Updated March 24, 2023
Introduction to LIKE Query in SQL
LIKE query is used to search for a particular pattern from the table rows and return the columns, which matches the pattern. When you only know a fragment of a text value and need to get the details from the table. Then you can get the values that match the pattern mentioned by using the “LIKE” query in SQL.
LIKE query has a two-wildcard match.
They are mentioned below:
- “%”: Matches any string with zero or more characters.
- “_”: Matches any single character.
Syntax for LIKE Query in SQL:
In this section let us discuss the significance of the “LIKE” and its syntax.
SELECT Col_name1, col_name2, .. , col_nameN
FROM <Table_name>
WHERE <Col_name1> LIKE <value>How to Use LIKE Query in SQL?
Let us take an example and see how the LIKE query works in the SQL.
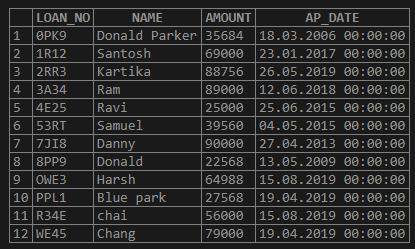
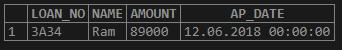
Let us consider the below LOAN_034 table:
Creating LOAN_034 Table:
Code:
CREATE TABLE LOAN_034(
LOAN_NO VARCHAR(25) PRIMARY KEY,
NAME VARCHAR(25),
AMOUNT INTEGER(10),
AP_DATE DATE
);Inserting Data into the LOAN_034 Table:
Code:
INSERT INTO LOAN_034 VALUES ("3A34","Ram", 89000, "2018-06-12");
INSERT INTO LOAN_034 VALUES ("4E25","Ravi", 25000, "2015-06-25");
INSERT INTO LOAN_034 VALUES ("1R12","Santosh", 69000, "2017-01-23");
INSERT INTO LOAN_034 VALUES ("53RT","Samuel", 39560,"2015-05-04");
INSERT INTO LOAN_034 VALUES ("2RR3","Kartika", 88756,"2019-05-26");
INSERT INTO LOAN_034 VALUES ("8PP9","Donald", 22568, "2009-05-13");
INSERT INTO LOAN_034 VALUES ("0PK9","Donald Parker", 35684, "2006-03-18");
INSERT INTO LOAN_034 VALUES ("7JI8","Danny", 90000, "2013-04-27");
INSERT INTO LOAN_034 VALUES ("OWE3","Harsh", 64988,"2019-08-15");
INSERT INTO LOAN_034 VALUES ("PPL1","Blue park", 27568, "2019-04-19");
INSERT INTO LOAN_034 VALUES ("R34E","chai", 56000, "2019-08-15");
INSERT INTO LOAN_034 VALUES ("WE45","Chang",79000, "2019-04-19");
select * from LOAN_034;Output:
Example #1
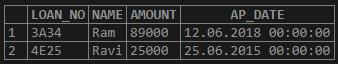
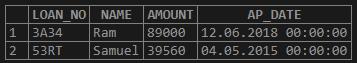
Get all the details of the people whose name’s start with “R” from the above table.
Code:
SELECT * FROM LOAN_034
WHERE UPPER (NAME) LIKE 'R%';Output:
Example #2
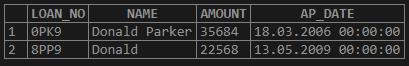
Get all the details of the people whose name’s start with “don” from the above table.
Code:
SELECT * FROM LOAN_034
WHERE UPPER (NAME) LIKE 'DON%';Output:
Example #3
Get all the details of the people whose name’s start with “cha” and “chan” from the above table.
Code:
SELECT * FROM LOAN_034
WHERE UPPER (NAME) LIKE UPPER ('CHA_') OR UPPER (NAME) LIKE UPPER ('CHAN_');Output:
Example #4
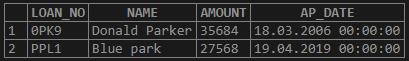
Get all the details of the people whose name contains “park” from the above table.
Code:
SELECT * FROM LOAN_034
WHERE UPPER (NAME) LIKE '%PARK%';Output:
Example #5
Get all details of the people whose names contain LETTER “M” from the above table.
Code:
SELECT * FROM LOAN_034
WHERE UPPER (NAME) LIKE '%M%';Output:
Example #6
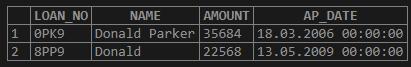
Get all the details of the people whose name contains “Donald” from the above table.
Code:
SELECT * FROM LOAN_034
WHERE UPPER (NAME) LIKE '%DONALD%';Output:
Example #7
Get all details of the people whose name STARTS WITH “A”, STARTS WITH “K”, and ENDS WITH “A” from the above table.
Code:
SELECT * FROM LOAN_034
WHERE UPPER (NAME) LIKE ‘A%’ OR UPPER (NAME) LIKE ‘K%’
OR UPPER (NAME) LIKE '%A';Output:
Example #8
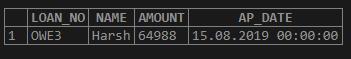
Get all details of the people whose NAME STARTS WITH “H” and ENDS WITH “H” from the above table.
Code:
SELECT * FROM LOAN_034
WHERE UPPER (NAME) LIKE 'H%H';Output:
Example #9
Get all details of the people whose NAME STARTS WITH “R” and ENDS WITH “M” and has only one letter in between them from the above table.
Code:
SELECT * FROM LOAN_034
WHERE UPPER (NAME) LIKE 'R_M';Output:
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to LIKE Query in SQL. Here we discuss the introduction and how to use LIKE queries in SQL along with a few examples and implementation of queries. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –