Updated May 22, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL Unnest
PostgreSQL unnest is the type of array functions; the unnest function in PostgreSQL is basically used to expand the array into rows. Unnest function is converting an array into a table-like structure; we can also generate a table structure of an array using unnest function in PostgreSQL. Unnest array function is very useful in PostgreSQL for expanding the array into the set of values or converting the array into the table structure. If we need a table-like structure of array simultaneously, we have to use the unnest function on the array on which we have converted array data into the table-like structure.
Syntax:
Below is the syntax:
Unnest(Any_array_number (Any array element number which was we have used with unnest function)Unnest (Any_array_text (Any array element text which was we have used with unnest function)Select unnest (any_array (Number of text value which was used in array.))Select unnest (any_array (Number of text value which was used in array.)) limit number;Below is the parameter description syntax of Unnest array function:
- Unnest: This function we defined in PostgreSQL to set the element in a table-like structure. We have used unnest element with text as well as number array. We must define the number or text element with the unnest array function in PostgreSQL.
- Any array text: This is defined as using an array of text values to convert the array into the table-like structure in PostgreSQL by using unnest array function.
- Any array number: This is defined as a number. Using the unnest array function, we have used any number values to convert an array into the table-like structure in PostgreSQL.
- Select: This operation selects the array’s value using the unnest array function in PostgreSQL. Select operations are very useful and important while using unnest array function in PostgreSQL.
- Limit: In PostgreSQL, we have also using the limit clause with unnest function in PostgreSQL. While using the limit clause will show the number as per the limit we have used with unnest function.
How does Unnest Function work in PostgreSQL?
- It has two overloads. The first overload has obvious usefulness, and the second overload is exotic.
- The first overload of usefulness aims to transform the values from an array into a single array.
- In the old version of PostgreSQL, when we have to convert an array into the table structure, we have to use an array with the cross join. After joining the array with cross join, we generated the same series.
- After generating the series, all the array elements will be structured into the table using cross join and generate series function.
The below example shows that in the old version, we used cross join with generate series function to convert the array into the table structure.
Code:
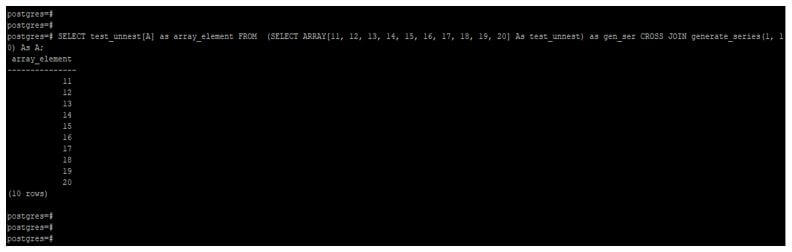
SELECT test_unnest[A] as array_element FROM (SELECT ARRAY[11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20] As test_unnest) as gen_ser CROSS JOIN generate_series(1, 10) As A;Output:
- The above example shows that we have used array element as [11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20]; we have used this array element with generate series function for converting an array into the table like structure.
- We have also used cross join with the array element and generated a series function for converting an array into a table-like structure.
- By using unnest function, we do not need to use a cross join or generate series function to convert an array into a table like structure. We have simply using unnest function with an array.
- In PostgreSQL, we have also utilised an array for a number or text to create a table-like structure.
- We can also use unnest function with an order by clause. Using an unnest function, we have an order by clause with a 1 in it.
- We have also use the limit clause with unnest function. After using a limit clause, it will show the output as per the number which was we have used with the limit.
Examples of PostgreSQL Unnest
Different examples are mentioned below:
Example #1 – Unnest function with array as a number.
Below example shows that unnest function with array as a number. In the below example, we use an array of numbers as [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10].
Code:
SELECT unnest(ARRAY[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]);Output:
Example #2 – Unnest function with array as text.
Below example shows that unnest function with array as text. In the below example, we are using an array of text as [‘ABC’, ‘PQR’, ‘XYZ’, ‘ABC’, ‘PQR’, ‘XYZ’, ‘ABC’, ‘PQR’, ‘XYZ’, ‘ABC’, ‘PQR’, ‘XYZ’].
Code:
SELECT unnest(ARRAY['ABC', 'PQR', 'XYZ', 'ABC', 'PQR', 'XYZ', 'ABC', 'PQR', 'XYZ', 'ABC', 'PQR', 'XYZ']);Output:
Example #3 – Unnest function with an order by clause.
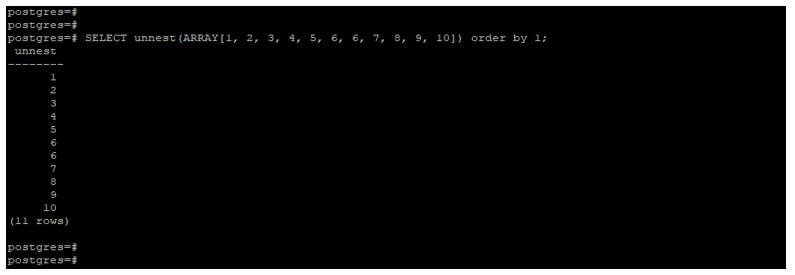
Below example shows that unnest function with an order by clause. In the below example, we use an array of numbers as [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10].
Code:
SELECT unnest(ARRAY[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]) order by 1;Output:
Example #4 – Unnest function with limit clause.
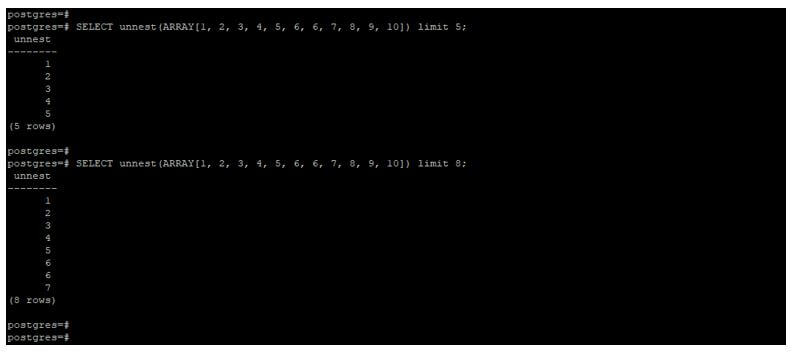
Below example shows that unnest function with a limit clause. In the below example, we use an array of numbers as [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10].
Code:
SELECT unnest(ARRAY[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]) limit 5;
SELECT unnest(ARRAY[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]) limit 8;Output:
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Unnest” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.