Updated May 26, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL EXISTS
The PostgreSQL EXISTS condition is used to check the existence of rows from the result set of the subquery by combining with a subquery, which is acceptable even if the result set is returned by the subquery contains at least one row which means the PostgreSQL EXISTS works with a subquery. The PostgreSQL EXISTS can be used with SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE SQL statements.
Syntax:
The syntax of the PostgreSQL EXISTS is as follows:
WHERE EXISTS ( subquery );Explanation:
Subquery: The SELECT statement, which we generally use with an asterisk (*) operator as SELECT * instead of defining the list of expressions or the list of names of the columns. We can use SELECT 1 instead of SELECT * to improve the performance as we are not bothered about the result of the SELECT statement what we need is only the rows returned.
How EXISTS works in PostgreSQL?
The result of the PostgreSQL EXISTS will be true if the result set of subquery contains at least one row. And it will be false if the result set of subquery has the result with no row.
The subquery written in the PostgreSQL EXISTS operator is inefficient as it executes each row of the outer query’s table. So it is not good practice to use EXISTS as we have other more efficient ways to write SQL queries.
If the PostgreSQL subquery returns us the NULL result, then the result of the PostgreSQL EXISTS will be true.
Examples of PostgreSQL EXISTS
Let’s create two tables named’ transaction’ and ‘invoices’ to understand the PostgreSQL NATURAL JOIN examples.
The following CREATE TABLE statements will create the transaction and invoices table.
CREATE TABLE transaction (
transaction_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
transaction_data VARCHAR (256) NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE invoices (
invoice_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
transaction_id INT NOT NULL,
invoice_data VARCHAR (256) NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY (transaction_id) REFERENCES transaction (transaction_id)
);The transaction_id is the primary key of the transaction table, referred to as the foreign key for the invoices table. So while performing the natural join operation, we will use the transaction_id column as it is the common column for both tables. The transaction may have zero or more invoices, and the invoice will belong to one and only one transaction.
Now insert some data into the transaction and invoices tables using the INSERT statement as follows:
INSERT INTO transaction (transaction_data)
VALUES
('Purchase of Mobile'),
('Purchase of PC'),
('Purchase of Headphone');
INSERT INTO invoices (invoice_data, transaction_id)
VALUES
('Purchase of Mobile', 1),
('Purchase of Mobile', 1),
('Purchase of PC', 2),
('Purchase of PC', 2),
('Purchase of Headphone', 3),
('Purchase of Headphone', 3);Illustrate the content of the transaction table using the following statement and snapshot.
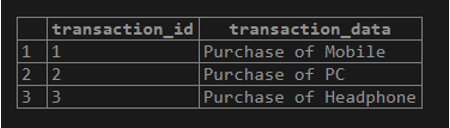
select * from transaction;Illustrate the content of the invoices table using the following statement and snapshot.
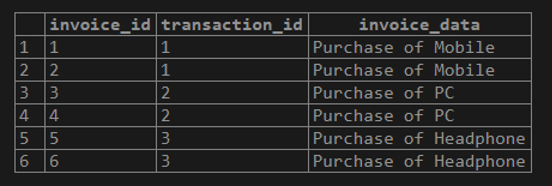
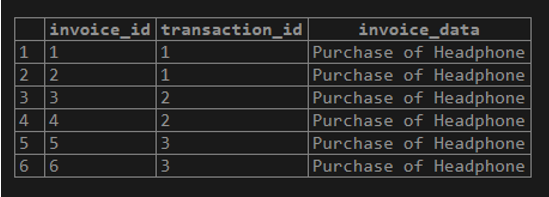
select * from invoices;Examples #1 – The PostgreSQL with SELECT statement
Use the operator with SELECT statement from the invoices table as follows:
SELECT *
FROM invoices
WHERE EXISTS (SELECT 1
FROM transaction
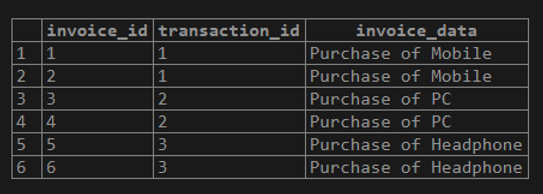
WHERE transaction.transaction_id = invoices.transaction_id);This example with the PostgreSQL EXISTS operator will return all rows from the invoices table where at least one row is present on the operator’s transaction table to match using column transaction_id. Here, we have defined 1 instead of an asterisk(*) with SELECT statement in the subquery to improve the performance.
The result returned by the subquery is irrelevant to us as we need the operator only to check the existence of rows.
Illustrate the result of the above statement using the following snapshot.
Example #2 – The PostgreSQL with an INSERT statement
Use the operator to INSERT the data in the invoices table as follows:
INSERT INTO invoices (transaction_id, invoice_data)
SELECT transaction_id, transaction_data
FROM transaction
WHERE EXISTS (SELECT 1
FROM transaction
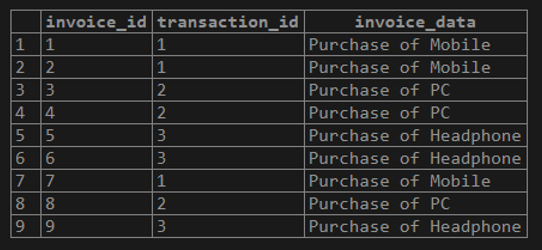
WHERE transaction.transaction_id = 2);Illustrate the result of the above statement using the following snapshot and SQL statement.
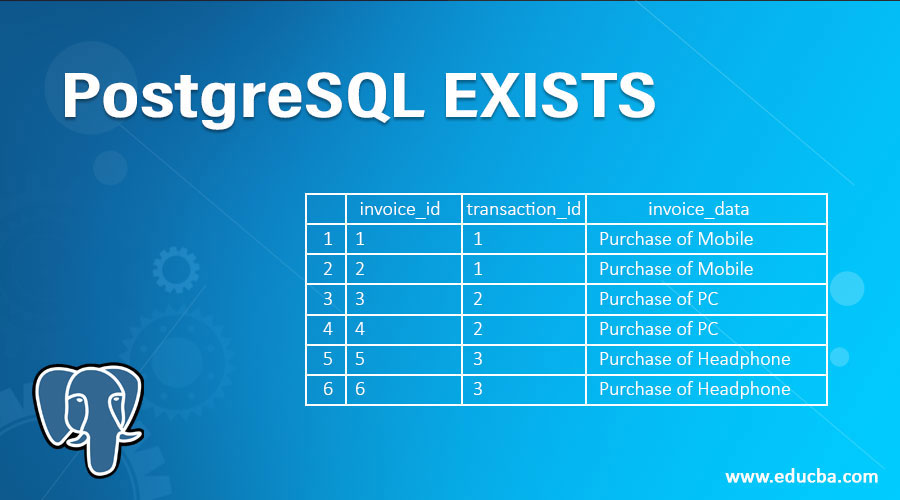
Select * from invoices;Example #3 – The PostgreSQL with an UPDATE statement
Use the operator to UPDATE the data in the invoices table as follows:
UPDATE invoices
SET invoice_data = (SELECT transaction.transaction_data
FROM transaction
WHERE transaction.transaction_id = 3)
WHERE EXISTS (SELECT 1
FROM transaction
WHERE transaction.transaction_id = 3);Illustrate the result of the above statement using the following snapshot and SQL statement.
select * from invoices;Example #4 – The PostgreSQL with the DELETE statement
Use the operator to DELETE the row from the invoices table as follows:
DELETE FROM invoices
WHERE EXISTS (SELECT 1
FROM transaction
WHERE transaction.transaction_id = 2);Advantages
- We can use the clause with a subquery in a SQL statement.
- We can use the operation with SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT, and DELETE SQL statements.
- The result depends on the number of rows returned by the subquery but does not depend on the column values of the table.
- The result will be true if the subquery returns at least one row or returns NULL.
Conclusion
From the above article, we hope you have learned about the PostgreSQL EXISTS operator and its advantages. Also, we have added some examples to demonstrate how to use the PostgreSQL EXISTS operator to query data.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL EXISTS” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.