Updated July 21, 2023
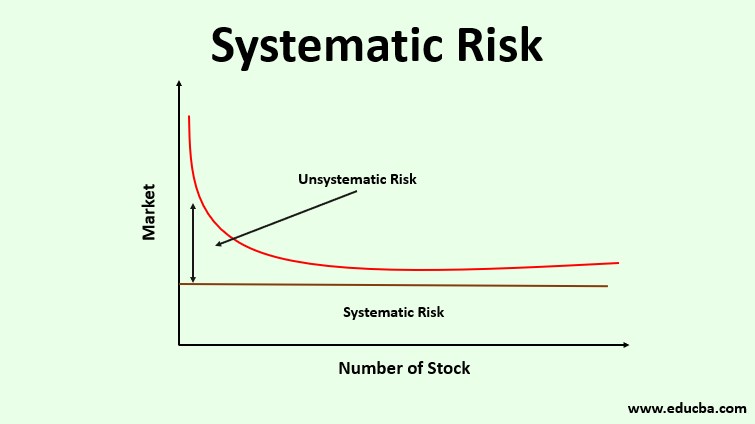
What is Systematic Risk?
Systematic risk, at times also known as non-diversifiable risk, is the risk pertaining to the entire market or the economy as a whole and is not specific to a particular company therefore, there is no measure for avoiding the same through diversification of a portfolio of securities because it is not an outcome of company-specific lack of abilities.
Formula
We know that the below is the CAPM equation:
- Er: Expected Return of the Security.
- Rf: Risk-Free Rate is generally the rate of government security or savings deposit rate.
- Rm: Return of the market portfolio or an appropriate index for the given security such as the S&P 500.
- β: Systematic risk coefficient of security in comparison to the market.
This beta can be calculated through time-series regression of stock returns to the market through a regression equation of the below generic form:
- α: Return on the stock independent of the market.
- ε: Error Term.
Or it can be calculated by solving the below equation if the inputs of the same are readily available:
- σm: Standard Deviation of market returns.
- σstock: Standard Deviation of stock returns.
- Correlation can be calculated using the covariance.
Explanation
Suppose the government imposes a higher tax regime on the entire corporate sector. All the companies are exposed to such a change in tax reform and laws and regulations of the land. Such risks can’t be diversified by holding stocks of different companies or industries in the investment portfolio.
There can be many such examples of systematic risk. It is different from the company-specific risks such as those of having a plant located in a disaster-prone city in a country where other competitors are not located in such places and therefore have a lower chance of getting impacted by natural disasters.
Examples of Systematic Risk (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation in a better manner.
Example #1
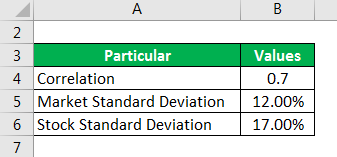
Suppose we are given the following data, for a bank stock, therefore, the relevant market is a banking index:
Solution:
Beta (β) is calculated as
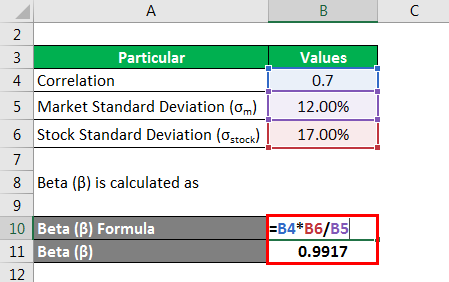
So from this, we can understand that the stock faces slightly less systematic risk as compared to the market but it can almost be said to equal 1 so the systematic risk is almost the same as that of the index.
Types of Systematic Risk
- Interest Rate Risk: We know that the Central bank such as the Federal Reserve increases or decreases the policy rate from time to time to boost or curtail money supply in the economy. This impacts the interest rates in the economy. In times when the central bank reduces the rates, the money supply increases, companies begin to borrow more and expand while the opposite is true when the policy rate is increased. This is related to the business cycle and therefore can’t be diversified.
- Inflation risk: When inflation breaches the desired mark, the purchasing power of the amount of money reduces. This leads to lower returns in the entire market because spending and consumption reduce which in turn leads to a fall in investments.
- Exchange Rate Risk: If the value of the currency in exchange of other currencies reduces then the value of the returns in that currency also reduces. In such cases, all the companies which are dealing in that currency for their transactions lose out and therefore the investors also lose out.
- Geopolitical Risks: If a country experiences severe geopolitical challenges, then all the companies in the country suffer from it. This can be diversified by investing in different countries, however, if foreign investment is not allowed in the country and domestic country experiences such threats then the entire available market of investable securities experiences losses.
- Natural calamity: All the companies in countries such as Japan, which are prone to earthquakes or volcanic eruptions, face the threat of such calamity. This can be diversified by not investing in Japan however, that is not a solution for many investors.
Therefore, it is not so that systematic risk can’t be avoided by some investors, instead, it is the risk that impacts all the investors and the companies functioning in a financial market, country, industry or so on collectively or in an aggregate manner and it is not a company-specific risk.
Impact of Systematic Risk
The degree of impact of the systematic risk on the return of the stock with respect to the market returns can be assessed by the magnitude of beta:
- When the β = 1 the systematic risk affects the stock returns as much as it affects the market
- When the β = 0 the systematic risk does not affect the stock returns but affects the market
- When the β < 1 the systematic risk affects the stock returns but less than how much it affects the market
- When the β > 1 the systematic risk affects the stock returns but more than how much it affects the market
The solution to systematic risk is in asset allocation. If one market is impacted by a certain systematic risk, some parts of the portfolio should be invested in another market. Now the definition of the market is dynamic, but here we can define it as different asset classes.
During inflation, commodities would help so fixed-income security portfolios should be complemented with some investment in commodities and so on.
Some confuse asset allocation with diversification, but that is not the case. Diversification means security selection within an asset class or a market, while asset allocation means investing in different markets.
Systematic Risk vs Unsystematic Risk
- Meaning: Unsystematic risk is the risk specific to a particular company or security such as the risk of the company’s plant being located in the area which experienced a natural calamity such as an earthquake. Other competing companies would not experience the losses experienced by this company due to this natural calamity.
- Diversification: Systematic Risk can’t be diversified while Unsystematic risk can be. Suppose you have a stock portfolio, so it experiences the loss of returns during inflation but adding commodity to the portfolio can reduce such risk, however.
- Factors affecting: Unsystematic risk is caused by internal or controllable factors while Systematic risk is caused by external non-controllable factors.
- Impact: Unsystematic risk only impacts some securities while systematic risk impacts the market as a whole.
- Remedy: Cure for systematic risk is asset allocation that is investing or not investing in certain assets while that for unsystematic risk is making portfolio diversification, that is, adding different securities of the same industry.
Conclusion
Therefore, systematic risk is the risk faced by the entire market as a whole and can’t be cured through diversification or security selection. The only cure for it is asset allocation, which implies investing in multiple markets to complement other markets facing systematic risk. However, it doesn’t completely eliminate systematic risk, it just reduces it to some extent.
Systematic risk can be measured through the beta coefficient, the calculation of which requires the use of regression analysis and statistics concepts and this measure may vary from one analyst to another bringing a degree of subjectivity in the analysis.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Systematic Risk. Here we discuss how to calculate with practical examples. We also provide a downloadable excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –


