Updated June 12, 2023
VBA Value
The journey of VBA starts with knowing how the values get stored in the cells. Therefore, knowing VALUE function under VBA is of more importance. After studying about VBA VALUE property, you will be able to know how the values get stored under VBA. This article explains all the types of VALUE functions in VBA, like how the value gets stored in cells, how to set the value, how to insert the value, and many more.
How to Use Excel VBA Value Function?
We will learn how to use the VBA Value function with a few examples in Excel.
Example #1 – Set Cell Value using range.Value function
The setting of cell/s value using the range. Value function roughly consists of two essential steps:
- Setting the range where you want the value to be stored.
- Assigning a value to the range set.
Follow the below steps to set value in Excel VBA:
Step 1: Insert a new module under Visual Basic Editor (VBE).
Step 2: To store a macro, define a new sub-procedure under the inserted module.
Code:
Sub VBA_Value_Ex1() End Sub
Step 3: Define a new variable as a range that can be used to define a range where you want to store the value.
Code:
Sub VBA_Value_Ex1() Dim setValue_Var As Range End Sub

Step 4: With the help of the VBA RANGE function, assign the cells in the range to a variable defined using the assignment operator.
Code:
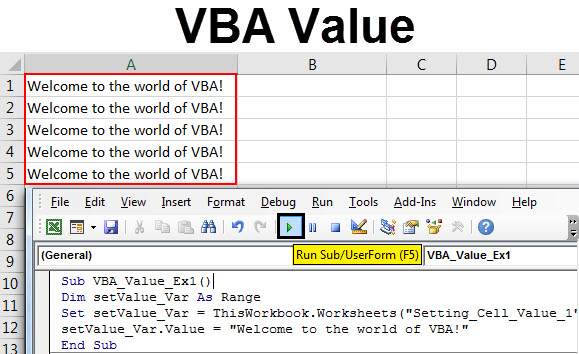
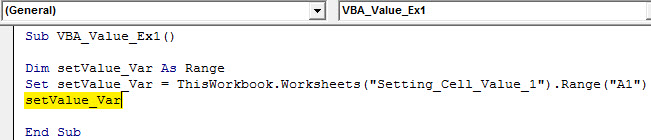
Sub VBA_Value_Ex1() Dim setValue_Var As Range Set setValue_Var = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Setting_Cell_Value_1").Range("A1") End Sub

Step 5: Now, use range.Value property to be able to assign value to the range defined. Type the variable name “setValue_Var” under which the range is defined.
Sub VBA_Value_Ex1() Dim setValue_Var As Range Set setValue_Var = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Setting_Cell_Value_1").Range("A1") setValue_Var End Sub
Step 6: Put a dot (.) after the variable to be able to select the IntelliSense list of functions available for this range variable defined.
Code:
Sub VBA_Value_Ex1() Dim setValue_Var As Range Set setValue_Var = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Setting_Cell_Value_1").Range("A1") setValue_Var. End Sub
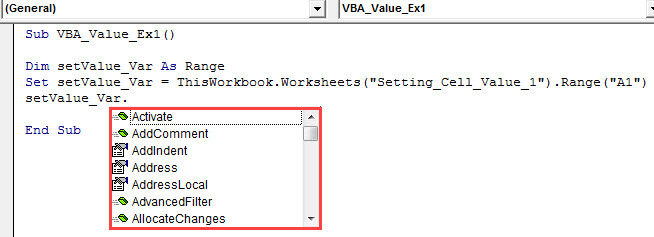
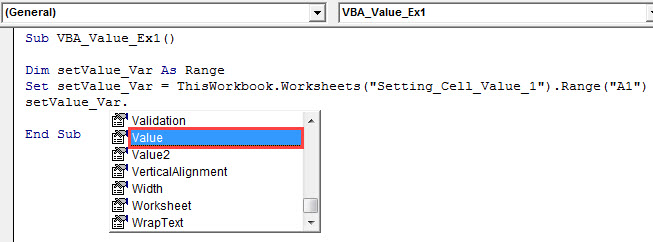
Step 7: Drag down the list and select the “Value” function to store the value under this range variable.
Code:
Sub VBA_Value_Ex1() Dim setValue_Var As Range Set setValue_Var = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Setting_Cell_Value_1").Range("A1") setValue_Var.Value End Sub
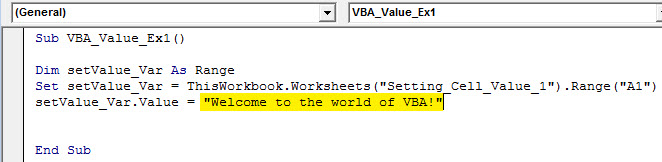
Step 8: Assign “Welcome to the world of VBA!” as a value to this range using the assignment operator.
Code:
Sub VBA_Value_Ex1() Dim setValue_Var As Range Set setValue_Var = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Setting_Cell_Value_1").Range("A1") setValue_Var.Value = "Welcome to the world of VBA!" End Sub
Step 9: We are done with the coding part. Run this code by hitting the F5 or Run button under VBE and see the output.
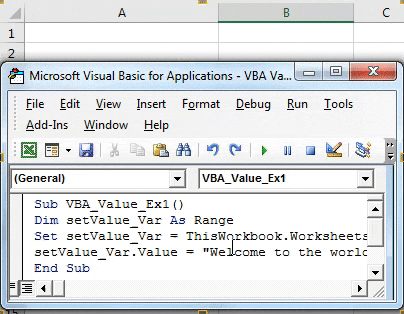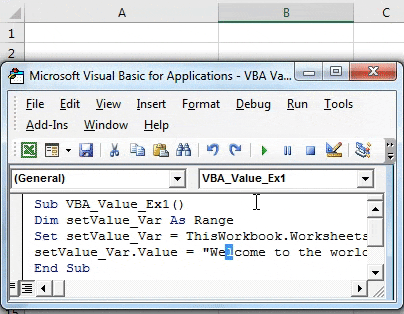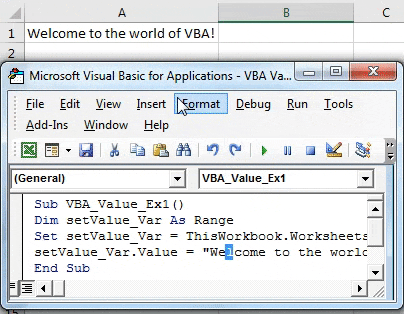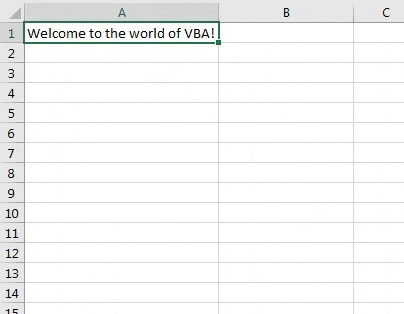
You also can assign the value to a range of cells. All you have to do is while setting the field for the output; you will give a one-dimensional array instead of a single-cell reference.
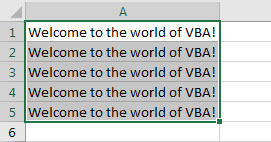
Step 10: Change the Range from “A1” to “A1: A5” in the same code above.
Code:
Sub VBA_Value_Ex1() Dim setValue_Var As Range Set setValue_Var = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Setting_Cell_Value_1").Range("A1:A5") setValue_Var.Value = "Welcome to the world of VBA!" End Sub
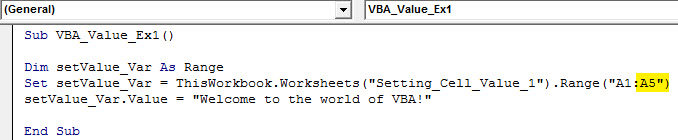
Step 11: Hit the F5 or Run button and see the output.
Example #2 – Set Cell Value using VBA Cells Property
This is another method for setting the cell value under VBA. Unlike the RANGE function, cells do not even need them. Value operator to be able to set value for the specific cell/s.
Follow the below steps to set the cell value in Excel VBA:
Step 1: Insert a new module under VBE where you can start writing your new piece of code.
Step 2: Add a new sub-procedure under the inserted module, where you can store your macro code.
Code:
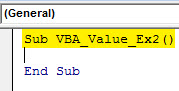
Sub VBA_Value_Ex2() End Sub
Step 3: Start typing thisWorkbook.Worksheet to access the sheet named “Setting_Cell_Value_2”.
Code:
Sub VBA_Value_Ex2 () ThisWorkbook.worksheets End Sub

Step 4: Mention the sheet name under parentheses in double-quotes.
Code:
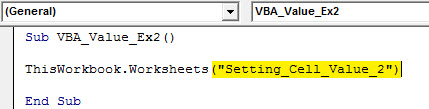
Sub VBA_Value_Ex2() ThisWorkbook.Worksheets ("Setting_Cell_Value_2") End Sub
Step 5: Use .Cells property to set the cell range from the given Excel sheet.
Code:
Sub VBA_Value_Ex2() ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Setting_Cell_Value_2").Cells(1, 1) End Sub
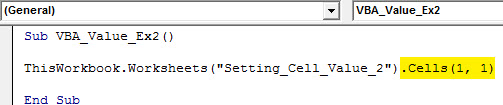
The first argument of the Cells property represents the rows, and the second argument represents the column. Therefore, Cells(1, 1) means cell associated with the first row and first column of the sheet “Setting_Cell_Value_2”.
Step 6: Now, with the help of the assignment operator, assign a value to this cell set.
Code:
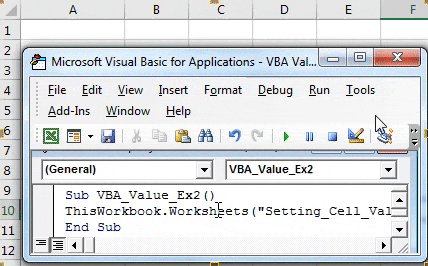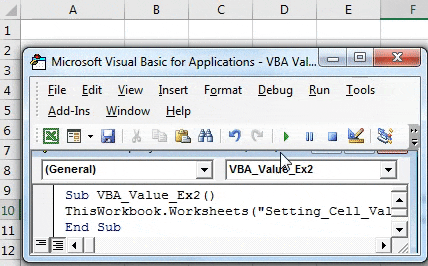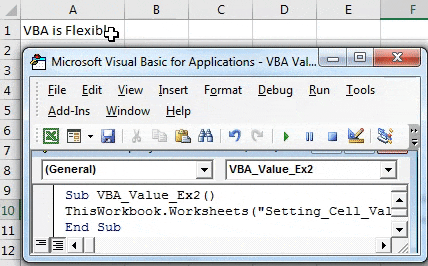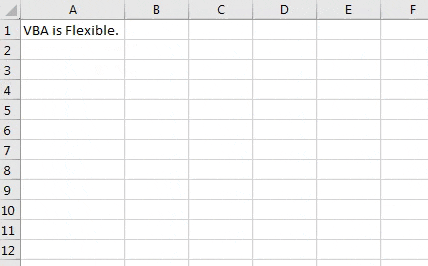
Sub VBA_Value_Ex2() ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Setting_Cell_Value_2").Cells(1, 1) = "VBA is Flexible." End Sub
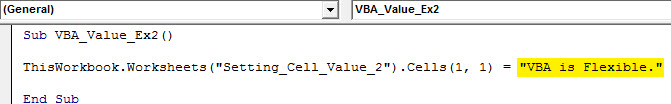
Have a look at that we don’t need .Value function, which we need to use while setting the value using the Range function. Cells Method does not have such IntelliSense options.
Step 7: Hit F5 or the Run button to run this code and see the output. You will see an output as shown in the screenshot below.
Example #3 – Get Cell Value in VBA
Until now, in two examples, we have seen how to set value for a cell or range of cells. Suppose a case is precisely reverse; we have to get the value assigned to a particular cell of an Excel sheet. How can we get that? Let’s go through a step-by-step guide.
Suppose I have assigned a value as shown in the screenshot below under the first cell of column A in the sheet “Getting_Cell_Value.”

Follow the below steps to get the cell value in Excel VBA:
Step 1: Insert a new module under VBE.
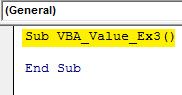
Step 2: Add a sub-procedure to store a macro as a code.
Code:
Sub VBA_Value_Ex3() End Sub
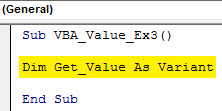
Step 3: Define a new variable called Get_Value as a Variant using the VBA Dim function.
Code:
Sub VBA_Value_Ex3() Dim Get_Value As Variant End Sub
Now, you have to assign the value present in cell A1 to the variable defined above.
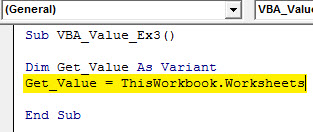
Step 4: Type “Get_Value = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets”. This will allow the VBA compiler to access the Excel sheet where your value is stored.
Code:
Sub VBA_Value_Ex3() Dim Get_Value As Variant Get_Value = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets End Sub
Step 5: Mention the worksheet name under parentheses with quotations in which the value is stored.
Code:
Sub VBA_Value_Ex3() Dim Get_Value As Variant Get_Value = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Getting_Cell_Value") End Sub

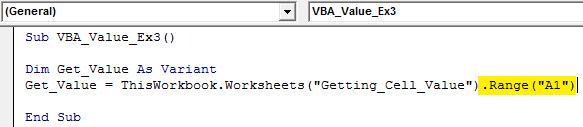
Step 6: Now, use dot (.) Range method to provide the exact cell where value is stored under sheet named “Getting_Cell_Value.”
Code:
Sub VBA_Value_Ex3() Dim Get_Value As Variant Get_Value = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Getting_Cell_Value").Range("A1") End Sub
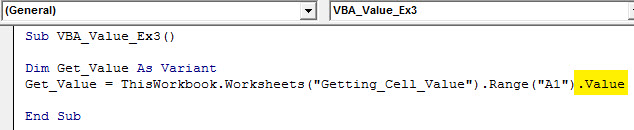
Step 7: Finally, use dot (.) Value method so the compiler can access the actual value under cell A1.
Code:
Sub VBA_Value_Ex3() Dim Get_Value As Variant Get_Value = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Getting_Cell_Value").Range("A1").Value End Sub
Step 8: As we discussed, we need to get the value stored in cell A1. For that, use MsgBox to show the value of the variable Get_Value (Which already has accessed the value typed in cell A1).
Code:
Sub VBA_Value_Ex3() Dim Get_Value As Variant Get_Value = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Getting_Cell_Value").Range("A1").Value MsgBox Get_Value End Sub
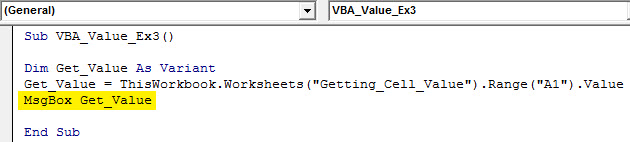
Step 9: Hit the F5 or Run button to run this code; you will get the value present in cell A1 under the message box.
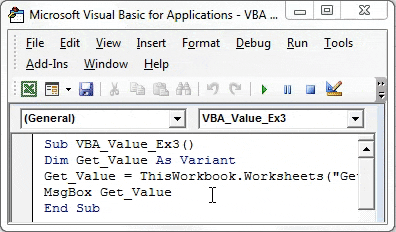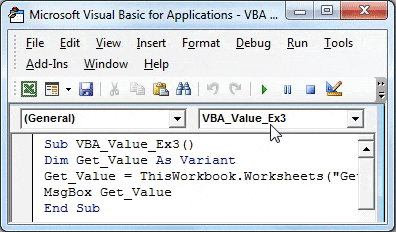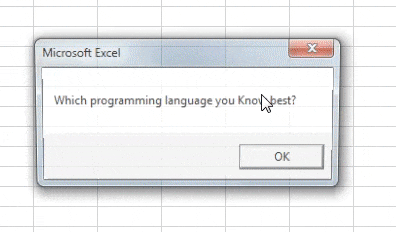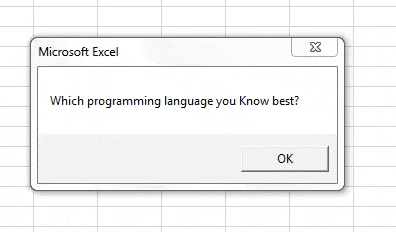
We mentioned This value under cell A1 of sheet “Getting_Cell_Value.” Right?
Example #4 – Can we get Multiple Cell Values at a Time?
Let’s assume I have values stored in three different cells, A1, A2, and A3, as shown in the screenshot below:

Don’t get confused if you see the text spread along columns A to E. It is just a visible layout (because I have merged the cells ), and the actual value is only stored under cells A1, A2, and A3.
Follow the below steps to use Excel VBA Value:
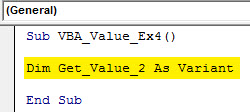
Step 1: Define a variable as a variant under a new sub-procedure in your VBA module.
Code: Sub VBA_Value_Ex4() Dim Get_Value_2 As Variant End Sub
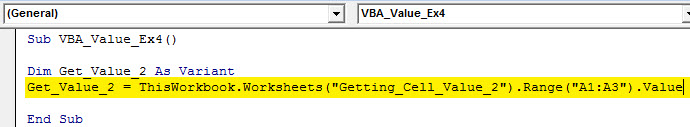
Step 2: Use Range.Value method to retrieve the value of cells A1: A3 and assign to a new variable defined in the previous step.
Code:
Sub VBA_Value_Ex4() Dim Get_Value_2 As Variant Get_Value_2 = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Getting_Cell_Value_2").Range("A1:A3").Value End Sub
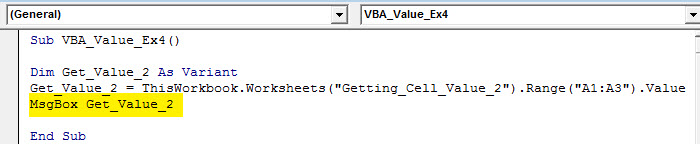
Step 3: Finally, use the MsgBox function to display the values stored in cells A1: A3.
Code:
Sub VBA_Value_Ex4() Dim Get_Value_2 As Variant Get_Value_2 = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Getting_Cell_Value_2").Range("A1:A3").Value MsgBox Get_Value_2 End Sub
Step 4: Hit the F5 or Run button and see the output for this code.
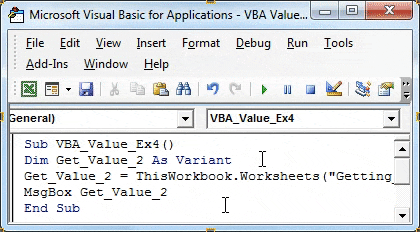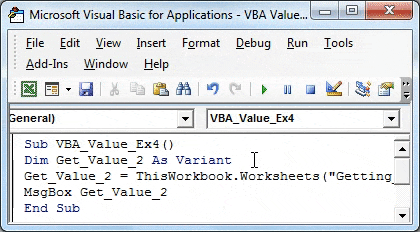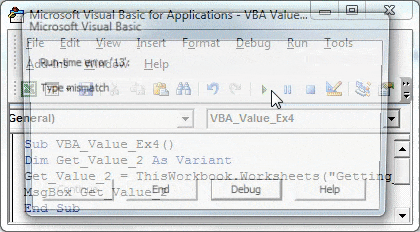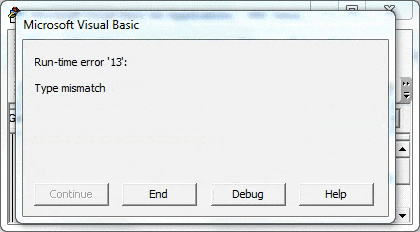
You’ll get a Run-time error’13’: Type Mismatch. The reason for getting this error is that we are defining a single variable and assigning values of a one-dimensional array (with three rows) to it, which is logically not possible.
This is from this article. Let’s wrap things up with some points to be remembered.
Things to Remember
Using the VBA CELLS method, you can’t set multiple cell values because it takes rows and columns as arguments. You can only specify the row number and column number in it.
You also can’t display values stored in multiple cells in a single message box. If you have to retrieve the range of values, you need to write separate get arguments for each value.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to VBA Value. Here we have discussed how to use Excel VBA Value Function, practical examples, and a downloadable Excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –

