Updated May 10, 2023

Introduction to PostgreSQL Temporary Table
PostgreSQL has a very useful database feature that has the ability to create temporary tables for a current transaction or the database session. It is helpful in managing the unprocessed data. As the name specifies, the PostgreSQL Temporary Table has a short life span and is not getting stored permanently; every time, we have to create a temporary table for each transaction or database session. The temporary table exists in the database for a particular session duration or the current transaction. The temporary tables automatically get dropped at the end of the current transaction or the end of the database session. Other transactions and database sessions cannot see the temporary tables.
Syntax:
To create a temporary table, we have to use the CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE statement as follows:
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE temp_table_name( … );Also, we can use the TEMP keyword instead of the TEMPORARY keyword in the CREATE statement defined above and can rewrite it as follows:
CREATE TEMP TABLE temp_table_name( … );How Temporary Table Works in PostgreSQL?
- The temporary tables are invisible to other transactions and database sessions.
- The temporary tables are visible to the current transaction or database session in which we create the table.
- We can create a temporary table with the same name as a permanent table in the database, which is not recommended. The temporary table hides the permanent table and is defined with the same name until it is not dropped for the respective database session or transaction.
- We can not access the permanent table if we have a temporary table with the same name as a permanent table.
How to Create a PostgreSQL Temporary Table?
We can use the TEMP or TEMPORARY keyword with the CREATE table statement to create a temporary table.
Consider the following example, which creates two tables, ‘student’ and ‘teacher’, with the help of TEMP and TEMPORARY keyword with CREATE TABLE statements, respectively.
1. With the TABLE Keyword
CREATE TEMP TABLE student(stud_id serial NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY, stud_name VARCHAR(80));Illustrate the created table using the above statement with the help of the following statement and syntax:
select * from student;2. With TEMPORARY Keyword
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE teacher(teacher_id serial NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY, teacher_name VARCHAR(80));Illustrate the created table using the above statement with the help of the following statement and syntax:
Select * from teacher;Now, consider that we have one table named ‘users’ that already exists in the database, which is a permanent table.
We will create the permanent ‘users’ table by using the following CREATE table statement.
CREATE TABLE users(id int, name VARCHAR(80));Now, we will add some data into the permanent ‘users’ table. The following INSERT INTO statement will add some records to the permanent ‘users’ table.
INSERT INTO users(id, name) VALUES (1,'Oliver'), (2,'Jake'), (3,'Harry');Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot and SQL statement.
Select * from users;Output:

We will create a temporary table with the same name, ‘users,’ as the permanent table we have created.
We will create the temporary ‘users’ table by using the following CREATE table statement.
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE users(id int, name VARCHAR(80));Now, we will add some data into the temporary ‘users’ table. The following INSERT INTO statement will add some records in the temporary ‘users’ table.
INSERT INTO users(id, name) VALUES (4, 'Callum');Now we have a users table which is permanent as well as temporary, but in PostgreSQL, the temporary table hides the definition of the permanent table within the transaction or database session.
Using the following statement, we will try to get all records from the user’s table.
select * from users;Output:
Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot.
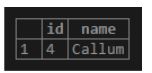
In the above snapshot, we can see the result set returned is from the temporary user’s table, not from the permanent user’s table.
How to Insert Data in PostgreSQL Temporary Table?
We will add some data to a temporary table created in the CREATE TABLE section.
The following INSERT INTO statement will add some records in both the ‘student’ and ‘teacher’ tables.
INSERT INTO student(stud_name) VALUES ('Oliver'), ('Jake'), ('Harry'), ('Callum');Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot and SQL statement.
select * from student;Output:
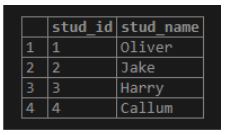
INSERT INTO teacher(teacher_name) VALUES ('Jack'), ('Connor'), ('Jacob'), ('John');Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot and SQL statement.
select * from teacher;Output:
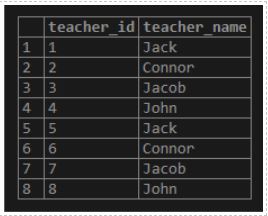
How to Delete PostgreSQL Temporary Table?
In order to drop a temporary table, we use the DROP TABLE statement as follows.
DROP TABLE temp_table_name;Consider the following example, which will delete both the ‘student’ and ‘teacher’ tables created in the CREATE table section above:
The following statement will delete the student table.
DROP TABLE student;The following statement will delete the teacher table.
DROP TABLE teacher;It is unnecessary to mention the TEMP or TEMPORARY keyword for dropping a table, like defining these keywords for the CREATE TABLE statement.
Conclusion
Here we have seen how to use the PostgreSQL Temporary tables and how the PostgreSQL Temporary tables work to store the data. Also, we have added some examples of PostgreSQL Temporary tables.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on the “PostgreSQL Temporary Table” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

