Updated May 3, 2023

Definition of PostgreSQL Constraints
PostgreSQL constraints enforce the rule on the table’s data columns; this is mainly useful to prevent invalid data from entering the table. PostgreSQL constraints are beneficial to find duplicate values; they will not accept the duplicate value or invalid data into the table. PostgreSQL constraints ensure the accuracy and reliability of data in the table. We have to define constraints on the table level as well as the column level. Table level constraints are applied to the whole table, whereas column-level constraints are applied to only one column.
PostgreSQL Constraints with Examples
The following are commonly used constraints available in PostgreSQL are as follows.
1. Not Null Constraints
- In PostgreSQL, by default, the column accepts null values; using no null constraints on the column will not accept any null values in a column.
- No null Constraint in PostgreSQL are always written as column constraints.
Syntax:
Create table table_name (
Column_name1 data type Not Null,
Column_nameN data type Not Null);Below is the description of the above syntax.
- Create: We have created not null Constraint on a column at the time of table creation.
- Table name: It is the name of the table.
- Column_name1 to column_nameN: Name of column.
- Data type: A Data type that we have defined as a column.
- Not Null: Constraint name, which does not accept null value in the column.
Example
Below is an example of not null constraints at the time of table creation.
CREATE TABLE Employee ( emp_id INT NOT NULL, emp_name character(10) NOT NULL, emp_address character(20) NOT NULL, emp_phone character(14), emp_salary INT NOT NULL, date_of_joining date NOT NULL);
INSERT INTO Employee (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (1, 'ABC', 'Pune', '1234567890', 20000, '01-01-2020');
select * from Employee;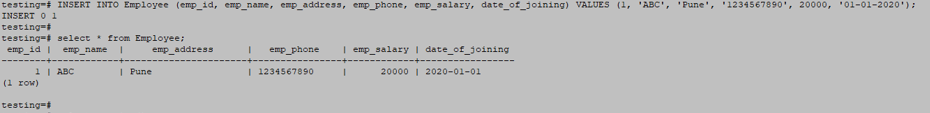
2. Unique Constraints
- Unique constraints are the same as its name; it will prevent adding two identical values in the table.
- Unique constraints ensure that all values in the column are identical.
Syntax:
Create table table_name (
Column_name1 data type Not Null Unique,
Column_nameN data type Not Null Unique);Below is the description of the above syntax.
- Create: We have created a unique constraint on the column at the time of table creation.
- Table name: It is the name of the table.
- Column_name1 to column_nameN: Name of column.
- Data type: Data type of column.
- Unique: Constraint name.
Example
Below is an example of unique constraints at the time of table creation.
CREATE TABLE department ( dept_name character(10) NOT NULL UNIQUE, dept_id int NOT NULL UNIQUE, dept_code varchar(10));![]()
INSERT INTO department (dept_name, dept_id, dept_code) VALUES ('IT', 101, 'IT101');![]()
INSERT INTO department (dept_name, dept_id, dept_code) VALUES ('IT', 101, 'IT101');
- In the second example, the same value insertion is not allowed in the table because we have used a unique constraint on the dept_id column.
3. Primary Key Constraints
- Primary Constraint, which uniquely identifies each record in the database table. We can define multiple primary key constraints on a single table. It will be allowed only one primary key Constraint on a single table.
- Below are the example and syntax of primary key constraints in PostgreSQL.
Syntax:
Create table table_name (
Column_name1 data type primary key Not Null,
Column_nameN data type Not Null);Below is the description of the above syntax.
- Create: We have created a primary constraint on a column at the time of table creation.
- Table name: Name of the table.
- Column_name1 to column_nameN: Name of column.
- Data type: Data type of column.
- Primary Key: Constraint name.
Example
Below is an example of a primary key constraint in PostgreSQL at the time of table creation.
CREATE TABLE Employee_test ( emp_id INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL, emp_name character(10) NOT NULL, emp_address character(20) NOT NULL, emp_phone character(14), emp_salary INT NOT NULL);![]()
INSERT INTO Employee_test (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary) VALUES (1, 'ABC', 'Pune', '1234567890', 20000);![]()
INSERT INTO Employee_test (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary) VALUES (1, 'PQR', 'MUMBAI', '1234567880', 25000);![]()
- In the second example, the same emp_id insertion is not allowed in the table because we have used the primary key Constraint on the emp_id column.
4. Foreign Key Constraints
- Foreign key constraints in PostgreSQL states that values in the first table column must appear with values in a second table column.
- Below are the syntax and examples of foreign key constraints in PostgreSQL.
Syntax:
Create table table_name (
Column_name1 data type primary key Not Null,
Column_nameN data type references table_name (column_name));Below is the description of the above syntax.
- Create: Create table statement.
- Table name: It is the name of the table.
- Column_name1 to column_nameN: Name of the column.
- Data type: Data type of column.
Example
Below is an example of foreign key constraints in PostgreSQL at the time of table creation.
CREATE TABLE Employee_test1 ( emp_id INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL, emp_name character(10) NOT NULL, emp_address character(20) NOT NULL, emp_phone character(14), emp_salary INT NOT NULL);![]()
CREATE TABLE Employee_test2 ( emp_id INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL, emp_name character(10) NOT NULL, emp_salary INT NOT NULL, id int references Employee_test1(emp_id));![]()
\d+ Employee_test1;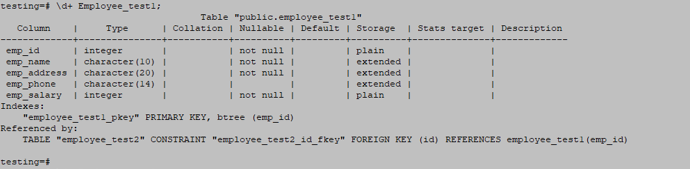
\d+ Employee_test2;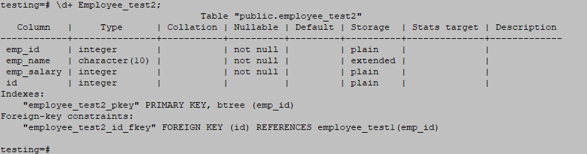
5. Check Constraints
- Check condition in PostgreSQL enables checking the condition that values are being entered into the record.
- Below is the syntax, and examples of check constraints in PostgreSQL are as follows.
Syntax:
Create table table_name (
Column_name1 data type primary key Not Null
Column_nameN data type Not Null check condition);Below is the description of the above syntax.
- Create: Create table statement.
- Table name: Name of the table.
- Column_name1 to column_nameN: Name of column.
- Data type: Data type of column.
- Check condition: check Constraint with the condition.
Example
CREATE TABLE EMP_TEST (ID INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL, NAME TEXT NOT NULL, SALARY REAL CHECK(SALARY > 1000));![]()
INSERT into EMP_TEST (ID, NAME, SALARY) VALUES (1, 'ABC', 5000);![]()
INSERT into EMP_TEST (ID, NAME, SALARY) VALUES (1, 'ABC', 500);
- In the second example, a salary less than 1000 insertion is not allowed in a table because we have used check constraints on the salary column.
Conclusion
PostgreSQL constraints are beneficial to validate data with duplicate and unwanted data from the table. We have mainly used not null, primary key, foreign key, check, and unique key constraints in PostgreSQL. Constraints are essential and useful in PostgreSQL.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Constraints” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

