Updated May 10, 2023

Introduction to PostgreSQL REGEXP_MATCHES()
The regular expression is a sequence of characters, the short name for the list of strings. Suppose any string matches with any of the string, which is part of the list of the strings defined by the regular expression. It supports the regular expression, and the function PostgreSQL REGEXP_MATCHES() provided by PostgreSQL is used to get all of the result strings from the regular expression. It uses a POSIX regular expression pattern.
Syntax:
regexp_matches(input_string, pattern [, flags ])Explanation:
- input_string: This defines the input string from which we want to extract all matched substrings for a specified pattern, a POSIX regular expression.
- pattern: This defines the POSIX regular expression to match the string.
- flags: This flag controls the behaviour of the REGEXP_MATCHES() function. This can have the value of one or more characters.
How does PostgreSQL REGEXP_MATCHES() Function work?
- It returns no rows if the regular expression pattern does not match with the input string.
- It returns a text array of single-element, which contains the substring that matches the pattern specified if the regular expression pattern is without the sub-expressions containing parenthesis.
- The REGEXP_MATCHES() function has a flags parameter, which is optional. The flag parameter contains zero or more characters. The flags parameter changes the REGEXP_MATCHES() function’s behaviour.
- If the output of the PostgreSQL REGEXP_MATCHES() function is a single element still, it returns a text set.
Examples
Given below are the examples:
Example #1
We are having a post related to trending content for current educational views as follows:
‘#EduCBA is the best learning platform for #PostgreSQL.’
We can extract substrings from the above text using the PostgreSQL REGEXP_MATCHES() function as follows, which returns all strings containing hashtags in the given string.
Code:
SELECT REGEXP_MATCHES('#EduCBA is best learning platform for #PostgreSQL', '#([A-Za-z0-9]+)', 'g');Output:
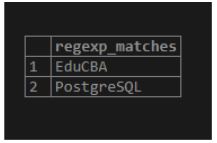
The output contains the ‘#eduCBA’ and ‘# PostgreSQL’ string, which means matching strings with regular expressions defined in a pattern. In the above example, the regular expression is “([A-Za-z0-9]+)”, which matches the string, which begins with a character hash(#) and is followed by any alphanumeric characters. We have used the ‘g’ flag, which is used for performing the global search, which allows searching for each occurrence, not only the first one.
Example #2
The PostgreSQL REGEXP_MATCHES() function returns results in array form but not in a string format.
The resulting array will have the groups if we use groups to return the string parts as follows:
Code:
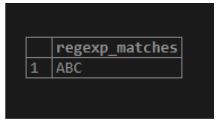
SELECT REGEXP_MATCHES
(
'ABC',
'^(A)(..)$',
'g'
);Output:
Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot.
Example #3
We will create a table named ‘student’ by using the CREATE TABLE statement as follows:
Code:
create table student
(
stud_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
stud_fname VARCHAR(80) NOT NULL,
stud_lname VARCHAR(80) NOT NULL
);Now, we will insert some data into the student table by using the INSERT INTO statement as follows:
Code:
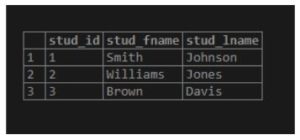
INSERT INTO student(stud_fname,stud_lname)
VALUES
('Smith','Johnson'),
('Williams','Jones'),
('Brown','Davis');Illustrate the above INSERT statement’s result using the following SQL statement and snapshot.
select * from student;Output:
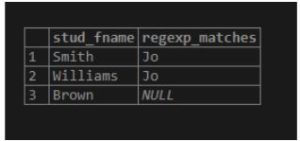
Consider the following SQL statement, which matches the ‘Jo’ pattern from the stud_lname column and returns the result as ‘Jo’ if the pattern matched otherwise, it returns as NULL.
Code:
SELECT stud_fname, (SELECT regexp_matches(stud_lname, '(Jo)')) FROM student;Output:
Advantages of PostgreSQL REGEXP_MATCHES()
Given below are the advantages:
1. The PostgreSQL REGEXP_MATCHES() function supports various flags.
Consider examples like:
- flag ‘i’ : match case-insensitively.
- flag ‘g’: search globally for each occurrence.
2. This function returns no row, one row, or multiple rows as per the pattern defined.
3. We can use this function to search all occurrence required string or only the first one, or we can search for at any position.
4. We can use the regular expression to extract the column values of a table as well.
5. We can use the PostgreSQL REGEXP_MATCHES() function for validity purpose.
6. We can use it to perform complicated tasks like string search with random characters.
Conclusion
Here we have seen how to use the PostgreSQL REGEXP_MATCHES() function and how the function works. Also, we have added several examples of the PostgreSQL REGEXP_MATCHES() function.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL REGEXP_MATCHES()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

