Updated March 6, 2023
Introduction to PowerShell Join-Path
The following article provides an outline for PowerShell Join-Path. There may be scenarios where a user might want to combine two paths into a single path; in that case, the user should use the join-path cmdlet. There will be one parent path, and multiple child paths can be appended to the parent path to create a new path. This can be used with several of the providers such as registry, filesystem and certificates, to name a few. The path parameter manipulates and returns the path in a format that is easily recognizable by PowerShell. Here we will see in detail about the various parameters and ways of joining multiple paths.
Syntax of PowerShell Join-Path
The syntax of the Join-Path cmdlet is as follows:
Name:
Join-Path
Syntax:
Join-Path [-Path] <string[]> [-ChildPath] <string> [-Resolve] [-Credential <pscredential>] [-UseTransaction]
[<CommonParameters>]
Aliases:
None
Example:
Code:
Write-Host "Demo of join path" -ForegroundColor Green
$path1="test"
$path2="test1"
Write-Host "Path one is " $path1
Write-Host "Path two is" $path2
Write-Host "Combined path is" -ForegroundColor Green
Join-Path -Path $path1 -ChildPath $path2
Output:

Parameters:
- -AdditionalPath: The datatype of this parameter is String[]. This represents the extra values that need to be added to the path. Even though this parameter is optional and specified, the child path parameter must be presented with a value. An indefinite number of paths can be joined using this parameter. The position of this parameter in the cmdlet is 2. None is the default value of this parameter. It accepts pipeline input, but this parameter does not support wildcard characters.
- -ChildPath: This parameter is mandatory. This represents a value that will be appended with the path parameter’s value. Its position in the cmdlet is one. The datatype of this parameter is a string. None is its default value. It accepts both wildcard characters and pipeline input.
- -Credential: This parameter is used only for impersonation purpose. The datatype is of PSCredential, and it’s an optional one. The default value is none. This can accept pipeline input, whereas wild card characters are not allowed.
- -Path: This represents the main path value to which the child paths will be appended. This is a mandatory parameter. The datatype is String[], and its alias is PSPath. The position of this parameter inside the cmdlet is 0. The default value is none. It accepts both pipeline input, and wild card characters are also permitted.
- -Resolve: This denotes to the cmdlet that the current provider should be used to resolve the joined path. In case if wild cards are supplied the cmdlet returns all the path that aligns with the joined path. If wildcards are not used, in case of no match, an error is thrown. The datatype of this parameter is a switch. This is an optional parameter. The default value is none. It doesn’t accept pipeline input and wild card characters.
Examples of PowerShell Join-Path
Given below are the examples of PowerShell Join-Path:
Example #1
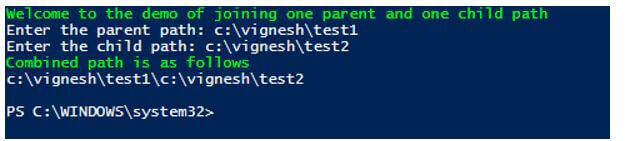
Joining one parent path and one child path.
Code:
Write-Host "Welcome to the demo of joining one parent and one child path" -ForegroundColor Green
$parentpath=Read-Host "Enter the parent path"
$childpath= Read-Host "Enter the child path"
Write-Host "Combined path is as follows" -ForegroundColor Green
Join-Path -Path $parentpath -ChildPath $childpath
Output:
Example #2
Display contents of the combined path using resolve and wild card characters.
Code:
Write-Host "Demo of using resolve parameter" -ForegroundColor Green
Write-Host "Demo of providing wild card matches in both parent and child" -ForegroundColor Green
$parent= Read-Host "Enter the parent path with wildcard"
$childp= Read-Host "Enter the child path with wildcard"
Write-Host "Display the contents using the join-path" -ForegroundColor Green
Join-Path $parent $childp -Resolve
Output:
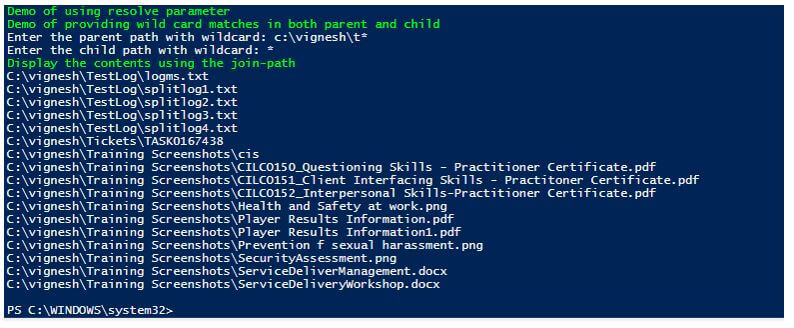
In the above example, the parent path is provided with a value c:\vignesh\t*, which means inside the Vignesh folder, whatever subfolder that starts with t is considered as parent value in the child path “*” is given, which denotes everything. Hence the output is a display of a list of all files that matches the condition.
Example #3
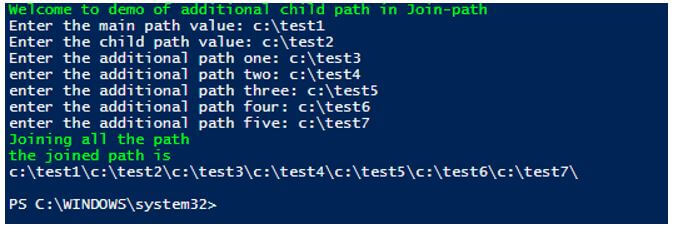
Usage of Additional Path Parameter.
Code:
Write-Host "Welcome to demo of additional child path in Join-path" -ForegroundColor Green
$mainpath= Read-Host "Enter the main path value"
$cpath= Read-Host "Enter the child path value"
$apath1= Read-Host "Enter the additional path one"
$apath2 = Read-Host "enter the additional path two"
$apath3 = Read-Host "enter the additional path three"
$apath4 = Read-Host "enter the additional path four"
$apath5 = Read-Host "enter the additional path five"
Write-Host "Joining all the path" -ForegroundColor Green
$path = Join-Path -Path $mainpath -ChildPath $cpath -AdditionalChildPaths($apath1, $apath2,$apath3,$apath4,$apath5)
Write-Host "the joined path is" -ForegroundColor Green
Output:
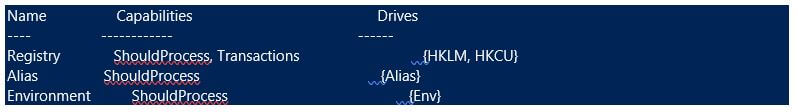
To find the list of providers supported by this cmdlet, we can run the get-psprovider cmdlet to identify those.
The below are the providers that are supported in the current session:

Example #4
Joining multiple paths using the pipeline.
Code:
Write-Host "Welcome to demo of joining path using pipeline input" -ForegroundColor Green
$mainpath= Read-Host "Enter the main path value"
$cpath= Read-Host "Enter the child path value"
$apath1= Read-Host "Enter the additional path one"
$apath2 = Read-Host "enter the additional path two"
$apath3 = Read-Host "enter the additional path three"
$apath4 = Read-Host "enter the additional path four"
$apath5 = Read-Host "enter the additional path five"
Write-Host "Joining all the path using pipeline input" -ForegroundColor Green
Join-Path $mainpath | Join-Path -ChildPath $cpath | Join-Path -ChildPath $apath1 | Join-Path -ChildPath $apath2 | Join-Path -ChildPath $apath3 | Join-Path -ChildPath $apath4 | Join-Path -ChildPath $apath5
Output:
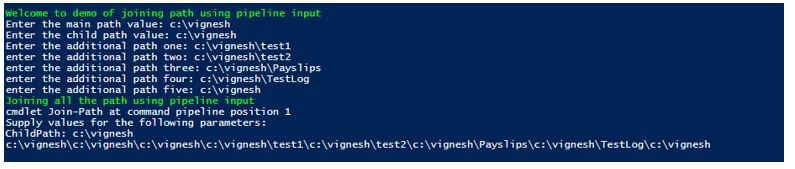
While joining, in the above cmdlet, if the child path parameter is specified, an error saying the cmdlet doesn’t accept pipeline input will be thrown. For that to not happen, from the second path, all the paths must be preceded with the child path parameter.
Conclusion
Thus, the article covered details about the Join-Path cmdlet and its various mandatory and optional parameters. It also showed with various examples of concatenation paths in different ways using the Join-Path cmdlet.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell Join-Path. Here we discuss the introduction and examples of PowerShell Join-Path for better understanding. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

