Updated May 10, 2023

Introduction to PostgreSQL Primary Key
The row of the table can be uniquely identified using a column or group of columns termed as a primary key. We can specify the primary keys using the primary key constraints. The PostgreSQL Primary Key constraint is the combination of a UNIQUE constraint and a NOT NULL constraint. The table can consist of only one PRIMARY KEY; adding a primary key on each table is a best practice in the database management system.
Syntax
Below are the syntax used in the Primary key:
Syntax #1 – Define the primary key
1. Add the primary key while creating the table. We can add the primary key constraint to a table while creating the table itself using the CREATE TABLE statement.
CREATE TABLE table_name (
column_name1 data_type PRIMARY KEY,
column_name2 data_type,
.
.
.
);2. We can create a primary key constraint containing two or more columns as follows:
CREATE TABLE table_name (
column_name1 data_type,
column_name2 data_type,
.
.
.
PRIMARY KEY (column_name1, column_name2)
);Syntax #2 – UPDATE PRIMARY KEY
We can add a primary key constraint for an existing table, which is rare. We can achieve the same using an ALTER TABLE statement as follows:
ALTER TABLE table ADD PRIMARY KEY (column1, column);Syntax #3 – Remove the primary key
With the help of the ALTER TABLE statement, we can remove an existing primary key constraint of the table as follows:
ALTER TABLE table_name DROP CONSTRAINT primary_key_constraint;How does Primary Key work in PostgreSQL?
The PostgreSQL creates a unique B-TREE index on PRIMARY KEY columns if we have added PRIMARY KEY on the table using a column or a group of columns of a table. If we don’t define the primary key constraint name explicitly then PostgreSQL assigns a default name to the primary key constraint. It assigns table_name_pkey as the default name for the primary key constraint. If we have a table named CITIES, then PostgreSQL creates the primary key constraint with the name cities_pkey for the same. We can use the CONSTRAINT clause as follows to assign the name for the same:
Code:
CONSTRAINT constraint_name PRIMARY KEY(column_name1, column_name2,...);Examples
Let’s create a table named COUNTRIES using the CREATE TABLE statement in order to understand the examples.
Example #1 – Single Column PRIMARY KEY
Code:
CREATE table COUNTRIES
(
country_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
country_name VARCHAR (256) NOT null,
last_updated DATE NULL
);The country_id is the COUNTRIES table’s primary key, which used to identify the country in the COUNTRIES table uniquely.
Example #2 – Multiple Columns PRIMARY KEY
The following statement will create a table named ‘CITIES’ whose primary key is a combination of city_id and country_id.
Code:
CREATE table CITIES
(
city_id serial,
country_id INT,
city_name VARCHAR (256) NOT NULL,
last_updated DATE null,
PRIMARY KEY (CITY_id, country_id)
);Example #3 – Adding PRIMARY KEY
Example to ALTER TABLE for adding PRIMARY KEY after table creation. The following statement creates a table named invoices which will not have any PRIMARY KEY.
Code:
CREATE TABLE invoices (
invoice_id INT,
invoice_data VARCHAR (256) NOT NULL
);- Now with the help of the following statement, we can add a primary key constraint to the invoices table.
Code:
ALTER TABLE invoices
ADD PRIMARY KEY (invoice_id);Example #4 – Auto-incremented PRIMARY KEY
Example to ALTER TABLE for adding auto-incremented PRIMARY KEY after table creation. Now with the help of the following statement, we can add an auto-incremented primary key constraint to the invoices table.
Code:
CREATE TABLE invoices (invoice_data VARCHAR(255));- NOW insert some data in the invoices table using the INSERT statement.
Code:
INSERT INTO invoices (invoice_data)
VALUES
('Purchase of Mobile'),
('Purchase of Laptop'),
('Purchase of PC'),
('Purchase of Tablet');- Illustrate the result of an INSERT statement with the help of the following SQL statement and snapshot.
Code:
SELECT * FROM Invoices;Output:
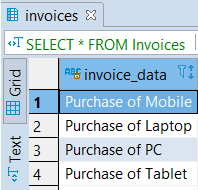
- Here we will add an auto-incremented by one primary key named invoice_id into the invoices table with the help of the following statement:
Code:
ALTER TABLE invoices ADD COLUMN invoice_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY;- Illustrate the result of an ALTER statement with the help of the following SQL statement and snapshot.
Code:
SELECT invoice_id,invoice_data FROM invoices;Output:
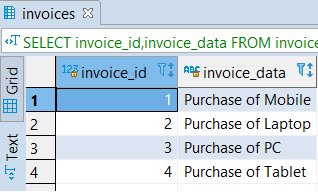
- Now the invoices table has the primary key invoice_id.
Example #5 – Remove a PRIMARY KEY of the table
In order to remove the primary key constraint of the invoices table, we have to use the following statement:
Code:
ALTER TABLE invoices
DROP CONSTRAINT invoices_pkey;Advantages of using Primary Key in PostgreSQL
- The PostgreSQL PRIMARY KEY helps us to search records quickly as the index is getting used based on the PRIMARY KEY.
- By using PostgreSQL PRIMARY KEY, we can uniquely identify the table records for an update or delete operation.
- The PostgreSQL PRIMARY KEY is used to sort the data based on it.
- By using PostgreSQL PRIMARY KEY, we can avoid duplicate row insertion in the table.
Conclusion
We hope from the above article you have understood how to add, update and remove primary key constraints using CREATE TABLE and ALTER TABLE statements. Also, with the help of examples and syntax explained in detail.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Primary Key” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

