Updated May 17, 2023

Definition of PostgreSQL Query Optimization
PostgreSQL provides the query optimization techniques to increase the database’s performance and minimizes the query’s complexity with the query optimization technique. As developers, we always consider how we can increase the database’s performance and avoid the query’s complexity. When we talk about relation operators in PostgreSQL, the more difficult to process is JOIN. The number of solutions we can use for this problem to avoid complexity, such as (nested loop, hashing, and B-tree, etc). Now a day’s, PostgreSQL uses a near-exhaustive search method to optimize the query.
PostgreSQL Query Optimization Techniques
Single query optimization is used to increase the performance of the database. If we have a 10TB database, then we can use a multi-column index. The speed of the database is increased by 112X. For more knowledge, let’s see different techniques as follows.
-
Explain analyze
PostgreSQL has two different commands, such as EXPLAIN and EXPLAIN ANALYZE. The difference between EXPLAIN and EXPLAIN ANALYZE is that the EXPLAIN command is used to see the cost of the query based on your system database and EXPLAIN ANALYZE command is used to show the process time of the query at every stage. Most of the time, we refer to the EXPLAIN ANALYZE command because it shows all the query details, meaning the query’s cost and processing time. On the other hand, the EXPLAIN command is used for specific indexes.
-
One index per query
In this technique, it uses a specific column from the table so we can quickly find data from the table. The column’s PostgreSQL index is also maintained as a row identifier or the address of the row to speed up the table scan.
-
Selection of random rows
In this approach, we select random rows from the table at the time of row selection it uses row identifier or row address. Main purpose of query optimization is to increase the performance of the database, and we advise creating a separate index per unique query to boost the performance of the database.
-
Column sequence in Multicolumn indexing
Sometimes we need to assign column order in multicolumn indexing to avoid overlapping indexing, or we can say to avoid redundancy of column name, and it is helpful to boost the speed and minimize the query complexity in the database.
Let’s see the scan type and Joins to understand the query optimization better.
It is necessary to understand different scan types and join types because when we learn query optimization techniques, we must know different scan types and join. A sequential scan technique is helpful to small tables to boost the performance of databases; different types of sequential scan and Join are as follows.
Scan Types
Different types of scan are as follows.
- Sequential Scan
- Brute force technique to access or retrieve data from disk.
- We can scan the entire
- A sequential scan is held full to a small
- Index scan
- Scan all rows or some rows from the table.
- Random seeks are costly for a spindle based disk.
- It is faster than a sequential scan when we access a small number of rows from the table.
- Indexing only scan
- It can scan all rows or some rows in the index.
- In which we already store the values, so there is no need to lookup rows in the table.
- Bitmap Heap scan
- It scans indexing, it creates bitmap pages to visit and look up relevant pages from disk.
Join Types
- Nested Join
- In which we can scan rows from the outer table to match rows with the inner table.
- It is fast to scan and better for the small size of a table.
- Merge Join
- It is good for large tables to increase the speed of databases. It required a high cost if it required additional sort.
- Hash Join
- In which we scan rows from the inner table to match rows with the outer
- It is useful for equality conditions, it requires a high cost, but execution of the query is fast.
Examples of PostgreSQL Query Optimization
Let’s see how to EXPLAIN ANALYZE commands work as follows.
First, we need to create a table by using the create table statement, so here, we create an emp table with different attributes with different data types. Below snapshot shows the details structure of the emp table as follows.
select * from emp;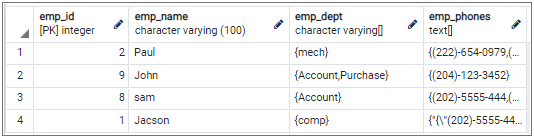
Now we use the EXPLAIN ANALYZE command to see the query plan as follows.
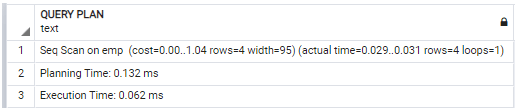
EXPLAIN ANALYZE select * from emp;Explanation:
In the above statement, we use a select clause with explain analyze command to see the query of the emp table with details. It shows the planning time and execution time of the query and also shows a sequential scan of the emp table. Illustrate the remaining end result of the above announcement by way of the usage of the following snapshot.
Now to see how we can create the index, it has a simple syntax to create an index as follows.
Example #1
create index emp_org on emp(emp_id);Explanation:
In the above example, we use the create index statement to create the index name as emp_org for the emp_id column on the emp table. Illustrate the remaining end result of the above announcement by way of the usage of the following snapshot.

We can see the query plan by executing the explain analyze command.
Example #2
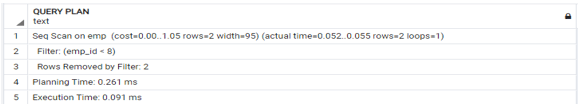
explain analyze select * from emp where emp_id < 8;Explanation:
In the above example, we use to select and where clauses with explain analyze command. It shows all filtered with execution time and planning time. Illustrate the remaining end result of the above announcement by way of the usage of the following snapshot.
Conclusion
We hope from this article, you have understood the PostgreSQL query optimization. From the above article, we have learned the basic syntax of creating indexes in PostgreSQL and different commands to see query plans. We have additionally discovered how we can enforce them in PostgreSQL with different examples of every technique. From this article, we have learned how we can handle query optimization in PostgreSQL.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Query Optimization” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

