Updated March 6, 2023
Introduction to PowerShell print
Writing output to the console or a file is an important requirement of any language. The output can generally be a single line, multi-lines or an expression or result of an expression. Printing values can also be used for debugging or as part of an error handling mechanism. There are multiple ways of printing output in PowerShell. Some of the ways in PowerShell to print are Write-Output, Write-Host, Write-Verbose, Write-Warning and Write-Error.
Different Ways of Printing Output in PowerShell
Given below are the different ways of printing output in PowerShell:
1. Write-Output
The first method of printing output is using the Write-Output cmdlet. This cmdlet is used to pass objects in the pipeline to the successive commands. In case of the command being last, the final object is written to the console. To pass on error objects, Write-Error cmdlet is used.
Syntax:
Write-Output [-InputObject] <PSObject[]> [-NoEnumerate] [<CommonParameters>]
Parameters:
- -InputObject: This denotes the objects that should be passed through the pipeline. It can be an expression, a variable of objects or an expression. The datatype of this parameter is PSObject[]. Its default value is none. It accepts pipeline input but doesn’t accept wildcard characters.
- -NoEnumerate: The write-output cmdlet by default enumerates the output. To avoid that, this parameter is used. The datatype of this parameter is Switch. None is the default value. It doesn’t accept pipeline input, as well as wildcard characters, which are also not permitted.
Example:
Code:
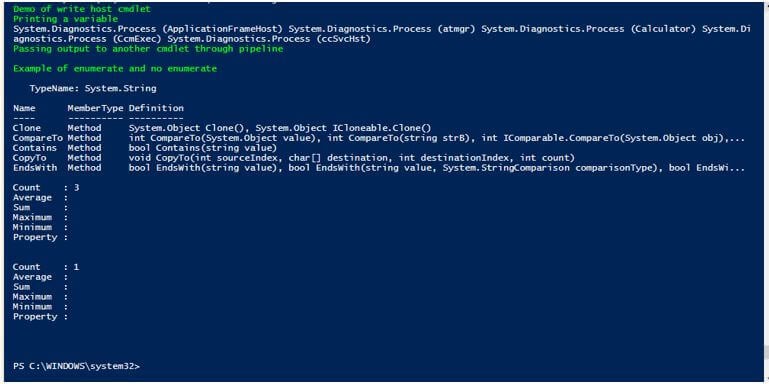
Write-Host "Demo of write host cmdlet" -ForegroundColor Green
$test= Get-Process
Write-Host "Printing a variable" -ForegroundColor Green
Write-Output $test
Write-Host "Passing output to another cmdlet through pipeline" -ForegroundColor Green
Write-Output "sample output" | Get-Member
Write-Host "Example of enumerate and no enumerate" -ForegroundColor Green
Write-Output 10,20,30 | Measure-Object
Write-Output 10,20,30 -NoEnumerate | Measure-Object
Output:
2. Write-Host
The primary usage of this cmdlet is to display the output in different colours. This works along with the read-host cmdlet, which retrieves the input from the user. This cmdlet uses the ToString() method to generate and write the output to the console. We can specify both the text color and background color of the output using the foreground and background parameters respectively. To separate the various objects in the output, a separator parameter is present as part of the cmdlert. There are two variables; $informationpreference and $Informationaction parameters that are associated with this parameter, but they don’t affect the output.
Parameters:
- -BackgroundColor: This denotes the color of the background. There is no default color. Some of the values are grey, green, blue, red, white, dark green, dark blue and magneta. The datatype of this parameter is console color. It doesn’t accept pipeline input, and wild card characters are also not permitted.
- -Foregroundcolor: This denotes the color of the text. There is no default color. Some of the values are grey, green, blue, red, white, dark green, dark blue and magneta. The datatype of this parameter is console color. It doesn’t accept pipeline input, and wild card characters are also not permitted.
- -NoNewLine: This denotes that all the output is written on the same line, and no newline is inserted between the outputs. The data type of the parameter is a switch. The default value is none. It doesn’t accept pipeline input, and wild card characters are also not permitted.
- -Object: This denotes the object to be written as output. The data type of this parameter is an object. The alias for this parameter is Msg and message. This is a mandatory parameter. The default value is none. It accepts pipeline input, whereas wild card characters are not permitted.
- -Separator: This denotes the separator to be inserted between objects. The data type of this parameter is an object. The default value is none. It doesn’t accept pipeline input, and wild card characters are not permitted.
Example:
Code:
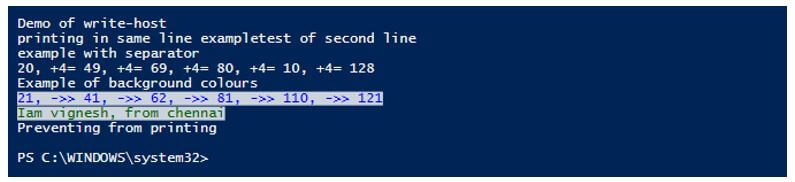
Write-Host "Demo of write-host"
Write-Host "printing in same line example" -NoNewline
Write-Host "test of second line"
Write-Host "example with separator"
Write-Host (20,49,69,80,10,128) -Separator ", +4= "
Write-Host "Example of background colours"
Write-Host (21,41,62,81,110,121) -Separator ", ->> " -ForegroundColor Blue -BackgroundColor White
Write-Host "Iam vignesh, from chennai" -ForegroundColor DarkGreen -BackgroundColor white
Write-Host "Preventing from printing"
Write-Host "this wont be displayed" -InformationAction Ignore
Write-Host "it wont be available on screen" 6>$null
Output:
3. Write-Debug
This is used for printing debug message in the console from a script or command. By default, the messages are not displayed but can be displayed whenever needed using the $debugPreference variable.
Syntax:
Write-Debug [-Message] <String> [<CommonParameters>]
Parameters:
- -Message: This denotes the debug message that needs to be displayed. The data type of this parameter is a string. This is a mandatory parameter. The alias of this parameter is msg. None is its default value. It accepts pipeline input, but wild card characters are not permitted.
Example:
Code:
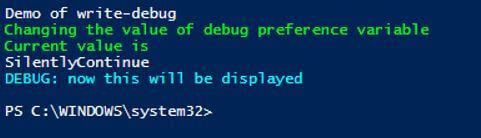
Write-Host "Demo of write-debug"
Write-Debug "This wont be printed"
Write-Debug "my name is vignesh"
Write-Host "Changing the value of debug preference variable" -ForegroundColor Green
Write-Host "Current value is" -ForegroundColor Green
$DebugPreference
Write-Debug "wont print this on console"
$DebugPreference = "Continue"
Write-Debug "now this will be displayed"
Output:
4. Write-Verbose
The Write-Verbose cmdlet writes text to the verbose message stream in PowerShell. Typically, the verbose message stream is employed to deliver more thorough information about command processing. By default, the verbose message stream isn’t displayed but can be displayed by changing the worth of the $VerbosePreference variable or using the Verbose common parameter in any command.
Syntax:
Write-Verbose [-Message] <String> [<CommonParameters>]
Parameters:
- -Message: This denotes the message that needs to be displayed. This is a mandatory parameter. The data type of this parameter is a string. The alias is msg. The default value is none. It accepts pipeline input, but wild card characters are not permitted.
Example:
Code:
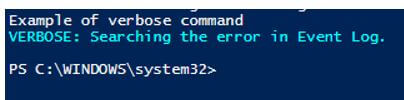
Write-Host "Example of verbose command"
Write-Verbose -Message "Searching the error in Event viewer."
Write-Verbose -Message "Searching the error in Event viewer." -Verbose
Output:
Conclusion – PowerShell print
Thus, the article covered in detail about printing in PowerShell. It explained in detail about the various ways in which output can be printed along with appropriate examples.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell print. Here we discuss the introduction and different ways of printing output in PowerShell. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –