Updated May 15, 2023

Introduction to Scala Tuples
A tuple is a data structure that can store elements of different data types. It is also used for storing and retrieving data. In Scala, tuples are immutable and store heterogeneous types of data. Immutable tuples mean the object cannot change its value once assigned. Using tuples, we can group different types of data, which can be easily accessed later. We have a student class where we can store its name, age, address, and id into a single data structure called tuples.
Syntax & parameters:
var variable_name = (Data_type1, Data_type1, Data_type1, Data_type1 ..so on...)Now we can see one practice syntax to see how to define it with different data types available in scala;
var myTuple = (Int, String, String, Int)
var myTuple1 = (001, "Amit", "Mumbai", 24)In this way, we can define our tuple in Scala. We have created one tuple with data type int and String and in the next line, we are trying to provide some values into the tuple.
How Does Tuples Work in Scala?
In Scala, tuples can store a fixed number of elements into it. The maximum limit for storing elements is 22. If we try to store elements greater its size, then it will generate one error. But in Scala, we have one alternative to overcome this problem: nested tuples by which we can create tuples inside tuples.
In Scala, we have types of tuples which are as follows:
- Tuple1
- Tuple2
- Tuple3
- Tuple4
- Tuple5, and so on.
For instance, this number is 22. If we want to store more elements, we should go for a collection in Scala. This can be useful where small data is available. We can access the tuple’s elements by using their index or position. We need to use._ syntax.
Now the question comes where can we use tuples? So if we want to group some elements of different types, we can go for a tuple in Scala. They maintain the order as well as part of the collection.
Try to create on tuple;
val myTuple1: (Int, String) = (2, "Hello")Here we are creating one tuple, but internally, it will use one of the classes of tuples, i.e., from tuple1 to tuple22. It’s an internal process. Tuples can be helpful when we want to return multiple values from our method. So we can say that the scala tuples are the ordered collection and elements inside tuples are either related to each other or not both can be possible.
Things to Remember
Some points we should keep in mind while working with tuples in scala are as follows;
- Suppose we have one requirement where our data inside the collection is not changing frequently, or we can say it once assigned and changes after a long period. Then, in this case, we should go for tuples.
- Tuples are very fast in operation, and it is considered the quickest data structure. Also, it contains only limited elements, so the memory consumption is significantly less.
- One advantage of using tuples is that it can store elements of different data types, which means it is heterogeneous in nature. But if we compare it with List, then in List collection, we can only store data of the same type.
- Here tuple in scala is immutable.
- Tuples can easily replace arrays because it is more efficient than all compared areas. They have similarities. They are fixed in nature.
Examples to Implement Scala Tuples
Below are the Example of Scala Tuples:
Example #1
In this example, we will create one simple tuple and print the output.
Code:
object Main extends App{
// Your code here!
// creating tuple object
val t = new Tuple1(1, 2, 3, "hello", "bye", "wait", 00.3)
// printing out the values
println("values inside the tuples are :: ")
println(t)
}Output:
![]()
Explanation: Here, we create one primary method in the above example. We are building a Tuple1 object and assigning it values inside this primary method. To create a tuple object,, we have just used the new keyword here to make the object. After the creation of the thing, we can assign them values.
Example #2
We can also use the toString() method to convert a tuple to a String. This method will concatenate all the data in the tuple to a string.
In this example, we show its use with a tuple in Scala.
Code:
object Main extends App{
// Your code here!
// creating tuple object
val t = new Tuple1(1, 2, 3, "hello", "bye", "wait", 00.3)
// printing out the values
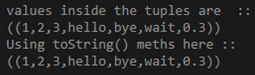
println("values inside the tuples are :: ")
println(t)
//print by using toString()
println("Using toString() meths here ::")
println(t.toString)
}Output:
Example #3
In this example, we will see another way of defining a tuple in Scala and accessing its elements by the variable name.
Code:
object Main extends App{
// Your code here!
// creating tuple object
var (t1, t2, t3, t4, t5)= (100, "Amit", "Sharma", 30, "Mumbai")
// printing out the values
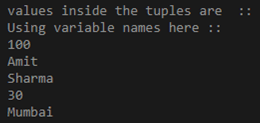
println("values inside the tuples are :: ")
//print by using toString()
println("Using variable names here ::")
println(t1)
println(t2)
println(t3)
println(t4)
println(t5)
}Output:
Example #4
In this example, we are iterating our tuples elements. We can perform any operation on this inside the iterator. For iterating the elements, we are using the product Iterator available in Scala.
Code:
object Main extends App{
// Your code here!
// creating tuple object
var myTuple = (100, "Amit", "Sharma", 30, "Mumbai", 1)
// printing out the values
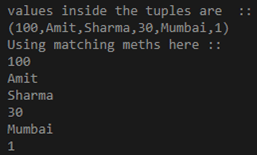
println("values inside the tuples are :: ")
println(myTuple)
//print by iterating elements of the tuples::
println("Using matching meths here ::")
myTuple.productIterator.foreach{x=>println(x)}
}Output:
Conclusion
In scala tuples, we can store heterogeneous elements. These elements are of different types. But they have their limits for element strings in Scala. We can store up to 22 element maximum. We can use nested tuples instead.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Scala Tuples” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

