Updated April 1, 2023
Definition of PL/SQL join
PL/SQL provides the different types of functionality to the user, in which that JOIN is one of the functionalities provided by the PL/SQL. Basically, JOIN is used to retrieve the records from more than one table. By using JOIN we can merge the result from different tables as per our requirement. Basically JOIN is a SQL statement and by using this SQL statement we can combine the different columns from the different tables as per the requirement. When we need to implement the JOIN at that time we must have the primary key and foreign key in tables then and then we can implement the JOIN.
Syntax:
select colm name 1, colm name2, ….colm name N from specified first table name(Table 1) JOIN specified second table name(Table 2) ON specified first table name.colm name= specified second table name.colm name;Explanation:
In the above syntax, we use JOIN with different parameters as follows.
- colm name 1: It is used to specify the column name from the first table that we want. Similarly, we can write multiple column names as per our requirements.
- specified first table name: After the FROM clause we need to specify the first table name that is specified first table name.
- JOIN: JOIN is a keyword and it is used to combine the two different tables.
- specified second table name: After the JOIN keyword we need to specify the second table name that is specified second table name.
- ON: ON is a keyword that we can also call clause and it is used to combine the two different columns from different tables.
Types of join in PL/SQL
Now let’s see the different types of JOIN in PL/SQL with examples as follows.
First, we need to create two different tables by using the create table statement as follows. One important point during the table creation, the left-hand table must have a primary key and the right-hand table must have a foreign key.
create table stud1(roll_no number(10) not null, name varchar2(30), city varchar(30), constraint stud_pk primary key(roll_no));Explanation
By using the above statement we created a stud1 table with different attributes and data types as shown.
create table dept(dept_id number(10) not null, dept_name varchar2(30), roll_no number(10) not null);Explanation
Now insert some records into both tables to implement JOIN. Here we need to perform the insert operation as follows.
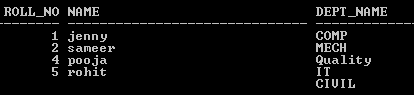
In the first table that stude1, we inserted five records as shown in the below screenshot as follow.
Similarly, we inserted five records into the second table that is dept as shown in the below screenshot as follows.
Now we have two tables with records, now perform different types of JOIN as follows.
1. INNER JOIN
This is a very simple type of JOIN; it is also called a simple join. By using this type we return the only matching rows from both tables. In another word, we can say that we intersect between the two tables as follows.
Syntax:
select colm name 1, colm name2, ….colm name N from specified first table name(Table 1) INNER JOIN specified second table name(Table 2) ON specified first table name.colm name= specified second table name.colm name;Example
In this, we use already created table stud1 and dept.
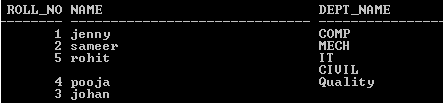
select stud1.roll_no, stud1.name, dept.dept_name from stud1 inner join dept on
stud1.roll_no=dept.roll_no;Explanation
In the above example, we try to implement the INNER JOIN as shown in the above SQL statement. The INNER JOIN returns all matching rows from both tables where roll_no is matching in both tables. The final output of the above statement we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
2. LEFT OUTER JOIN
This is the second type of join, by using this type we can return all rows from the first table that is a left-hand table.
Syntax:
select colm name 1, colm name2, ….colm name N from specified first table name(Table 1) LEFT OUTER JOIN specified second table name(Table 2) ON specified first table name.colm name= specified second table name.colm name;Example
select stud1.roll_no, stud1.name, dept.dept_name from stud1 left outer join dept on
stud1.roll_no=dept.roll_no;Explanation
In the above example, we try to implement the left outer join. In this example, we return all rows from the stud1 table and only matching rows from the dept table. The final output of the above statement we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
3. RIGHT OUTER JOIN
This is another type of join, in this type, it returns all rows from the right-hand side and only matching rows from the left-hand side.
Syntax:
select colm name 1, colm name2, ….colm name N from specified first table name(Table 1) RIGHT OUTER JOIN specified second table name(Table 2) ON specified first table name.colm name= specified second table name.colm name;Example
select stud1.roll_no, stud1.name, dept.dept_name from stud1 right outer join dept on
stud1.roll_no=dept.roll_no;Explantion
In the above example, we try to implement the right outer join as shown. In this example, we return all rows from the dept table and only matching rows from the stud1 table. The final output of the above statement we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
4. FULL OUTER JOIN
This is another type of JOIN that is FULL OUTER JOIN; in this type, it returns all rows from the stud1 table that is the left-hand table, and the dept table that is the right-hand table.
Syntax:
select colm name 1, colm name2, ….colm name N from specified first table name(Table 1) FULL OUTER JOIN specified second table name(Table 2) ON specified first table name.colm name= specified second table name.colm name;Example
select stud1.roll_no, stud1.name, dept.dept_name from stud1 full outer join dept on
stud1.roll_no=dept.roll_no;Explanation
In the above example, we try to implement the full outer join. The final output of the above statement we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
In this way, we can also implement cross join, anti join, and semi-join as per our requirements.
Conclusion
We hope from this article you learn PL/SQL JOIN. From the above article, we have learned the basic syntax of JOIN with different types and we also see different examples of JOINS. From this article, we learned how and when we use PL/SQL JOIN.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PL/SQL join” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.