytelling in Marketing
In a competitive market, businesses need more than just a good product; they need a strong brand and a compelling story. Branding and storytelling together shape how people perceive, connect with, and remember a business.
1. What Is a Brand?
Your brand is how people see and experience your business. It includes your logo, colors, tone, and values, but it is also the feeling customers associate with your name.
2. Why Branding Matters?
A strong brand:
- Builds trust with consistent messaging
- Creates emotional bonds with customers
- Boosts recognition through a distinct visual and verbal identity
A clear brand helps you stay top-of-mind and win customer loyalty.
3. What Is Storytelling?
Storytelling uses real or relatable narratives to communicate your brand’s message. Instead of promoting features, marketers share stories that:
- Highlight customer experiences
- Show the brand’s purpose or journey
- Trigger emotions and build connections
Stories turn products into experiences.
4. How Branding and Storytelling Work Together?
Branding shows “who you are”, while storytelling shows “why it matters”. When used together:
- Messages feel more authentic
- Customers connect on a deeper level
- Brands become more memorable and relatable
Together, they turn one-time buyers into loyal advocates.
Marketing Ethics and Responsibility
Modern consumers expect more than just quality products—they expect companies to act with integrity. Ethical marketing is not just a choice; it is a responsibility that shapes brand reputation and long-term success.
1. Be Honest in Messaging
Marketers must present products truthfully and avoid misleading claims. Accurate descriptions, transparent pricing, and honest advertising help build trust and reduce the risk of reputational damage.
2. Respect Consumer Privacy
Ethical marketers safeguard personal data and use it responsibly. They adhere to data protection laws, obtain user consent, and are transparent about how information is collected and used.
3. Promote Fair Competition
Responsible marketing avoids tactics that attack competitors unfairly or manipulate consumer behavior. Fair competition encourages innovation and gives consumers better choices.
4. Embrace Social and Environmental Responsibility
Ethical marketing considers its broader impact. Brands that support sustainability, diversity, and social causes demonstrate a commitment that extends beyond profit. This approach appeals to conscious consumers and adds long-term value.
5. Act with Integrity and Transparency
Customers value brands that practice what they preach. Authenticity in actions, not just words, builds stronger emotional connections and customer loyalty. Integrity should be at the core of every campaign and business decision.
Final Thoughts
Marketing is more than just promoting products; it is about understanding customer needs, building meaningful relationships, and delivering consistent value. It blends creativity with strategy to attract, engage, and retain audiences while supporting business growth. Whether through traditional methods or digital innovation, effective marketing enables brands to stand out and adapt in a rapidly changing world. When done ethically and authentically, it is not only drives profit but also fosters trust, loyalty, and a lasting impact.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
Q1. What is the difference between marketing and advertising?
Answer: Marketing is a comprehensive strategy that encompasses research, product development, promotion, and customer relationship management. Advertising is a subset of marketing focused solely on promoting a product or service through paid channels.
Q2. What is a marketing funnel?
Answer: A marketing funnel represents the journey a customer takes from first learning about a product to making a purchase, typically broken into stages such as awareness, consideration, and decision.
Q3. What role does AI play in modern marketing?
Answer: AI supports marketers through data analysis, personalized content delivery, predictive analytics, chatbots, and automated customer interactions, making campaigns more efficient and effective.
Q4. How does marketing evolve in a crisis or economic downturn?
Answer: In challenging times, marketing adapts by focusing more on customer retention, empathy-driven messaging, value-based offers, and digital channels that offer measurable ROI.
Q5. What is integrated marketing communication (IMC)?
Answer: IMC refers to unifying all promotional tools, including advertising, PR, digital marketing, and sales promotions, into a seamless and consistent strategy that delivers a coherent brand message.
Recommended Articles
We hope this comprehensive guide to marketing has helped you understand its principles, process, and importance. Check out these related articles for deeper insights into essential areas of marketing:
