Updated March 16, 2023
Introduction to SQLAlchemy update object
The sqlalchemy update object is used to modify the user input datas with specific attributes of the object and also needs to assign the new value of the datas to commit the recent changes from the existing values to make the same in the persistent object from the table whose the unique identifier or any other constraints like primary key identifiers of the database tables.
Overviews SQLAlchemy update object
The sqlalchemy update is the main object for updating the user inputs from the user end to the backend database. It will update the existing table rows and columns using the sql alchemy stages based on the filter condition and update the parameters arguments to commit the table transactions. We can create a table with all the existing and new tables to modify the existing datas for certain attributes and column values of any objects that can be assigned to the new type of values. We will commit the changes to be the data persistent. The primary key identifier is the main objective role of the unique set of records; it will store and fetch the data results from the table using the primary key identifier attribute like id or any other integer type of attribute values.
SQLAlchemy table update object
To modify the datas of any specific type of attribute values from the existing or new tables which are already created from the user end database. We identified the unique primary key identifier to use cureate and existing database tables to retrieve records from the get() method of the user session as the display content of the specific objects on the table. The parameters pass and bound the query limit paths with respective datas; the table datas will be retrieved using the row and column formats. The sqlalchemy update table datas will calculate the user session and retrieve the datas using the session manager; the sqlalchemy stages will change based on the filtering conditions and update the existing parameters, and other arguments will commit the database transactions to the table.
The session object will be called in the table class, which creates the SQLAlchemy Query object to the given session with procedure call and follow the criteria like Query.filter(criterion) passing the previous set of type results with the comma-separated as criterion sequence of filtering criterion. We can call the session by using the session.query() method, which passes the arguments like a session. Query (Class) with the SQLAlchemy Session; the object created will correspond to the query session, and the values will be updated using the Query.update(values) with exact results of the form dictionary to update the rows which matched by the current Query of the values.
We can update the values using the update() method with a minimum of two parameters required with the dictionary, like key-value pairs. Whenever we update the table object, it must be followed the below steps.
1. To first import the update from the sqlalchemy packages.
2. Before that, please ensure the database connection is connected and the engine is called for the specific tables.
3. Then we can call and update the values by using the reference that will be initialized and call the table values like below,
4. Reference=(update(table).where(table.column == ‘’). Values(column=’’))
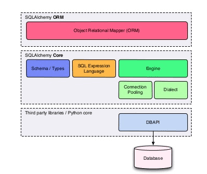
5. The following diagram explains the sqlalchemy Core and ORM that will be mapped, the datas upgraded, and the object workflow.
6. DB update will be one of the transaction types. The several statements like a database transaction and connections will follow the feature like the method begin() that returns the transaction id or references.
7. It mainly comes under the DML statements to help the data manipulation of the database and the schema.
8. Sometimes, the update will write the expressions for usage. Based on the other columns, we can execute the statement along with an updated or modified table row count.
9. By using for or any other loop statement, the condition will be triggered, and the datas will be iterated and printed on the console.
10. Finally, we can commit all the user transactions with the help of specified sessions with comments like session.commit().
Examples of SQLAlchemy update object
Different examples are mentioned below:
Example 1
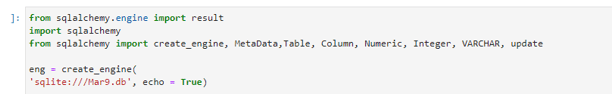
from sqlalchemy.engine import result
from sqlalchemy import update
import sqlalchemy
from sqlalchemy import create_engine, MetaData,Table, Column, Numeric, Integer, VARCHAR, update
from sqlalchemy import update
eng = create_engine(
'sqlite:///Mar9.db', echo = True)
vars = MetaData(bind=eng)
MetaData.reflect(vars)
emp = Table(
'employees', vars,
Column('employ_id', Integer, primary_key=True),
Column('rollno', Numeric),
Column('name', VARCHAR),
Column('city', VARCHAR)
)
vars.create_all(eng)
vars1 = emp.insert().values(employ_id=1,
rollno=10.1,
name='Siva',
city='Tup')
vars2 = emp.insert().values(employ_id=2,
rollno=11.2,
name='Raman',
city='Chennai')
vars3 = emp.insert().values(employ_id=3,
rollno=12.3,
name='Sivaraman',
city='Mumbai')
vars4 = emp.insert().values(employ_id=4,
rollno=13.4,
name='Arun',
city='Tup')
vars5 = emp.insert().values(employ_id=5,
rollno=14.5,
name='Kumar',
city='Coimbatore')
eng.execute(vars1)
eng.execute(vars2)
eng.execute(vars3)
eng.execute(vars4)
eng.execute(vars5)
outs = vars.tables['employees']
a = update(outs)
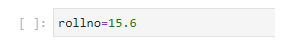
val = a.values({"rollno": 15.6})
res = val.where(outs.c.employ_id == 5)
eng.execute(res)
fin = text("SELECT * from employees")
result = eng.execute(fin).fetchall()
for b in result:
print("\n", b)Sample Output:
- In the above example, we first created the table called employees with the id, rollno, name, and city columns.
- We have declared the separate datatypes and the values for each column.
- After creating the table of employees, we can insert the values for each column.
- Then using the eng.execute() method, we can execute the statements.
- Finally, if we want to update any column values with the help of unique column values like emp_id = “” we will update the new values instead of the old value
Example 2
from sqlalchemy.engine import result
import sqlalchemy
from sqlalchemy import create_engine, MetaData,Table, Column, Numeric, Integer, VARCHAR, update
eng = create_engine(
'sqlite:///Mar9.db', echo = True)
varss = MetaData(bind=eng)
MetaData.reflect(varss)
employees = varss.tables['employees']
a = update(employees)
a = a.values({"'name'": "newname"})
a = a.where(employees.c.employ_id' == 3)
eng.execute(a)
res = text("SELECT * from employees")
outs = eng.execute(res).fetchall()
for b in outs:
print("\n", b)Sample Output:
- In the second example, I have updated only the column values which are already created on the existing table[employees]
- First, we can create the database connection using the engine and the Metadata; we can bind the engine.
- With the help of reference[a], we can update the values using the update() method.
Conclusion
In sqlalchemy, the update is one of the inbuilt methods, and it will help track and update the existing values with certain conditions. It is also being called with the existing table references and is mapped by using the unique identifier attributes to update new values from the table.
Recommended Article
This is a guide to SQLAlchemy update object. Here we discuss the introduction, SQLAlchemy table update object, examples, code implementation, and output. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –