Introduction to SAS Format
The SAS format is one of the statements that can be used to declare and assign the values like numeric, date, and characters for performing the operations with the help of these types of user inputs and the steps for permanently associated with the data format variables to operate the SAS changes with the descriptor information when we used data set in the variable contains it uses BEST w. format is the default format of the number type.
Overview of SAS Format
We use SAS informats and formats and will review the n number of internal informats and formats that provides the data readable into the SAS. Mainly it gives the format inputs and outputs for pitfalls to watching, reading, and formatting the datas from the external files called the flat files, which include the text files, ASCII files, and other sequential files. It informats instructs the datas to the SAS and reads the datas into SAS variables into different categories like character, numeric, and date/time formats. Informats are named, which include the syntax characters like $Informatw. INFORMATw.d for Numeric Informats and Date/Time Informats on the INFORMATw. The $ indicates the character for the Informat, which refers to the SAS informat name.
Creating SAS Format
The SAS informats are in the DATA type of the step codes, which include the conjunction with the input statements to read the data into the SAS variables. It will consist of the hypothetical data file containing the credit card transaction datas and other safety confidential datas to list the records for separate transactions with a set of variables. The w indicates the width of the variable, and the d denotes the numeric datas to specify the number of digits to the right of the decimal places. All informats must contain the decimal point to differentiate the SAS informat variable. The Asian characters and Hebrew characters provide the large number of informats that is available on the SAS help and documentation for reviewing the most common informats for reading unusual datas.
SAS informats of the data step codes in conjunction with the input statements for reading the datas into the SAS type of variables will look at the hypothetical data files because each datas of the list files will maintain as a separate record for the hypothetical transaction data file with constant and other identifier variables for the transaction data sets. We informats and format the shared set of common patterns for reading the input data, including the writing set of values. The main difference is whether we applied the same interpretation stage to the formats and informats.
Steps to Create SAS Format
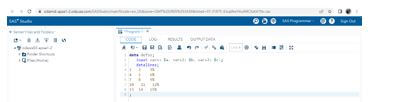
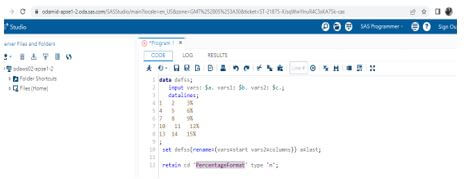
1. First, we need to create the temporary data set node with named scales like the one below.
2. Next, we can pass the inputs to the control data sets by using the command like CTRL and setting the variable label and lengths.
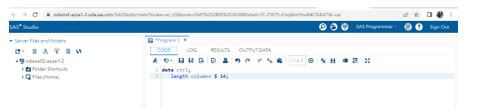
3. We can then rename the variables and create the file like the end of the file flags.
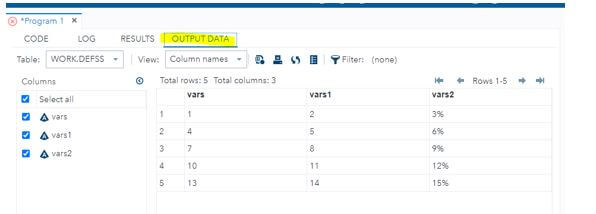
4. Create the variables from the Fmt name and will Type with the fixed values, which helps to retain the statement for more efficiency other than the assignment statement of the cases.
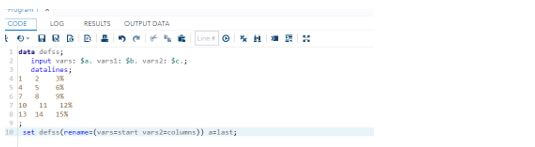
5. We can get and observe the output by using the data set with the help of the output tab.
SAS Format Character
The character format is one of the formats that can be used to cover the special characters with the variable in the SAS data set. It’s an in-built character format, denoted as the $UPCASEw format, and can be used as the can-format, and it converts all the letter characters in the variable upper case. Informats and formats will share common design patterns for reading and writing sets of data values with different sets and apply them at the interpretation changes.
Example #1
Code:
DATA emps;
SET examples;
FORMAT emp_birthdate MMDDYY10.;
RUN;Output:
Example #2
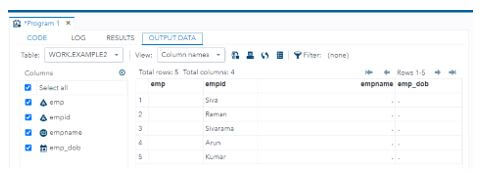
Code:
INPUT emp $ empid $ empname 3. emp_dob MMDDYY10.;
FORMAT emp_dob MMDDYY8.;
DATALINES;
Siva IT 01 10/05/1989
Raman CSE 02 11/05/1989
Sivaraman Accounts 03 12/05/1989
Arun Engineering 04 13/05/1989
Kumar Development 05 14/05/1989
;
RUNOutput:
SAS Format Numeric
It is the other type of SAS format; it has two types: informat and output format. Suppose an informat is specified for how SAS should access and read the data with the output format of the layout specification for how the variable data should be displayed in the output console screen. It has many internal informats and output formats in SAS, similar to applying the data output of the SAS program with a maximum number of digits in no decimal point. The zeros will be appended if the number of digits calculated after the decimal point is less than that of the format specifier. If several digits are used after the decimal point is more significant than the format specifier, then the values will be rounded off.
Example #1
Code:
input a 2.;
format b 4.5;
datalines;
1234
56.7
.8910
11.234
PROC PRINT DATA = Example3;
RUN;Example #2
Code:
input a 6.;
format b 5.2;
datalines;
2134
56.7
.8901
32.6543
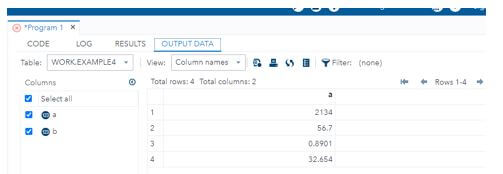
PROC PRINT DATA = Example4;
RUN;
DATA Example5;
input a 6.;
format b DOLLAR10.2;
datalines;
5432
12.6
.7890
42.321
PROC PRINT DATA = Example5;
RUN;Output:
Format Date
When SAS source data can be read and properly using the specific date informats with the digits at the end of the informat to indicate the date’s minimum range width, the strings to be read are completely used at the informat type and will give the exact set of results.
Example
Code:
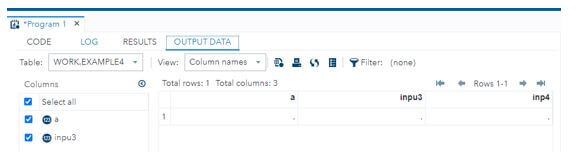
INPUT @1 a inp12. @23 inpu3 vars123. @45 inp4 mmddyy12. ;
DATALINES;
10-may-1989 4/01/1990 6/03/1991
;
PROC PRINT DATA = Example4;
RUN;Output:
Conclusion
The SAS format is one of the features used to read the variable data, whereas the format will use the SAS to display and write the values of the specified variable. In both format and informats, read the sample set of datas for creating the cards and datalines statement to read the user inputs.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to SAS Format. Here we discuss the introduction, steps to create SAS format, character, numeric, and date. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –