Updated March 15, 2023
Introduction to SAS Grid
SAS Grid is a type of manager support. It is most widely used to distribute or spread the user tasks across multiple computers through the network connection, enabling the workload balance to accelerate the data process. The job schedules is more flexible and sophisticated on the grid computing, which already has a centralized environment with peak areas, and computing demands cost efficiency and reliability.
Key Takeaways
- It distributes the n number of tasks to multiple computers on the same network.
- It enabled the workforce load balancing algorithm to process the accelerated jobs and schedules.
- It is a more flexible and centralized one.
- It has faster data processing in the migrated environment.
- To increase power and save money.
What is SAS Grid?
In SAS Enterprise guide, the architecture is mainly called and used for sharing multiple computer resources via a network. It acts as the manager role, so it’s named SAS Grid Manager, which provides:
- The load balancing algorithm.
- Application connectivity access like Policy enforcement and more resource allocation.
- Prioritization is highly available in the analytical environment.
It needs several types of machines, which looks like a cluster setup across the same network, and it has several software products. Using the server-side load balancing algorithm, it used the workspace server, which sends the job at a busy set of nodes through config via if the grid is available, the project is configured, or else the grid is configured to a specific set of tasks that already run on the grid table.
SAS Grid Computing
SAS Grid manager, which delivers the load balancing algorithm available on all the set of work tasks and high availability with faster when compared to other computing environments. The cluster is the set or group of computers with their efficiency and specifications across the networks. Workload is also split up of each computer, and it is called the tasks with the help of Workload balancing algorithm for sharing the resource pool and accelerated processing for allowing multiple users with the same sharing datas.
The grid enabled the user tasks as the subtasks for running across the parallel set of computing resources which completes faster when compared to other data resources. We can also schedule the user jobs performed or act as the daily routine tasks with the same shared resource pool for the appropriate time.
The workload distribution helps to enable the functionality of the SAS grid as the below:
- Workload Balancing: Mainly, it enables the n number of users that are more than 1 user to be performed in the SAS environment, which distributes the data workload to the shared resource pool.
- Accelerated Processing: It helps to distribute tasks similar to subtask child processes, so it splits the SAS single job into a shared resources pool.
- Scheduling Jobs: The jobs allowed users to route the shared resources pool at the exact scheduled time.
SAS Grid Legacy
- The grid legacy mainly enabled the users for computing to develop the shared environment and control the larger volume of data that processed and analyzed the program code.
- It helps fast the code, which accomplishes the user dynamics to reload the data load resources to balance the split and multiple nodes.
Steps to Create SAS Grid
Given below are the steps mentioned:
1. Navigate to the below URL.
https://welcome.oda.sas.com/login
2. And paste the below code for to create the grid table.
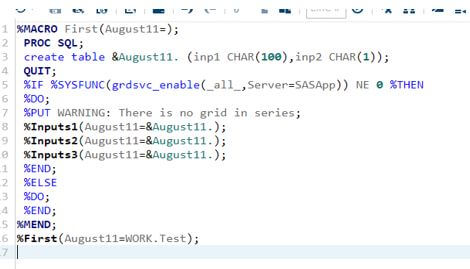
3. %MACRO First(August11=);
4. PROC SQL;
5. create table &August11. (inp1 CHAR(100),inp2 CHAR(1));
6. QUIT;
7. %IF %SYSFUNC(grdsvc_enable(_all_,Server=SASApp)) NE 0 %THEN
8. %DO;
9. %PUT WARNING: There is no grid in series;
10. %Inputs1(August11=&August11.);
11. %Inputs2(August11=&August11.);
12. %Inputs3(August11=&August11.);
13. %END;
14. %ELSE
15. %DO;
16. %END;
17. %MEND;
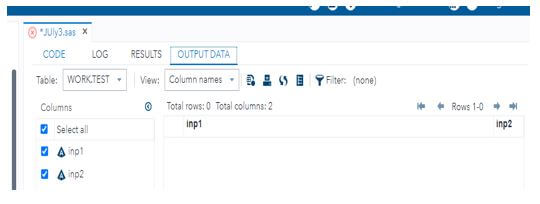
18. %First(August11=WORK.Test);
19. In the above code we used Macro for initializing and created the table like &August11 with 2 input parameters.
SAS Grid on AWS
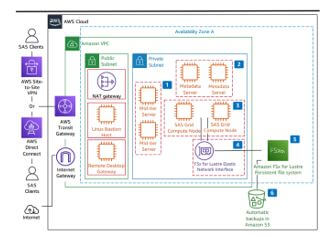
SAS on AWS is one of the run time environments for allowing the organizations which deployed the application on either open source or some other feature in the SAS models. We used the data infrastructure to support the wide variety of analytics the patterns will support the AWS devops. For mid-tier architecture, we used Amazon EC2 or r5 instances and types to load the data share client contents by using two or more number of instances in the SAS requirement. Unless we used high availability metadata servers in the EC2 instance types which exceed the minimum requirement from SAS memory recommendations.
The above diagram explains about the AWS cloud in the SAS platform through the Gateway and the amazon VPC[Virtual Private Cloud].
Example of SAS Grid
Given below are the examples mentioned:
Code:
%MACRO Second(vars=, AUgust11= );
PROC SQL;
create table &AUgust11. (inps1 CHAR(25),inps2 CHAR(3));
QUIT;
%IF %SYSFUNC(grdsvc_enable(_all_,Server=SASApp)) NE 0 %THEN
%DO;
%PUT WARNING: There is no grid table on this series;
%a(AUgust11=&AUgust11.);
%b(AUgust11=&AUgust11.);
%c(AUgust11=&AUgust11.);
%END;
%ELSE
%DO;
%PUT WARNING: Its Grid and used parallel macros;
%IF %UPCASE(&vars.) = WORK %THEN
%DO;
%PUT ERROR: Specified Work is not shared in RSUBMITs;
%GOTO Finish;
%END;
%methd(d=aug11,g=&vars.);
%methd(e=aug12,h=&vars.);
%methd(f=aug13,i=&vars.);
PROC SQL;
CREATE TABLE aug11.AUgust11 AS SELECT * FROM &AUgust11.;
CREATE TABLE aug12.AUgust11 AS SELECT * FROM &AUgust11.;
CREATE TABLE aug13.AUgust11 AS SELECT * FROM &AUgust11.;
QUIT;
%END;
%Finish:
%MEND;
LIBNAME Sandboxtesting '\\MyNetwork\';
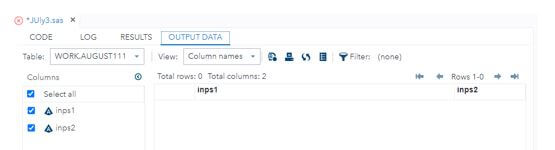
%Second(vars=Sandboxtesting, AUgust11=WORK.August111);Output:
Explanation:
- In the above example, we created SAS grid by using the macro along with procedure SQL.
- By using IF and another conditional statement we can validate the inputs.
- Table will be created for each session with parallel macros.
- Network location is shared at the end of the method.
FAQ
Given below are the FAQs mentioned:
Q1. What is SAS Grid?
Answer:
The computing tasks are split into sub-tasks and assigned to multiple PCs with the network.
Q2. How SAS Grid works?
Answer:
By using the workload the SAS grid will be enabled and operated in the environment.
Q3. What are the advantages of SAS Grid?
Answer:
- Load Balancing
- Policy Enforcement
- Time Saving
- Money Saving
- Efficient Resource Allocation
Q4. Define Grid Manager.
Answer:
It’s a web-based tool to monitor the resources, users, and jobs which already scheduled.
Q5. What is SAS Grid Server?
Answer:
It serves as an intermediate between the SAS application and grid environment.
Conclusion
The SAS grid helps to convert the existing codes to the parallel processing system on the remote sessions like a straightforward approach. By using SAS keywords like RSUBMIT, %SYSLPUT, INHERITLIB are handled, and executing the macros for merging datasets without causing any errors. More complexities exist, and parallel processes will be used by the SAS Grid to perform independent and synchronized data operations.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to SAS Grid. Here we discuss the introduction, SAS grid computing and legacy, example, and FAQ respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –