Updated March 27, 2023
Introduction to SQL Delete Join
DELETE JOIN is an advanced structured query language(SQL) statement that is used to perform delete operations in multiple tables while using SQL JOIN such that all rows are deleted from the first table and the matching rows in another table or based on the kind of join operation used in the query. It is basically a combination of DELETE and JOIN statements. In this article, we will be learning about four types of DELETE operations, namely, DELETE while using INNER JOIN, LEFT JOIN, RIGHT JOIN and FULL JOIN.
Syntax and Parameters of SQL Delete Join
The following are the basic syntax of Delete Join with its parameters.
Syntax 1:
The basic syntax for Delete Join in SQL Server is as follows:
DELETE t1
FROM table_name1 AS t1 JOIN {INNER, RIGHT,LEFT,FULL} table_name1 AS t2
ON t1.column_name = t2.column_name
WHERE condition;Syntax 2:
The basic syntax for Delete Join in MySQL is as follows:
DELETE t1.*
FROM table_name1 AS t1 JOIN {INNER, RIGHT,LEFT, FULL} table_name1 AS t2
ON t1.column_name = t2.column_name
WHERE condition;Parameters of SQL Delete Join
The different parameters used in the syntax are:
- DELETE t1: It is used to delete the required table from the database. Here, you may choose from the first table’s instance t1 and the second table’s instance t2.
- FROM table_name1 as t1 JOIN table_name2 as t2: It is used to specify the source from which data has to be fetched and deleted. Here, table_name1 is the name of the left table and table_name2 is the name of the right table. To join, you may choose from INNER, LEFT, FULL and RIGHT joins.
- ON t1.column_name = t2.column_name: It is used to specify the common conditions on which the two tables will be joined. It can be a pair of primary and foreign keys.
- WHERE condition: It is used to specify the conditions to filter records.
Of the above-mentioned parameters, all the parameters except the WHERE clause are mandatory. Go ahead, we will be understanding delete joins in detail one by one.
Examples of SQL Delete Join
Following are the different examples of SQL Delete Join.
DELETE with INNER JOIN
Delete with inner join is used to delete all the records from the first table and all the matching records from the second table. In order to understand the concept better, we will take the help of two tables, Employees (this contains personal details of all the employees) and departments (it contains details like department id, name, and its hod).
The data in the department’s table look something like this:
| departmentid | departmentname | head |
| 4001 | Sales & Marketing | Lina Krishna |
| 4002 | Products | David Jackson |
| 4003 | Human Resources | David Mayers |
The data in the employee’s table is as follows:
| employeeid | lastname | firstname | departmentid | address | city |
| 10028 | Becker | Todd | 4001 | 27 street | Oslo |
| 10029 | Rebecca | Ginny | 4001 | 27 street | Manhattan |
| 10027 | Tobby | Riya | 4002 | 31 street | Manhattan |
| 10026 | Sharma | Deepak | 4002 | 10th street | New Delhi |
| 10024 | Krishna | Lina | 4001 | 27 street | Oslo |
| 10023 | Jackson | David | 4002 | 27 street | Manhattan |
| 10022 | Mayers | David | 4003 | 27 street | Manhattan |
Example #1 – SQL Query to Illustrate DELETE INNER JOIN
Suppose in this example, a company wants to shut down the “sales & marketing” department. It would like to remove all the employees from this department from the company’s database. How will you perform this operation? It can be done by writing multiple sub-queries but we will do this simply by writing a delete join statement.
Code:
DELETE t1
FROM employees AS t1 INNER JOIN department AS t2
ON t1.departmentid = t2.departmentid
WHERE t2.departmentname = 'Sales & Marketing';Output:
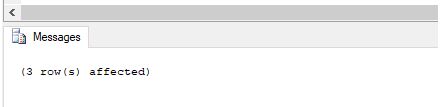
We can check using the SELECT statement that all the information for sales and marketing employees has been successfully deleted.
Code:
SELECT TOP 1000 [employeeid],
[lastname],
[firstname],
[departmentid],
[address],
[city]
FROM [practice_db].[dbo].[employees]Output:
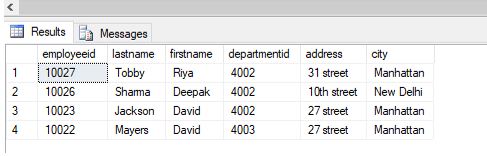
DELETE with LEFT JOIN
A SQL DELETE LEFT join should be used in cases when we want to delete all data from one table(left) and only matching data from the other table.
Example #2 – SQL Query to Illustrate DELETE LEFT JOIN
Since in the previous steps, we have already shut down the sales and marketing department. Then we might further want to remove data pertaining to it from other database tables like tasks.
The tasks table looks something like this:
| taskid | departmentid | employeeid |
| hr12 | 4003 | 10022 |
| p123 | 4002 | 10026 |
| p23 | 4002 | 10026 |
| p231 | 4002 | 10023 |
| sm12 | 4001 | 10028 |
| sm45 | 4001 | 10029 |
The following SQL code will delete all the tasks for the sales and marketing department. We want to delete everything from the first table “tasks” but not from “departments”. So, we will be using a LEFT JOIN.
Code:
DELETE t1
FROM tasks AS t1 LEFT JOIN department AS t2
ON t1.departmentid = t2.departmentid
WHERE t2.departmentname = 'Sales & Marketing';Output:
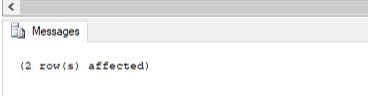
Let’s check if all the tasks pertaining to the sales and marketing department have been removed from the table.
Code:
SELECT TOP 1000 [taskid],
[departmentid],
[employeeid],
FROM [practice_db].[dbo].[tasks]Output:
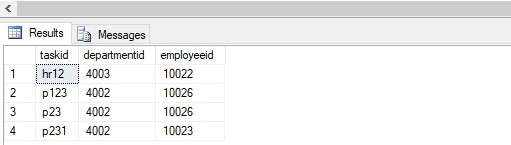
As you can see it has been successfully deleted.
DELETE with RIGHT JOIN
A SQL DELETE RIGHT join should be used in cases when we want to delete all data from one table (right) and only matching data from the other table.
Example #3 – SQL Query to Illustrate DELETE RIGHT JOIN
Since we have already deleted everything pertaining to the sales and marketing department in the tasks and employee table. Let’s now delete the department from the department table using a DELETE with RIGHT JOIN.
Code:
DELETE t2
FROM employees AS t1 RIGHT JOIN department AS t2
ON t1.departmentid = t2.departmentid
WHERE t2.departmentid NOT IN (SELECT t1.departmentid FROM employees as t1);Output:
Let’s check if everything has been successfully deleted or not from the department’s table.
Code:
SELECT TOP 1000 [departmentid],
[departmentname],
[head]
FROM [practice_db].[dbo].[department]Output:
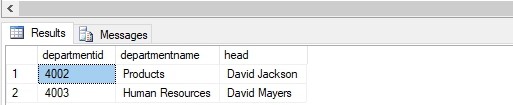
As you can see we have successfully achieved it.
DELETE with FULL JOIN
DELETE with FULL JOIN is similar to an INNER join. It is helpful in deleting all the data as FULL join returns all records from both the tables and will substitute the non-matching columns with NULL values.
Example #4 – SQL Query to Illustrate DELETE FULL JOIN
Finally, let’s try performing a delete operation with full join on employees and task tables. Assume that there is an additional column in the tasks table which shows the status of a particular task. Our aim is to delete all the employees(assuming they were freelancers) whose task has been completed.
Code:
DELETE t1
FROM employees AS t1 FULL JOIN tasks AS t2
ON t1.employeeid = t2.employeeid
WHERE t2.status = 'completed';Output:
Let’s check if everything has been successfully deleted or not from the employee’s table.
Code:
SELECT TOP 1000 [employeeid],
[lastname],
[firstname],
[departmentid],
[address],
[city]
FROM [practice_db].[dbo].[employees]Output:
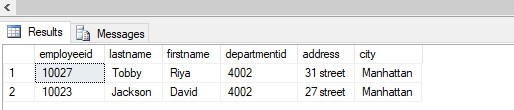
As you can see we have successfully achieved it.
Conclusion
DELETE JOINS is a combination of delete and joins in SQL. They help us in performing complex delete queries very efficiently. If we did not have delete joins, then we might have to write complex SQL subqueries within the delete statements.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Delete Join” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

