Updated May 12, 2023

Introduction to PostgreSQL GRANT
In PostgreSQL, you can use the GRANT query statement whenever you want to assign privileges for a certain database object. GRANT query also provides us with one more facility to grant membership to a particular role. Whenever a new user is created, it has the default privileges on the database object. The GRANT command overrides these access privileges. The database objects include the tables, columns on tables, stored procedures, functions, sequences, database servers, foreign-data wrapper, views, schemas, foreign servers, tablespace, and procedural languages. Any of these database objects can be allowed to access a particular role by using a PostgreSQL grant.
Examples of PostgreSQL GRANT
Given below are the examples:
Example #1
We can create a new user using the CREATE USER command and check the user’s privileges from the table table_privileges in information_schema by firing the select query for a particular grantee.
Let us check the list of users in my database server by firing \du metacommand.
Code:
\duOutput:
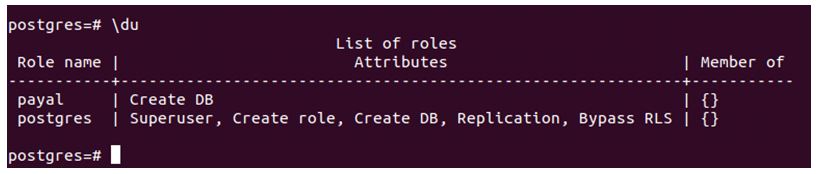
We have two users named Payal and Postgres. Postgres is the default user present in the PostgreSQL database that is the superuser and has all privileges, while I create a Payal user for demonstration purpose that does not has any privileges.
We can check that by firing the following query.
Code:
SELECT table_schema as schema, table_name as table, privilege_type as privilege
FROM information_schema.table_privileges
WHERE grantee = 'postgres';Output:

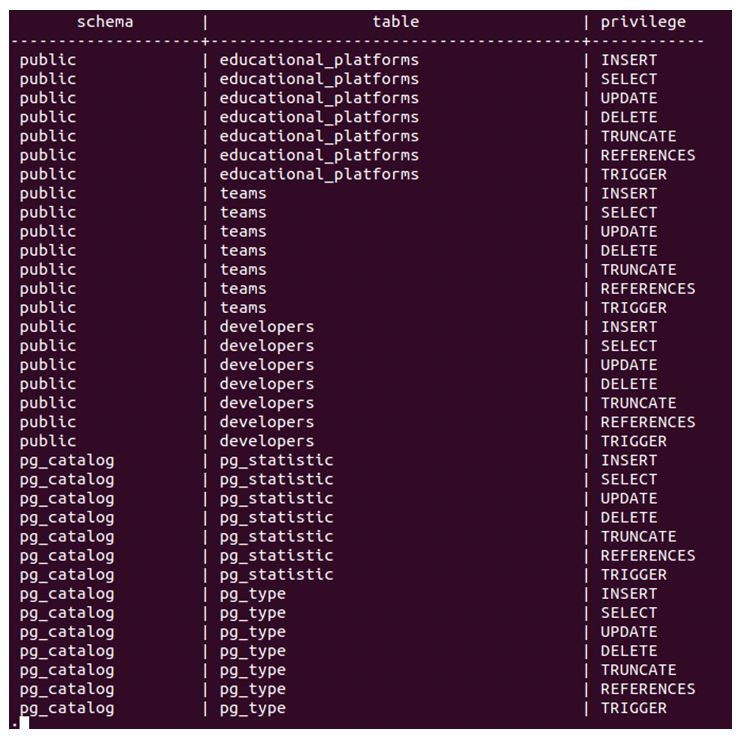
Firing the above command for Payal users.
Code:
SELECT table_schema as schema, table_name as table, privilege_type as privilege
FROM information_schema.table_privileges
WHERE grantee = 'payal';Output:
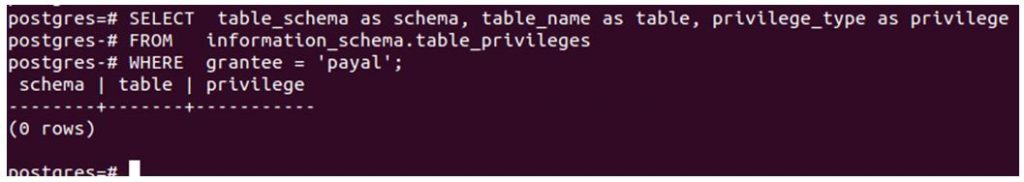
Now we will see the grant query syntax and example one by one by assigning different database object privileges to our user named Payal.
Example #2
We are granting table privileges.
Syntax:
GRANT { { SELECT | INSERT | UPDATE | DELETE | TRUNCATE | REFERENCES | TRIGGER }
[,...] | ALL [ PRIVILEGES ] }
ON { [ TABLE ] name_of_table [, ...]
| ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA name_of_schema [, ...] }
TO { [ GROUP ] name_of_role | PUBLIC } [, ...] [ WITH GRANT OPTION ]The above syntax for granting privilege on a certain table name to the particular user has name_of_table as the table name that you want to grant the privilege of, name_of_schema as the schema name to which that table belongs, and name_of_role as the user name in our case is Payal.
Let us check the list of tables present in the Postgres database by firing the \dt command.
Now, we have to give insert privilege to the Payal user on the team’s table.
Code:
GRANT INSERT ON TABLE teams TO payal;Output:
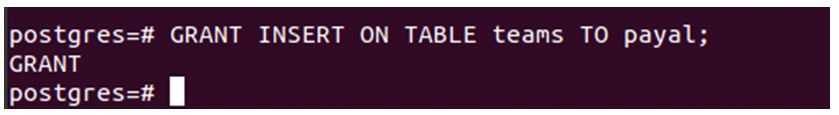
Now, after firing the select command for privilege checking.
Code:
SELECT table_schema as schema, table_name as table, privilege_type as privilege
FROM information_schema.table_privileges
WHERE grantee = 'payal';Output:
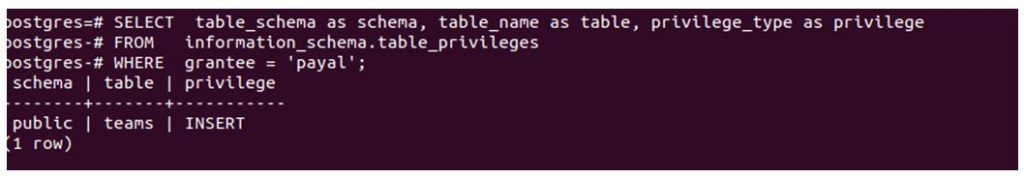
Hence, insert privilege is granted to the Payal user on table teams.
Example #3
Granting table column privileges.
Syntax:
GRANT { { SELECT | INSERT | UPDATE | REFERENCES } ( column [, ...] )
[,...] | ALL [ PRIVILEGES ] ( column [, ...] ) }
ON [ TABLE ] name_of_table [, ...]
TO { [ GROUP ] name_of_role | PUBLIC } [, ...] [ WITH GRANT OPTION ]Now, we will grant the update privilege on certain columns of the educba table. Let us describe the educba table by using \d educba; metacommand.
Code:
\d educba;Output:
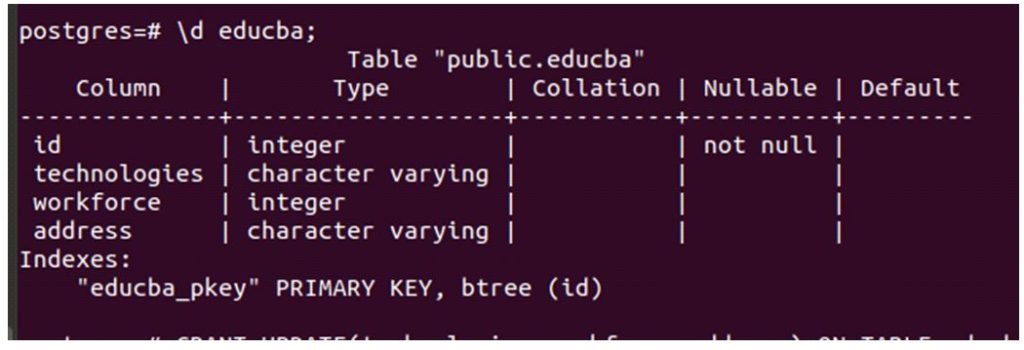
Now we will use format 2 of the grant query statement to assign update privilege on certain columns of the educba table using the following query.
Code:
GRANT UPDATE(technologies, workforce, address) ON TABLE educba TO payal;Output:

Example #4
Granting sequence privileges.
Syntax:
GRANT { { USAGE | SELECT | UPDATE }
[,...] | ALL [ PRIVILEGES ] }
ON { SEQUENCE name_of_sequence [, ...]
| ALL SEQUENCES IN SCHEMA name_of_schema [, ...] }
TO { [ GROUP ] name_of_role | PUBLIC } [, ...] [ WITH GRANT OPTION ]For granting all privileges on all sequences to the Payal user, we will use format 3 of the grant query.
Code:
GRANT ALL ON ALL SEQUENCES IN SCHEMA public TO payal;Output:

Example #5
Granting database privileges.
Syntax:
GRANT { { CREATE | CONNECT | TEMPORARY | TEMP } [,...] | ALL [ PRIVILEGES ] }
ON DATABASE name_of_database [, ...]
TO { [ GROUP ] name_of_role | PUBLIC } [, ...] [ WITH GRANT OPTION ]Let us check all databases using the \l command.
Code:
\lOutput:
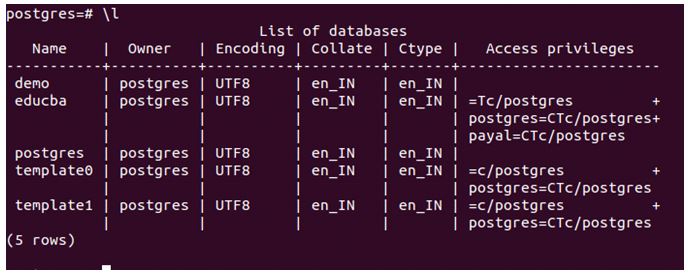
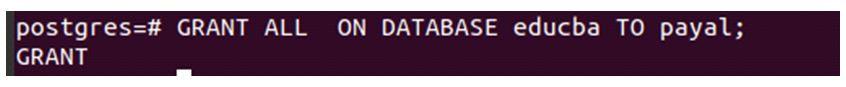
We will use the following query statement to grant the Payal user all privileges on the educba database.
Code:
GRANT ALL ON DATABASE educba TO payal;Output:
Example #6
Granting function privileges.
Syntax:
GRANT { EXECUTE | ALL [ PRIVILEGES ] }
ON { FUNCTION name_of_function ( [ [ argmode ] [ arg_name ] arg_type [, ...] ] ) [, ...]
| ALL FUNCTIONS IN SCHEMA name_of_schema [, ...] }
TO { [ GROUP ] name_of_role | PUBLIC } [, ...] [ WITH GRANT OPTION ]Let us create one function.
Code:
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION iseligible(int) RETURNS void AS $$
DECLARE
age int:=$1;
BEGIN
IF age > 18 THEN RAISE NOTICE 'You are eligible to vote as your age is %!', age;
END IF;
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;Now, we can use the following query statement to grant all privileges to the Payal user on an eligible() function.
Code:
GRANT ALL ON FUNCTION iseligible TO payal;Output:
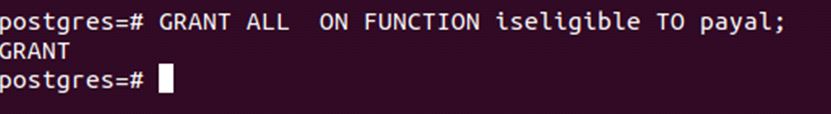
Example #7
Granting schema privileges.
Syntax:
GRANT { { CREATE | USAGE } [,...] | ALL [ PRIVILEGES ] }
ON SCHEMA name_of_schema [, ...]
TO { [ GROUP ] name_of_role | PUBLIC } [, ...] [ WITH GRANT OPTION ]We can use the following query statement to grant the Payal user all permissions on the public schema.
Code:
GRANT ALL ON SCHEMA public TO payal;Output:

Example #8
Granting membership privileges.
We can grant membership of a certain role, user to other role, or user using the grant’s following format.
Syntax:
GRANT name_of_role [, ...] TO name_of_role [, ...] [ WITH ADMIN OPTION ]We can fire the following query statement to grant the Postgres role to payal.
Code:
GRANT postgres TO payal;Output:
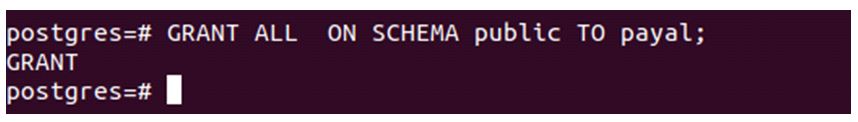
Let us check the output of the \du command now.
Code:
\duOutput:
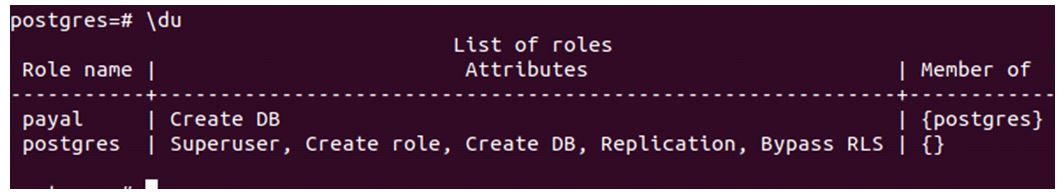
The payal user is now a member of Postgres.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL GRANT” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

