Updated July 5, 2023

Introduction to SQL DATEADD()
In the SQL server, if we want to add or subtract date or time intervals, then we use DATEADD(), which will return the modified date value.
Syntax
Below is the syntax for SQL DATEADD()
DATEADD(interval, number, date)As we can see in this function, there are three arguments, and all are mandatory for this function to work and return the integer result
1. Interval
This is also called datepart, and it is provided as a string to this function. This argument can be anything that represents a time interval, like a month, week, day, or year. We can also specify the quarter of the year.
- year, yyyy, yy = Year
- quarter, qq, q = Quarter
- month, mm, m = month
- dayofyear = Day of the year
- day, dy, y = Day
- week, ww, wk = Week
- weekday, dw, w = Weekday
- hour, hh = hour
- minute, mi, n = Minute
- second, ss, s = Second
- millisecond, ms = Millisecond
- microsecond, mcs = Microsecond
- nanosecond, ns = Nanosecond
- TZoffset, tz = Time zone offset
SELECT DATEADD(month, 1,'20100720');
SELECT DATEADD(month, 1,'20100622');The above statements add a month to the date. In this case, the month is the datepart.
2. Number
The number argument should be an int, and it should not exceed its limit positively or negatively.
SELECT DATEADD(year,2147483648,'20070728');
SELECT DATEADD(year,-2147483649,'20070728');The above query statements both return an error message “Msg 8115, Level 16, State 2, Line 7Arithmetic overflow error converting expression to data type int. Msg 8115, Level 16, State 2, Line 8Arithmetic overflow error converting expression to data type int.”
3. Date
This is the actual date to add value. This is a mandatory parameter. It should be an expression that resolves in date, datetime, datetimeoffset, datetime2, smalldatetime, or time value. It can be a string literal or user-defined variable.
This function works in the SQL server starting from the 2008 version, Azure SQL Data Warehouse, Azure SQL Database, Parallel Data Warehouse.
Examples to Implement SQL DATEADD()
Below are the examples mentioned:
1. Calculating Age
Code:
select ID,emp_name,emp_dateOfBirth from EmployeeOutput:
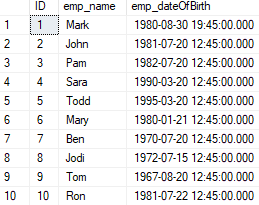
We have the above table Employee, which consists of the date of birth, and from this, we will calculate the age in terms of a year, month, and days in 2 steps
Step 1 – Creating a function
Code:
CREATE FUNCTION fnEmp_ComputeAge(@Emp_DOB DATE TIME)
RETURNS NVARCHAR(50)
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @Age_Tempdate DATETIME, @Age_Years INT, @Age_Months INT, @Age_Days INT
SELECT @Age_Tempdate= @Emp_DOB
SELECT @Age_Years=DATEDIFF(YEAR, @Age_Tempdate,GETDATE())-CASE WHEN (MONTH(@Emp_DOB)>MONTH(GETDATE()))OR(MONTH(@Emp_DOB)=MONTH(GETDATE())AND DAY(@Emp_DOB)>DAY(GETDATE()))THEN 1 ELSE 0 END
SELECT @Age_Tempdate=DATEADD(YEAR, @Age_Years, @Age_Tempdate)
SELECT @Age_Months=DATEDIFF(MONTH, @Age_Tempdate,GETDATE())-CASE WHEN DAY(@Emp_DOB)>DAY(GETDATE())THEN 1 ELSE 0 END
SELECT @Age_Tempdate=DATEADD(MONTH, @Age_Months, @Age_Tempdate)
SELECT @Age_Days=DATEDIFF(DAY, @Age_Tempdate,GETDATE())
DECLARE @Emp_Age NVARCHAR(50)
SET @Emp_Age=Cast(@Age_Years AS NVARCHAR(4))+' Age_Years '+Cast(@Age_Months AS NVARCHAR(2))+' Age_Months '+Cast(@Age_Days AS NVARCHAR(2))+' Age_Days Old'
RETURN @Emp_Age
EndOutput:
In the above example, we have created a SQL Function to calculate the age of the employee from the DOB, so the function takes @Emp_DOBas as a parameter and returns NVARCHAR(50). We will see this in action when we run this function. In step, we have created this function.
Then we have declared @Age_Tempdate DATETIME, @Age_YearsINT, @Age_MonthsINT, @Age_DaysINT variables. First, we have set the @Age_Tempdateto @Emp_DOB. The next statement is crucial in which we use the DATEDIFF function to get the year difference from the dob and current date, which is calculated using the GETDATE function, and then we subtract 1 or 0 depending on whether the dob month is greater than a current month or if the dob month is same as a current month and the dob date is greater than current date then in those cases we add 1 or else we add 0.
Then we add the calculated years in the @Age_Tempdate using DATEADD function. Similarly, we calculated the month and added in @Age_Tempdate, and then it is used to calculate days. Next, we declared @Emp_Age and set it to the concatenation of the final output. Since the calculation result is in int, we used the Cast function to convert it into nvarchar.
Step 2 – Using the function in query
Code:
select ID,emp_name,emp_dateOfBirth,dbo.fnEmp_ComputeAge(emp_dateOfBirth) as Emp_Age from Employee;Output:
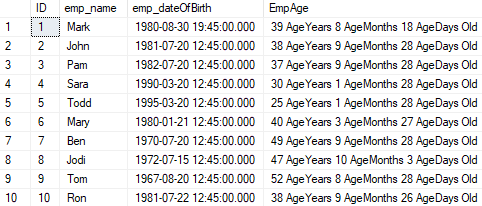
As we can see, we have used dbo.fnEmp_ComputeAge function and passed emp_dateOfBirth to calculate Emp_Age, and the result is as above.
2. Precisions for fractional seconds
In this example, we have declared the date and added milliseconds, microseconds, and nanoseconds to it to check the scale factor.
Code:
DECLARE @datetime datetime2 ='2015-01-01 14:12:08.1111111';
SELECT '2 millisecond' as time, DATEADD(ms,1,@datetime) as [modified date]
UNION ALL
SELECT '4 milliseconds', DATEADD(ms,2,@datetime)
UNION ALL
SELECT '2 microsecond', DATEADD(mcs,1,@datetime)
UNION ALL
SELECT '4 microseconds', DATEADD(mcs,2,@datetime)
UNION ALL
SELECT '49 nanoseconds', DATEADD(ns,49,@datetime)
UNION ALL
SELECT '50 nanoseconds', DATEADD(ns,50,@datetime)
UNION ALL
SELECT'150 nanoseconds', DATEADD(ns,150,@datetime);Output:
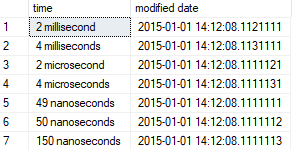
- Milliseconds: scale is 3 (.111)
- Microseconds: scale is 6 (.111111)
- Nanoseconds: scale is 9 (.111111111)
Time, datetimeoffset, and datetime2 have a scale of 7 (.1111111). So, the nanosecond should be a minimum of 100 to count in the calculation; for this number, 1-49 is rounded to 0, and 50-99 is rounded to 100. Also, this function does not allow the addition of a timezone offset.
3. Arguments are expressions or column name
Code:
SELECT SalesOrderID as orderID, OrderDate as dateOfOrder,
DATEADD(day,3,OrderDate) AS PromisedDateOfShipping FROM Sales.SalesOrderHeader;Output:
In this example, we have added 3 days to the order date to calculate the estimated shipping date using DATEADD().
4. User-defined variables
Code:
DECLARE @daysToAdd int= 365,
@datetimeValue datetime='2020-01-01 01:01:01.111';
SELECT DATEADD(day, @daysToAdd, @datetimeValue) as ModifiedDate;Output:
![]()
5. UsingScalar system functions
Code:
SELECT DATEADD(year, 2,SYSDATETIME()) as ModifiedDate;Output:
![]()
In this example, we add 2 years to the current system time.
Conclusion
Hopefully, now you know what DATEADD() is in the SQL server and how it is used to calculate the addition and subtraction of time intervals in a given specified date.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL DATEADD()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

