Updated May 9, 2023

Introduction to PostgreSQL Auto Increment
The following article provides an outline of PostgreSQL Auto Increment. PostgreSQL has a special database object called a SEQUENCE object that lists ordered integer values. Developers often use the SEQUENCE when describing a unique key or primary key or a column that auto-increments in database tables. When developers declare a particular column as a pseudo-type SERIAL, PostgreSQL generates a SEQUENCE object.
SEQUENCE Database Object
- First, you need to understand how the SEQUENCE object works.
- SEQUENCE is completely a schema-bound object defined by the user according to their special requirements. {11, 12 ,13, 14, 15,…} is completely a different sequence than {100, 99, 98,97,..} sequence.
- Developers can create a sequence using the ‘CREATE SEQUENCE’ statement.
- We can define the minimum and maximum value, incremental step value, name, and owner of the SEQUENCE and cache space, which needs to be pre-allocated space in the memory of the sequenced list.
SERIAL pseudo-type
- While creating a table in PostgreSQL, if we declare any column of the type SERIAL, internally, the SERIAL pseudo-type also creates a new SEQUENCE object for that column and table default values.
- That further helps us achieve the auto-incrementation of the values of certain columns declared as SERIAL type.
Internal Working
When we declare the column named “student_id” of type SERIAL in the table creation query for the “educba” table in the following way.
Code:
CREATE TABLE educba(student_id SERIAL,name VARCHAR(100));Internally, PostgreSQL executes a series of commands.
Some of them are as follows:
CREATE SEQUENCE educba_student_id_seq;CREATE TABLE educba (student_id integer NOT NULL DEFAULT nextval('educba_student_id_seq'), name VARCHAR(100));ALTER SEQUENCE educba_student_id_seq OWNED BY educba.student_id;PostgreSQL executes the above-mentioned internal queries when declaring any column of type SERIAL in a table.
- When a table with a SERIAL column called “student_id” is created in PostgreSQL, the system automatically generates a new SEQUENCE object for that column. It assigns the default value of the “student_id” column to the next value of that sequence.
- As a sequence always generates a non-null integer value, the column student_id will be assigned with the NOT NULL constraint.
- Deleting the student_id column should also lead to deleting the SEQUENCE object associated with it.
- For this purpose, the owner of the created sequence educba_student_id_seq is set to the student_id column of the educba table.
Types of SERIAL pseudo-types
In PostgreSQL, we can create a SERIAL pseudo-type that can belong to either of the following three types.
- SMALLSERIAL
- SERIAL
- BIGSERIAL
Which differ in their storage space and range limits. This is similar to short int, int, and long int.
The storage space and range of all the three pseudo-types of the serial are as follows:
| Pseudo-type name | Storage size required | Range of its values in the list |
| SMALLSERIAL | 2 bytes of space | 1 – 32,767 |
| SERIAL | 4 bytes of space | 1 – 2,147,483,647 |
| BIGSERIAL | 8 bytes of space | 1 – 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 |
Example of SERIAL pseudo-type
Let us now take an example of how serial pseudo-type helps us achieve auto-incrementation. Declaring a column of type SERIAL does not automatically create an index on that column or consider it as its primary key. To do so, you will externally need to define the column as the PRIMARY KEY.
Code:
CREATE TABLE educba(student_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY ,name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL);Output:
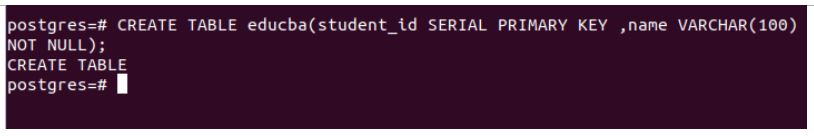
To verify our table creation, let us fire the \dt command.
Output:
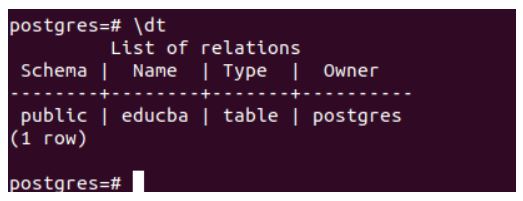
As it can be seen that the table named educba is created successfully. When you insert the records in the table with auto-incremented valued columns, you can either skip inserting those column values or specify the DEFAULT keyword for those columns in your INSERT query statement. We will insert the records using both methods. Firstly, skipping the student_id column.
Code:
INSERT INTO educba(name) VALUES('Payal');Output:

Saying that 1 row is inserted successfully. Now, let us insert a record specifying the DEFAULT value for our student_id column.
Code:
INSERT INTO educba(student_id,name) VALUES(DEFAULT,'Piyush');Output:

Saying our one more row is inserted. Now, let us check our educba table records and see whether values are inserted for the student_id column and auto-incremented.
Code:
SELECT * FROM educba;Output:
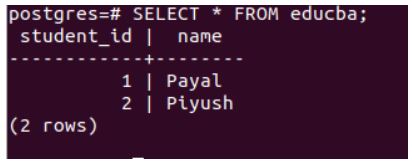
Hence, we can see that the student_id column works as the auto-incremented field now.
Methods of Sequence Value
Developers use methods related to the sequence object created in the database, such as fetching the name of the sequence object and retrieving the current maximum value of that sequence object. Developers use the ‘pg_get_serial_sequence’ method to get the name of a sequence object created for a particular table’s serial-typed column. It takes two parameters the name of the table and the name of a column of that table.
Code:
pg_get_serial_sequence('tableName','columnName');Let us retrieve the name of the sequence object created for the student_id column.
Code:
SELECT pg_get_serial_sequence('educba','student_id');Output:
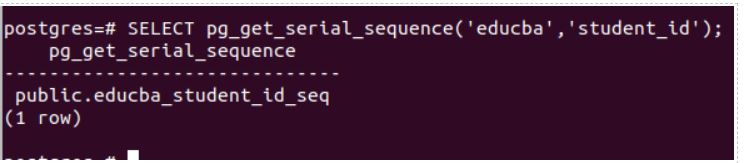
So, educba_student_id_seq is the sequence object’s name.
We will retrieve the maximum value or the last value assigned by this sequence object to the column student_id using the method currval(nameOfSequence) that takes only one parameter: the name of the sequence object.
Code:
SELECT currval(pg_get_serial_sequence('educba', 'student_id'));Output:
It’s essential to know that the sequence value of a serial-typed column is not a transaction-safe value. In two instances, accessing the same database table inserts the record. Both will get different sequence values and if one of them reverts or roll back the transaction, then the value that that session retrieved remains unchanged, creating a gap in the table values of auto-incremented fields.
Conclusion- PostgreSQL Auto Increment
PostgreSQL achieves auto-incrementation by declaring columns of the pseudo-datatype ‘SERIAL’ internally managed by the SEQUENCE database object. The SEQUENCE database object is an ordered list.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Auto Increment” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

