Updated March 13, 2023

Introduction to PowerShell Get-ADGroup
The following article provides an outline for PowerShell Get-ADGroup. The Get-ADGroup cmdlet is used to fetch information about one or more Active directory groups. A group can be identified in many ways like using its Distinguished name, GUID of the group, SID of the group or SAM account name. In scenarios that involve retrieving multiple Active directory groups Filter or LDAPFilter is used. The queries used by the filter condition are written using the PowerShell expression language which supports type conversion to different types.This
Syntax of PowerShell Get-ADGroup
Given below are the syntax of the Get-ADGroup cmdlet:
Get-ADGroup [-AuthType <ADAuthType>] [-Credential <PSCredential>] -Filter <String> [-Properties <String[]>] [-ResultPageSize <Int32>] [-ResultSetSize <Int32>] [-SearchBase <String>] [-SearchScope <ADSearchScope>] [-Server <String>] [<CommonParameters>]
Get-ADGrou [-AuthType <ADAuthType>] [-Credential <PSCredential>] [-Identity] <ADGroup> [-Partition <String>] [-Properties <String[]>] [-Server <String>] [<CommonParameters>]
Get-ADGroup [-AuthType <ADAuthType>] [-Credential <PSCredential>] -LDAPFilter <String> [-Properties <String[]>] [-ResultPageSize <Int32>] [-ResultSetSize <Int32>] [-SearchBase <String>] [-SearchScope <ADSearchScope>] [-Server <String>] [<CommonParameters>]
Parameters:
1. Credential: This alludes to the client account that will be utilized to run the cmdlet. By default, the qualifications of the current client are considered unless the cmdlet is run from the active directory drive. In such a situation, the account that’s related to the drive is considered. Either a username or PSCredential is provided as esteem to the parameter. In case a username is indicated, a prompt is given for the password. The account indicated ought to have directory-level authorization else the cmdlet will come up with an error message. Its sort is PSCredential. The parameter cannot acknowledge pipeline input and wild card characters are too not permitted.
2. Authtype: This signifies the verification strategy to be utilized to put through to the active directory. It can be either of two values, negotiate(0) or basic(1), with negotiate being the default authentication mode. An SSL association is required for the basic authentication mechanism to work. The sort of param is ADAuthType. It doesn’t acknowledge pipeline input; wildcard characters are too not permitted.
3. Identity: This is an obligatory parameter. This indicates the Active directory group that needs to be fetched. A unique title, GUID of the client within the Dynamic registry, SID, or SAM account title can be passed as the value. The sort of this parameter is ADGroup. Its default esteem is none. This parameter acknowledges pipeline input but doesn’t allow wild card characters.
Example of unique name:
CN=test, OU=test, CN=users, DC=corp, DC=test, DC=com
Example of GUID:
050c3d2e-f73e-4f20-8a99-030d92425f20
4. Filter: This indicates the inquiry that’s utilized to bring the objects from the Active directory. It follows the sentence structure of PowerShell express dialect. PowerShell express dialect has great type-conversion back. Its sort is a string and default esteem is none. This parameter doesn’t acknowledge pipeline input and wild card characters are too not backed.
Example:
Get-ADGroup -Filter “GroupCategory -eq’Distribution’”
Get-ADGroup -Filter “GroupScope -eq ‘Universal’”
5. LDAPFilter: This refers to the LDAP condition that is used for filtering purposes. It’s like the filter of LDAP syntax. The datatype of this parameter is a string. This parameter doesn’t acknowledge pipeline input and wild card characters are too not backed.
6. Partition: This alludes to an Active directory block. It must be the title of one of the current registry servers. This partition is looked to distinguish the question that’s alluded to by the character parameter. On the off chance that no esteem is indicated, default esteem is utilized. In case the esteem passed to the identity parameter may be a recognized title, the default esteem is naturally created from this and treated as the partition title. On the off chance that the cmdlets are run from the dynamic catalog supplier, the current way within the drive is treated as the default esteem of the segment. The information sort for this parameter is a string and default esteem is none. Both pipeline input and wild card characters are not acknowledged by this parameter.
7. Properties: This indicates the list of properties of the Active directory protest to be returned. To recover different properties, partition them employing a comma. To recover all properties, utilize the *. The information sort of this parameter is string[]. The default esteem is none. Both pipeline input and wild card characters are not acknowledged by this parameter.
8. ResultPageSize: This signifies the number of objects to be displayed on a single page of the inquiry comes about. Its sort is int32. The default is 256. Both pipeline input and wild card characters are not acknowledged by this parameter.
9. ResultSetSize: This indicates the most extreme number of objects that ought to be returned by the inquiry. If all the properties ought to be returned, null esteem must be passed to this parameter. Its information sort is int32. Both pipeline input and wild card characters are not acknowledged by this parameter.
10. -SearchBase: This indicates the pathway beneath which the seek for the object search must happen. On the off chance that the cmdlet is run from the dynamic catalog drive, the current way of the drive is considered as the default esteem. On the off chance that the cmdlet is run from the exterior, at that point, the target’s drive is taken as default esteem. The information sort is string and default esteem is none. Both pipeline input and wild card characters are not acknowledged by this parameter.
11. SearchScope: This indicates the scope of the rummage around for the search objects. It can accept three values as Base or 0, one level or 1, and subtree or 2. Base scope searches only for the specified client. One level rummages around for the children of protest, subtree looks for all children of the said question.
12. Server: This signifies the dynamic registry to put through to. The space values can be either of FQDN or netbios title. The default esteem can be either the space where the cmdlet is run or the active directory drive server or the one that’s passed to the parameter.
Example of PowerShell Get-ADGroup
Given below is the example of PowerShell Get-ADGroup:
Code:
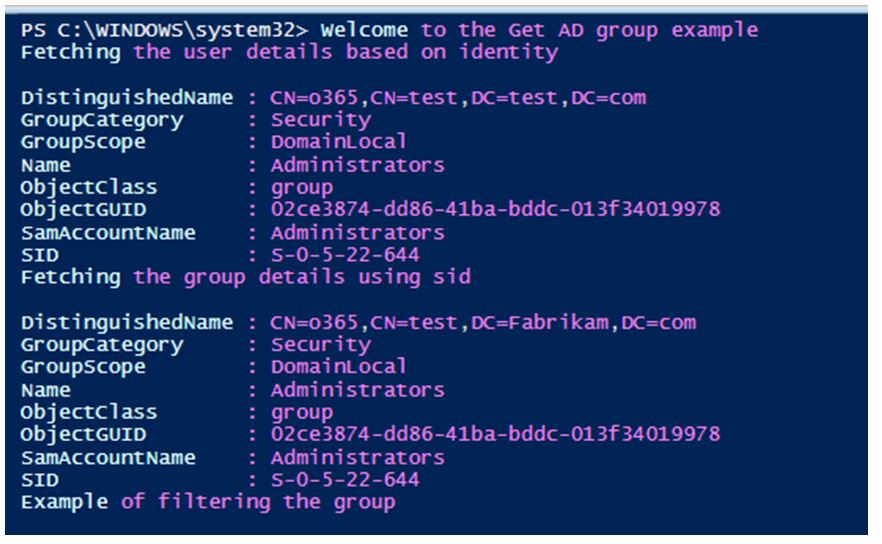
Write-Host "Welcome to the Get AD group example"
write-host "Fetching the user details based on identity"
Get-ADGroup -Identity o365
Write-Host "Fetching the group details using sid"
Get-ADGroup -Identity 'S-0-5-22-644'
write-host "Example of filtering the group"
Get-ADGroup -Filter "GroupScope -eq 'DomainLocal'"
Output:
Conclusion
In this way, the article clarified in detail approximately the Get-ADGroup cmdlet in PowerShell. It secured the parameters that are related to the cmdlet alongside channels. To memorize more in detail, it is fitting to compose test scripts and hone them.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell Get-ADGroup. Here we discuss the introduction to PowerShell Get-ADGroup along with examples respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

