Updated March 16, 2023

Introduction to T-SQL pivot
The T-SQL pivot is a relational operator that can be utilized to transform a table expression into another. It can be used to create a versatile report. The pivot has been utilized if we want to convert data from row-level to column level. It allows rotating the expression of a table having values by turning the unique values from one column of the expression into the various columns in the output. Also, with the help of pivot, we can execute the aggregate operation where we need them.
What is a T-SQL pivot?
The T-SQL pivot is the relational operator which can be used for transforming the table-valued expression into the other table; the pivot can be used to turn a table-valued expression by turning the unique values from one column to the various columns in terms of output in the expression, if we want to persists the column values which we want in the output that can be carried out by using aggregations, and when we want to transform the data from row-level to the column level then pivot can be used, in the T-SQL pivot the FROM clause can be used with the ‘SELECT,’ ‘UPDATE,’ and ‘DELETE’ statements; generally the ‘SELECT’ clause can be used with ‘FROM’ clause that the pivot operator can use.
In T-SQL, the dynamic tables and the operators are also used in which the pivot table can outline the information from massive datasets, which can be used for creating reports. Operators can be used for turning the unique value from one column to another.
Using T-SQL pivot
Let us see the procedure which can be used in T-SQL by using pivot to get the result as the columns of pivot and value column are cluster columns,
- It accomplishes the GROUP BY on its input_table in opposition to the grouping column and generates one output row for every group.
The output row of the grouping columns can acquire the communicating column values for that set in the input_table.
- We have to perform some steps for creating values in a list of columns for every output,
- In grouping, one extra row has been created in the GROUP BY in the first step in opposition to the column in the pivot.
For every output column in the list of columns, it can select a subgroup that can fulfill the given condition which has been given below,
pivot_column = CONVERT(<data_type of pivot column>, 'output_column')- Then aggregate_function has been calculated in opposition to the value_column over the subgroup; then we can get the result keeping in touch with the output_column; if we do not have any value in the subgroup, then the server can create a null value for that output_column.
We get zero output if we have a COUNT aggregate function and an empty subgroup.
- Let us see the above explanation using syntax in which we can read the complex series of SELECT….CASE in a simple way,

T-SQL pivot Dynamic Tables
Let us see how a dynamic pivot table has been generated in T-SQL, in which the pivot table is the segment of condensed information that can be created from the vast fundamental dataset; basically, it has been utilized to report on particular dimensions from the extensive datasets, fundamentally user can able to transform rows into the columns as it can provide the ability to the user to convert the columns from server to the table in a simple way, and it can generate the reports as per the demands.
Pivot tables can also help generate data analysis such as slicing and dicing, which can create queries, let us understand the pivot table,

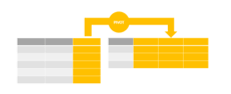
In the above figure, we have two tables in which the left table has original records and the right table is the pivot table that has been created by transforming the rows from the original table into columns; generally pivot table can have rows, columns, and values, in which in the pivot table the rows have been come up from the Student columns and columns are come up from the Subject column. The values have been generated by aggregating the Marks column of the left table; we have to execute the script for creating pivot tables.
T-SQL pivot operator
- The pivot operator can transform each row into the aggregate output, in which it can put the communicating columns into the resultant set, and this operator has been used to turn the unique value from one column into the various columns in which we can say that by rotating the columns as shown in the below figure,
- Let us see the structure of the query to which we can able to refer,

- Let us see how to implement the pivot operator by using below ‘Sales’ table,
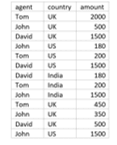
So, in this way, the pivot operator can be used to get the data.
- We want to write the query for getting the total amount of each agent as per the country; then, we can solve this by using,
- aggregation and GROUP BY clause:
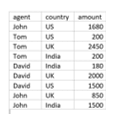
Using aggregation and GROUP BY clause, we can able to write the below query,
"SELECT AGENT, COUNTRY, SUM(AMOUNT) AS TOTAL
FROM SALES
GROUP BY AGENT, COUNTRY
ORDER BY SUM(AMOUNT);"Then we get the output as per the below screenshot,
- Aggregation and pivot operator:
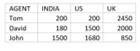
Let us see the query by using the pivot operator,
"SELECT AGENT, INDIA, US, UK FROM SALES
PIVOT
(SUM(AMOUNT)
FOR COUNTRY
IN ([INDIA], [US], [UK])
)AS PIVOTTABLE
ORDER BY INDIA, US, UK;”
We will get the output as:
Conclusion
In this article, we conclude that the pivot in the T-SQL has been utilized to transform the table-valued expression into another table; it can run the aggregate function whenever it is needful; we have also discussed the pivot operator, the dynamic table, and using of the pivot operator in T-SQL.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “T-SQL pivot” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

