Updated March 13, 2023

Introduction to PowerShell Write to File
The following article provides an outline for PowerShell Write to File. There are various scenarios in which the output generated needs to be written to a file. For example, it can be for documentation purposes, error logging or for debugging purposes. There are multiple ways in which output can be written to a file in PowerShell, and there are cmdlets for generating various types of files such as text, csv, xml or html files.
Different Cmdlet
Given below are the different cmdlets, their parameters and usage in detail, along with appropriate examples.
1. Out-File
This is a basic cmdlet which sends the output to a file of the user’s choice. By default, it uses the inbuilt formatting mechanism to generate the output file. The output is written in the same format as to how it is displayed in the console.
Syntax:
Out-File [-FilePath] <string> [[-Encoding] <Encoding>] [-Append] [-Force] [-NoClobber] [-Width <int>] [-NoNewline] [-InputObject <psobject>] [-WhatIf] [-Confirm] [<CommonParameters>]
Parameters:
- -Append: This adds the output to the existing file. The data type of this parameter is a switch. None is the default value. This parameter does not recognize pipeline input; also, wild card characters are not permitted.
- -Confirm: This ensures that user confirmation is received before the cmdlet is run. The data type of the parameter is a switch. Cf is the alias of this parameter. False is the default value. This parameter does not recognize pipeline input; also, wild card characters are not permitted.
- -Encoding: This denotes the encoding mechanism that should be used by PowerShell while generating the output file. The various types of encoding are as follows: ascii, utf32, utf8BOM, utf8NoBOM, utf7, utf8, oem and Unicode. The default value is utf8NoBOM. The datatype of this parameter is Encoding. This parameter does not recognize pipeline input; also, wild card characters are not permitted.
- -FilePath: This represents the location of the output file. The data type of this parameter is a string. Its alias is the path. None is the default value. This parameter does not recognize pipeline input; also, wild card characters are not permitted.
- -Force: This parameter is used to overwrite an existing read-only file. A switch is the data type of this parameter. None is the default value. This parameter does not recognize pipeline input; also, wild card characters are not permitted.
- -InputObject: It represents the objects that need to be sent to the output file. It can be a variable which holds objects or an expression whose result is a collection of objects. The data type of this parameter is PSObject. None is the default value. This parameter recognizes pipeline input, but wild card characters are not permitted.
- -LiteralPath: This also represents the location of the output file. A string is the data type of this parameter, and its aliases are PSPath and LP. None is the default value. This parameter recognizes pipeline input, but wild card characters are not permitted.
- -NoClobber: This is used for preventing overwriting of files. If the output file exists, a message is displayed. If this is not used, then the file is overwritten. The data type of this parameter is a switch. The default value is none. This parameter does not recognize pipeline input; also, wild card characters are not permitted.
- -NoNewLine: This is used to prevent new lines from getting inserted into the output. No newlines are added. The data type of this parameter is a switch. None is the default value. This parameter does not recognize pipeline input; also, wild card characters are not permitted.
- -Width: This represents how many characters should be there in each line of output. If the length exceeds this limit, those characters are truncated. The default limit is 80. Therefore, the data type of this parameter is 80. None is the default value. This parameter does not recognize pipeline input; also, wild card characters are not permitted.
Example:
Code:
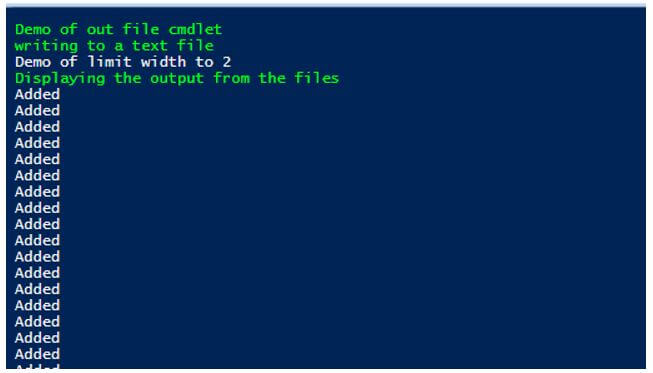
Write-Host "Demo of out file cmdlet" -ForegroundColor Green
Write-Host "writing to a text file" -ForegroundColor Green
for($i=0;$i -le 10; $i++)
{
$out="Added" | Out-File -FilePath C:\vignesh\demo.txt -Append
}
Write-Host "Demo of limit width to 2"
for($i=10000;$i -le 10010; $i++)
{
$out="Added" | Out-File -FilePath C:\vignesh\demo1.txt -Append -Width 2
}
Write-Host "Displaying the output from the files" -ForegroundColor Green
Get-Content -Path "C:\vignesh\demo.txt"
Get-Content -Path "C:\vignesh\demo1.txt"
Output:
2. Set-Content
This cmdlet is also like add-content, except that it overwrites the file’s existing contents and won’t append.
Syntax:
Set-Content [-Path] <string[]> [-Value] <Object[]> [-PassThru] [-Filter <string>] [-Include <string[]>] [-Exclude <string[]>] [-Force] [-Credential <pscredential>] [-WhatIf] [-Confirm] [-NoNewline] [-Encoding <Encoding>] [-AsByteStream] [-Stream <string>] [<CommonParameters>]
Parameters:
- -Confirm: This ensures that user confirmation is received before the cmdlet is run. The data type of the parameter is a switch. Cf is the alias of this parameter. False is the default value. This parameter does not recognize pipeline input; also, wild card characters are not permitted.
- -Encoding: This denotes the encoding mechanism that should be used by PowerShell while generating the output file. The various types of encoding are as follows: ascii, utf32, utf8BOM, utf8NoBOM, utf7, utf8, oem and Unicode. The default value is utf8NoBOM. The datatype of this parameter is Encoding Pipeline input is not recognized by this parameter also wild card characters are not permitted.
- -FilePath: This represents the location of the output file. The data type of this parameter is a string. Its alias is the path. None is the default value. This parameter does not recognize pipeline input; also, wild card characters are not permitted.
- -Force: This parameter is used to overwrite an existing read-only file. A switch is the data type of this parameter. None is the default value. This parameter does not recognize pipeline input; also, wild card characters are not permitted.
Example:
Code:
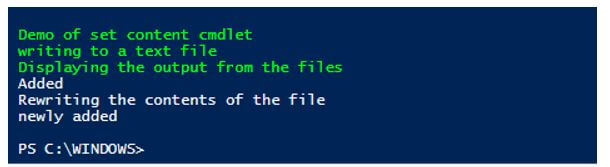
Write-Host "Demo of set content cmdlet" -ForegroundColor Green
Write-Host "writing to a text file" -ForegroundColor Green
for($i=0;$i -le 10; $i++)
{
$out="Added" | Set-Content -Path C:\vignesh\demo.txt
}
Write-Host "Displaying the output from the files" -ForegroundColor Green
Get-Content -Path "C:\vignesh\demo.txt"
Write-Host "Rewriting the contents of the file"
$out="newly added" | Set-Content -Path C:\vignesh\demo.txt
Get-Content -Path "C:\vignesh\demo.txt"
Output:
Conclusion – PowerShell Write to File
Thus, the article explained in detail about how writing to a file is done in PowerShell. It explained the various methods, their parameters and syntax, along with appropriate examples. This can be learnt in detail by writing and practicing sample scripts.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell Write to File. Here we discuss the introduction and different cmdlet for a better understanding. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –