Updated May 8, 2023

Introduction to PostgreSQL MD5
PostgreSQL MD5 function is used to convert a string into 32 character text string in PostgreSQL.It is essential to utilize this in a crucial setting to ensure the utmost data safety. A cryptographic hash function called MD5 generates a 32-character text string in the form of a hexadecimal value, representing a 128-bit checksum. The MD5 algorithm in PostgreSQL is designed to convert a string into a 32-character text string using 128-bit encryption. MD5 function is very useful and important.
Syntax:
Md5 (string (Any character string that we want to convert into 32 character text string ))
Select column_name1, md5 (Column_name2 (Column name that we have used to convert string into 32 character text string)), md5(column_name3(Column name that we have used to convert string into 32 character text string)), .., Column_nameN from table_name;
Select MD5 ('String');Parameters:
Below is the parameter description of the above syntax as follows:
- MD5: The MD5 cryptographic hash function creates a 32-character text string in hexadecimal format, serving as a checksum for a 128-bit value. MD5 function is very useful and important.
- String: Any character string that we want to convert into 32 character text string in PostgreSQL. We can use any string to convert a string into a 32-bit text string.
- Select: To convert a character string into a 32-character text string using the MD5 function, one can use the SELECT statement in PostgreSQL.
- Column 1 to Column N: Column name used to convert the data into text string in PostgreSQL.We can convert character data type column data into 32 character text string.
- Table Name: The “Table name” feature displays information from a specific table.
How PostgreSQL MD5 Function Works?
- MD5 function in PostgreSQL accepts one string or argument as an input string while converting a string into a text string.
- People often use this in critical applications where they prioritize securing data.
- MD5 function is very useful and important in PostgreSQL.
- When transforming a string into a 32-character text string in PostgreSQL, the MD5 function is utilized.
- We can use an MD5 function at the time of user creation to provide an encrypted password for the user.
- MD5 function will consider every word as a string in PostgreSQL. It will work only on a string, not for the integer value.
- The below example shows that it will consider every string as a character, not an integer value. We need to define a string in a single quote to convert a string into a text string.
select MD5 (10);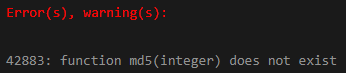
select MD5 ('10');![]()
- In the above first example, we have passed 10 values without a single quote; passing this value will show an error that the MD5 function did not exist.
- But when we pass the 10 value in a single quote, it will display the 32 character string.
- MD5 function is not working in integer data type data. In the below example data type, while we have to display the emp_id of integer types, it will not display the data; it will show an error.
select MD5 (emp_id) from Employee limit 2;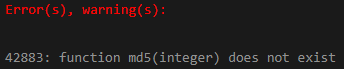
select MD5 (emp_name) from Employee limit 2;
- In the above figure first example, we have retrieved data from the integer data type column same time; it will show an error. But when we have retrieved data from the character data type, it will not issue an error; it will display the result in 32 character string in text format.
Examples to Implement MD5 Function in PostgreSQL
Given below are the examples mentioned:
We are using the employee table to describe the example of the MD5 function in PostgreSQL as follows.
select * from employee;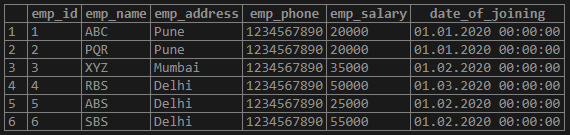
Figure: Example of an employee table to describe the example of MD5 function in PostgreSQL.
1. Convert a Single String into 32 Bit String
Below is an example of converting a single string into a 32-bit character text string in PostgreSQL. In the below example, we have to convert the ABC string into a 32-bit character text string.
select MD5 ('ABC');![]()
In the above example, the ABC string will return the “902fbdd2b1df0c4f70b4a5d23525e932” string using an MD5 function in PostgreSQL.
2. Convert Table Data
The below example shows to convert a character string into 32 Bit text string in PostgreSQL.
SELECT emp_id, md5 (emp_name), md5 (emp_address), emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining FROM employee;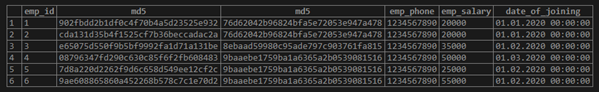
In the above example, we have to convert an emp_name and emp_address column in 32 string text format using md5 functions in PostgreSQL.
3. MD5 Function using UUID
The below example shows how the UUID function works using an MD5 function in PostgreSQL.
SELECT md5('MD5 String')::uuid;![]()
Advantages
Given below are the advantages mentioned:
- In PostgreSQL, you can use the MD5 function to convert a string into a 32-character text string
- The MD5 function is commonly used in critical functions where data security is a major concern. MD5 function is essential in PostgreSQL.
- It uses the MD5 function to convert a character string into a 32-character text string.
- We can use the MD5 function to store user password in text format.
- We used the MD5 function for data security and privacy in a critical application.
Conclusion
Users utilize the MD5 function to turn a string into a 32-character text string representing a 128-bit checksum in hexadecimal form. They frequently apply this cryptographic hash function in important applications where security is of utmost importance.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL MD5” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

