Updated March 23, 2023
Introduction to Variable in PowerShell
The variable in PowerShell is a block of memory that can be used to store values. PowerShell variables are denoted using the “$” symbol. A variable name can be anything from numbers, alphabets or even underscores. PowerShell variables are not case sensitive. PowerShell variables are not just text-based, instead, they are objects like that of Microsoft.Net objects.
Creation of Variables with Syntax
The below example shows the creation of a variable
$test
$test is a variable and it can be assigned a value using the = or assignment operator
$test=” This is a variable”
To get the value of a variable, we just need to simply enter the variable
Example #1
The following example is used to show introduction to variable
Code:
Write-Host "Introduction to the variable"
$test="This is a variable"
Write-Host "The value of the variable is below"
$test
Output:
Introduction to variable
The value of the variable is below
This is a variable
Example #2
The following example is used to show arithmetic operations on a variable
Code:
Write-Host "Example of arithmetic operation"
$v1 = 11111
$v2 = 3333454
$v3 = $v1 + $v2
$v3
Output:
Example of arithmetic operation
3344565
Variable Types in PowerShell
In PowerShell, if the datatype of the variable is not specified, PowerShell automatically detects the variable type when the variable is initialized.
The following are the types of the array variable
1. Array: An array variable is the first type of variable. An array variable can be declared as follows
[int32[]]$inttest = 1,2,3,4
or
$test=1..99
2. Bool: A Boolean variable can be defined as follows.
[bool] $test = 1
Or
[bool] $test= $true
3. DateTime: A datetime variable can be declared as follows
$a = [DateTime] "07/06/2015 05:00 AM"
4. Guid: A guid value can be assigned to a variable as follows
$a=New-Guid
5. HashTable: The hashtable variable is storing a key-value pair. A hashtable can be defined as follows
$test = @{ key1= 1; key2= 2; key3= 3}
or
$test = @{}
6. PSObject: A PSobject variable is similar to the hashtable and uses a key-value pair structure. It can be defined as follows.
$test = [PSCustomObject]@{
Key1 = 'Value1'
Key2 = 'Value2'
}
Automatic Variables in PowerShell
These variables are created by PowerShell itself. They are used to maintain the state of the PowerShell. Users will not change the value of these variables and PowerShell changes them to maintain accuracy. The following are some of the automatic variables.
| Variable | Description |
| $HOME | Contains the path of the user’s home directory |
| $HOST | Represent the application for PowerShell |
| $NULL | Null Value |
| $PROFILE | Represents the full path of the current user profile |
| $STACKTRACE | Contains the stack trace of the recent error |
| $PSCOMMANDPATH | Contains the path of the running script |
| $PID | Contains the processor id of the current session |
| $ErrorActionPreference | Represents the action taken when an error message is delivered |
| $PSCulture | Represents the current culture of the Powershell session |
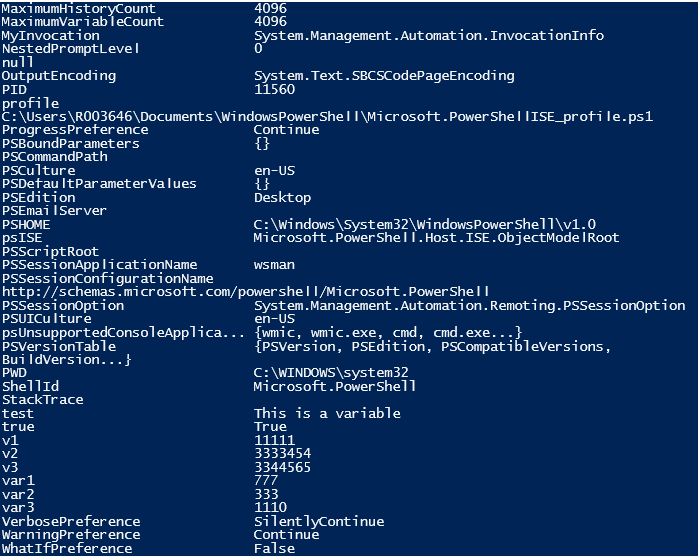
All the automatic variable is PowerShell can be found by running the below command.
Code:
Get-Variable
Output:
Different Types of Variable Scopes
The scope is nothing but the life shell of a variable. A variable is alive only within the scope specified.
- $Global: A variable is available throughout the script in the current session.
- $Script: The variable is accessible only inside the script and is discarded after the script is finished executing.
- $Private: Variable is valid only within a function.
- $local: Variable is valid only in the current scope of the session.
- Cmdlets associated with variables:
- Clear-Variable: Deletes the value of a variable
- Get-Variable: Gets the list of variables that are present in the current session.
- New-Variable: Used to create a new variable
- Remove-Variable: Deletes the variable
- Set-Variable: Used to change the value of a variable
Examples #1
To check if the last ran cmdlet was successful or not.
Code:
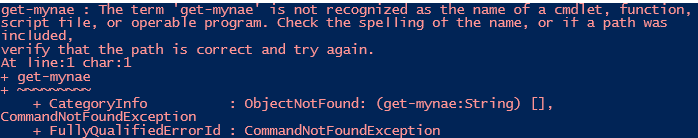
$? is used for the above-said purpose
The previous cmdlet ran
get-mynae
Corresponding output
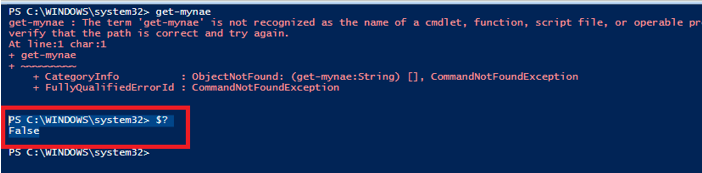
As it is evident from the above, the cmdlet execution was unsuccessful. After that, the cmdlet was executed.
Code
$?
Output:
False denotes the last cmdlet was unsuccessful and true denotes successful execution.
Example #2
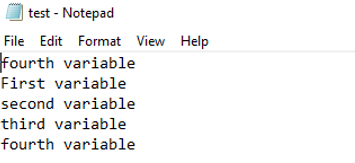
To Store the value of a variable to a word or csv file
Code:
Write-Host "variable example"
$test = "First variable"
$test1 = "second variable"
$test2 = "third variable"
$test3 = "fourth variable"
$test | Out-File C:\test.txt -Append
$test1 | Out-File C:\test.txt -Append
$test2 | Out-File C:\test.txt -Append
$test3 | Out-File C:\test.txt -Append
Output:
Example #3
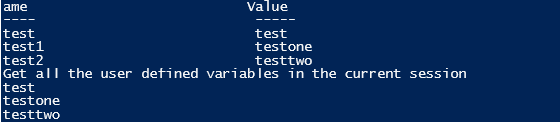
Set and Get a Variable
Code:
Set-Variable -Name "test" -Value "test"
Get-Variable -Name "test"
Set-Variable -Name "test1" -Value "testone"
Get-Variable -Name "test1"
Set-Variable -Name "test2" -Value "testtwo"
Get-Variable -Name "test2"
Write-Host "Get all the user defined variables in the current session"
Get-Variable test* -ValueOnly
Output:
Conclusion
Thus, the articles covered in detail about variables in PowerShell. It also explained the data types associated with a variable, variable scope and the types of variables that are available in PowerShell. To understand much deeper about variables it is advisable to create sample programs and have fun working around them.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Variable in PowerShell. Here we discuss how to create variables, different Types of Variable Scopes and automatic variables in PowerShell along with the examples. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more–