Updated June 16, 2023

Introduction to SQL Hour()
HOUR() function is a date/time function in standard query language (SQL) that extracts the hour part from a given datetime or timestamp data. This function is primarily supported in databases such as MYSQL and ORACLE. At the same time, other popular database management servers such as PostgreSQL and SQL Server use other similar functions, EXTRACT( ‘hour’ from ‘date_expression’) and DATE_PART(‘hour’ from ‘date_expression’). In this article, we will discuss the HOUR() function, in particular, with the help of some practical examples. To begin with, let’s discuss the syntax and parameters used in this function.
Syntax and Parameters
The basic syntax for HOUR() function in MYSQL and ORACLE databases is as follows :
HOUR('expression')The parameter and output of the function are as follows :
- expression: expression is the input value. It can be of date, datetime, timestamp, or string convertible to a similar data type.
- Output: The function returns an integer value corresponding to the value of the hour part of the given expression in 24-hour format.
The hour function can be used as a part of the SELECT statement for selecting the hour part, WHERE OR HAVING clause to filter based on the hour part in the filtering expression, ORDER BY clause to sort records based on the hour part of the expression or GROUP BY clause to group records by hour part of a given date/timestamp column.
Having discussed the basic syntax and parameters used for working with HOUR() function, let us go ahead and discuss a few examples to understand the functionality in great detail.
Examples of SQL HOUR()
Following are the examples are given below:
Example #1
Extract the hour part from the given timestamp/datetime/time expressions.
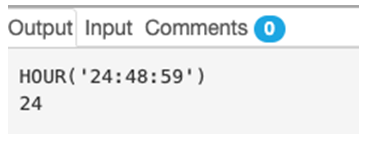
1. 24:48:59
SELECT HOUR('24:48:59');Output:
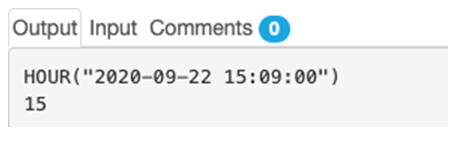
2. 2020-09-22 15:09:00
SELECT HOUR("2020-09-22 15:09:00");Output:
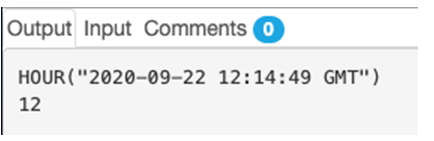
3. 2020-09-22 12:14:49 GMT
SELECT HOUR("2020-09-22 12:14:49 GMT");Output:
In the example mentioned above, you might have noticed three different kinds of datetime/timestamp expressions. In the first one, we just have time; in the second one, we have datetime, and in the third one, we have a timestamp along with the timezone. The hour function of MYSQL/Oracle works well with all such data types.
In order to illustrate the usage of HOUR() function, let’s create a table ‘orders’ with order_id, order_amount, and order_time as columns. The CREATE statement for the orders table looks something as follows:
CREATE TABLE orders(
order_id VARCHAR(10),
order_amount REAL,
order_time DATETIME
);After creating the orders table, insert a few records in it to work with. You may use the following INSERT statement for the same.
INSERT INTO orders (order_id,order_amount,order_time)
VALUES ('o1',345,'2020-09-22 10:23:32'),
('o2',143.54,'2020-09-22 10:13:20'),
('o3',564.32,'2020-09-22 12:23:32'),
('o4',345,'2020-09-22 11:11:21'),
('o5',125.78,'2020-09-22 11:23:32'),
('o6',34.98,'2020-09-22 11:13:25'),
('o7',78.92,'2020-09-22 10:23:32'),
('o8',132.67,'2020-09-22 12:28:26'),
('o9',786.54,'2020-09-22 10:37:29');Having inserted the given records in the orders table, we are all set to try a few examples based on the HOUR() function with the help of this table.
Example #2
Find the order details for the orders with the hour of ordering, order_id, and order_amount in the result set.
SELECT HOUR(order_time) as "Hour of Ordering", order_id, order_amount
FROM orders;Output:
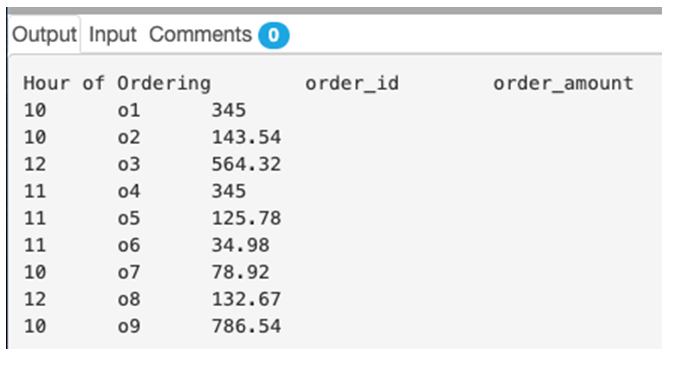
In this example, we have used the HOUR() function as a part of the SELECT statement. The HOUR() function extracts the hour from the corresponding order_time column.
Example #3
Find the order details for the orders which were placed between 10 a.m. and 11 a.m. on 22nd September 2020.
SELECT order_id, order_amount, order_time
FROM orders
WHERE HOUR(order_time) >= 10 AND HOUR(order_time) < 11;Output:
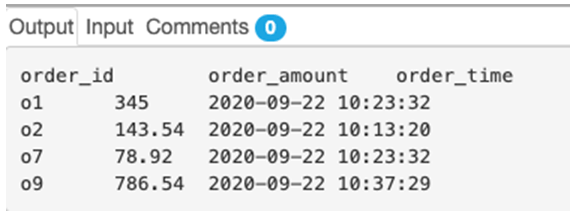
Here, we have used HOUR() function as a part of WHERE clause to filter rows based on the hour of ordering. The function returns an integer value corresponding to the hour part of the given order_time column and compares it with the comparison expression.
Example #4
Sort the order details for the orders on 22nd September 2020 based on the hour of order, starting from earliest to latest.
SELECT order_id, order_amount, order_time
FROM orders
ORDER BY HOUR(order_time) ASC;Output:
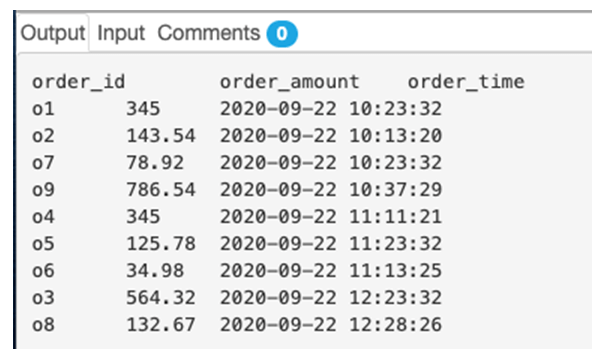
In this example, we have used the HOUR() function to extract the hour part of the ordering time and then used it to order the fetched records in ascending order.
Example #5
Find the hourly revenue generated from the orders placed on 22nd September 2020.
SELECT HOUR(order_time) as "Hour of Ordering",
SUM(order_amount) as "Total_Revenue"
FROM orders
GROUP BY HOUR(order_time);Output:
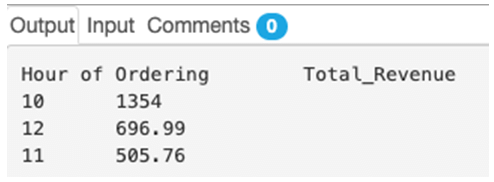
Here, we have used HOUR() function as a part of the GROUP BY clause.
Conclusion
In this post, we have covered the HOUR() function in SQL, which extracts the hour part from a given input datetime/timestamp expression. The function returns an integer value between 0 and 24. This function is available only in MYSQL and Oracle databases.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL HOUR()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

